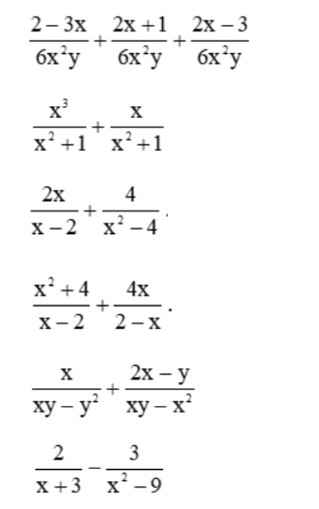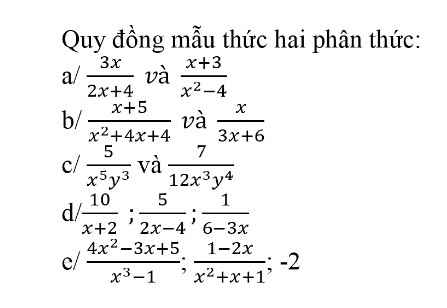Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


Ta có : |x - 2| ; |x - 5| ; |x - 18| ≥0∀x∈R≥0∀x∈R
=> |x - 2| + |x - 5| + |x - 18| ≥0∀x∈R≥0∀x∈R
=> D có giá trị nhỏ nhất khi x = 2;5;18
Mà x ko thể đồng thời nhận 3 giá trị
Nên GTNN của D là : 16 khi x = 5 ok nha bạn
x^2/x-1 = x^2-4x+4/x-1 + 4 = (x-2)^1/x-1 + 4 >= 4
Dấu "=" xảy ra <=> x-2 = 0 <=> x = 2 (tm)
Vậy GTNN của x^2/x-1 = 4 <=> x= 2
k mk nha


Ta có: \(6x^2-x-2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow6x^2-4x+3x-2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x.\left(3x-2\right)+\left(3x-2\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(2x+1\right).\left(3x-2\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}2x+1=0\\3x-2=0\end{cases}}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x=-\frac{1}{2}\\x=\frac{2}{3}\end{cases}}\)
6x2 - 2 - x = 0
=> 6x2 + 3x - 4x - 2 = 0
=> 3x(2x + 1) - 2(2x + 1) = 0
=> (3x - 2)(2x + 1) = 0
=> \(\orbr{\begin{cases}3x-2=0\\2x+1=0\end{cases}}\Rightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}3x=2\\2x=-1\end{cases}}\Rightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x=\frac{2}{3}\\x=-\frac{1}{2}\end{cases}}\)

3x2 + 3x - 5( x + 1 ) = 0
<=> ( 3x2 + 3x ) - 5( x + 1 ) = 0
<=> 3x( x + 1 ) - 5( x + 1 ) = 0
<=> ( x + 1 )( 3x - 5 ) = 0
<=> x + 1 = 0 hoặc 3x - 5 = 0
<=> x = -1 hoặc x = 5/3

| Vt | Tgian | Q.duong | |
| luc di | 45 | x | 45x |
| luc ve | 60 | x-50 | 60(x-50) |
ta co ph trinh
45x=60(x-50)
x=200 km
cho mk cai h nha

4: Đặt \(x=\dfrac{a+b}{a-b};y=\dfrac{b+c}{b-c};z=\dfrac{c+a}{c-a}\).
Ta có \(\left(x+1\right)\left(y+1\right)\left(z+1\right)=\dfrac{2a.2b.2c}{\left(a-b\right)\left(b-c\right)\left(c-a\right)}=\left(x-1\right)\left(y-1\right)\left(z-1\right)\)
\(\Rightarrow xy+yz+zx=-1\).
Bất đẳng thức đã cho tương đương:
\(x^2+y^2+z^2\ge2\Leftrightarrow\left(x+y+z\right)^2-2\left(xy+yz+zx\right)-2\ge0\Leftrightarrow\left(x+y+z\right)^2\ge0\) (luôn đúng).
Vậy ta có đpcm
mình xí câu 45,47,51 :>
45. a) Áp dụng bất đẳng thức Cauchy-Schwarz dạng Engel ta có :
\(\dfrac{1}{a}+\dfrac{2}{b}=\dfrac{1}{a}+\dfrac{4}{2b}\ge\dfrac{\left(1+2\right)^2}{a+2b}=\dfrac{9}{a+2b}\left(đpcm\right)\)
Đẳng thức xảy ra <=> a=b
b) Áp dụng bất đẳng thức Cauchy-Schwarz dạng Engel ta có :
\(\dfrac{1}{a}+\dfrac{1}{b}+\dfrac{1}{b}\ge\dfrac{\left(1+1+1\right)^2}{a+b+b}=\dfrac{9}{a+2b}\)(1)
\(\dfrac{1}{b}+\dfrac{1}{c}+\dfrac{1}{c}\ge\dfrac{\left(1+1+1\right)^2}{b+c+c}=\dfrac{9}{b+2c}\)(2)
\(\dfrac{1}{c}+\dfrac{1}{a}+\dfrac{1}{a}\ge\dfrac{\left(1+1+1\right)^2}{c+a+a}=\dfrac{9}{c+2a}\)(3)
Cộng (1),(2),(3) theo vế ta có đpcm
Đẳng thức xảy ra <=> a=b=c

biểu thức đó = (a-2)(a-1)a(a+1)(a+2)
Trong 5 số nguyên liên tiếp tồn tại 1 số chia hết cho 3, 1 số chia hết cho 5, có 2 số chẵn, trong đó 1 số chia hết cho 2, 1 số chia hết cho 4
Vậy tích của chúng chia hết cho 3.5.2.4= 120
ok nhé bn!!!!! 45436545475966264634657856321423434546545476879

\(\dfrac{2-3x+2x+1+2x-3}{6x^2y}=\dfrac{x}{6x^2y}=\dfrac{1}{6xy}\)

\(a,\dfrac{3x}{2x+4}=\dfrac{3x\left(x-2\right)}{2\left(x+2\right)\left(x-2\right)};\dfrac{x+3}{x^2-4}=\dfrac{2\left(x+3\right)}{2\left(x-2\right)\left(x+2\right)}\\ b,\dfrac{x+5}{x^2+4x+4}=\dfrac{3\left(x+5\right)}{3\left(x+2\right)^2};\dfrac{x}{3x+6}=\dfrac{x\left(x+2\right)}{3\left(x+2\right)^2}\\ c,\dfrac{5}{x^5y^3}=\dfrac{60y}{12x^5y^4};\dfrac{7}{12x^3y^4}=\dfrac{7x^2}{12x^5y^4}\\ d,\dfrac{10}{x+2}=\dfrac{60\left(x-2\right)}{6\left(x+2\right)\left(x-2\right)};\dfrac{5}{2x-4}=\dfrac{15\left(x+2\right)}{6\left(x-2\right)\left(x+2\right)};\dfrac{1}{6-3x}=\dfrac{-2\left(x+2\right)}{6\left(x-2\right)\left(x+2\right)}\)
\(e,\dfrac{4x^2-3x+5}{x^3-1}=\dfrac{4x^2-3x+5}{\left(x-1\right)\left(x^2+x+1\right)}\\ \dfrac{1-2x}{x^2+x+1}=\dfrac{\left(x-1\right)\left(1-2x\right)}{\left(x-1\right)\left(x^2+x+1\right)}\\ -2=\dfrac{-2\left(x^3-1\right)}{\left(x-1\right)\left(x^2+x+1\right)}\)