
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


Bài 1:
Xét tứ giác ABDC có \(\widehat{A}+\widehat{D}=180^0\)
nên ABDC là tứ giác nội tiếp

a: Đặt 1/x=a
1/(y-2)=b
Hệ phương trình trở thành:
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}2a+3b=4\\4a+b=1\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}4a+6b=8\\4a+b=1\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}5b=7\\4a+b=1\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}b=\dfrac{7}{5}\\a=-\dfrac{1}{10}\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\dfrac{1}{x}=\dfrac{-1}{10}\\\dfrac{1}{y-2}=\dfrac{7}{5}\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=-10\\y-2=\dfrac{5}{7}\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=-10\\y=\dfrac{19}{7}\end{matrix}\right.\)
b: \(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}-\dfrac{2}{y}=0\\\dfrac{2}{x+1}+\dfrac{3}{y}=-1\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>Hệ phương trình vô nghiệm
a) \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\dfrac{2}{x}+\dfrac{3}{y-2}=4.\\\dfrac{4}{x}+\dfrac{1}{y-2}=1.\end{matrix}\right.\) \(ĐK:x\ne0;y\ne2.\)
Đặt \(\dfrac{1}{x}=a;\dfrac{1}{y-2}=b\left(a;b\ne0\right).\)
\(\Rightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}2a+3b=4.\\4a+b=1.\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}a=\dfrac{-1}{10}.\\b=\dfrac{7}{5}.\end{matrix}\right.\) (TM).
\(\Rightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\dfrac{1}{x}=\dfrac{-1}{10}.\\\dfrac{1}{y-2}=\dfrac{7}{5}.\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=-10\left(TM\right).\\y=\dfrac{19}{7}\left(TM\right).\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy hệ phương trình có nghiệm \(\left(x;y\right)=\left(-10;\dfrac{19}{7}\right).\)

\(tana=\dfrac{\sqrt{5}}{3}\)
=>\(\dfrac{sina}{cosa}=\dfrac{\sqrt{5}}{3}\)
=>\(sina=cosa\cdot\dfrac{\sqrt{5}}{3}\)
\(B=\dfrac{2\cdot cosa+\dfrac{\sqrt{5}}{3}\cdot cosa}{5\cdot cosa-3\cdot\dfrac{\sqrt{5}}{3}\cdot cosa}=\left(2+\dfrac{\sqrt{5}}{3}\right):\left(5-\sqrt{5}\right)\)
\(=\dfrac{6+\sqrt{5}}{3\left(5-\sqrt{5}\right)}=\dfrac{35+11\sqrt{5}}{40}\)



Lời giải:
a. Khi $x=64$ thì: $Q=\frac{\sqrt{64}-2}{\sqrt{64}-3}=\frac{8-2}{8-3}=\frac{6}{5}$
b.
\(P=\frac{x}{(\sqrt{x}-2)(\sqrt{x}+2)}+\frac{\sqrt{x}+2}{(\sqrt{x}-2)(\sqrt{x}+2)}+\frac{\sqrt{x}-2}{(\sqrt{x}+2)(\sqrt{x}-2)}\)
\(=\frac{x+\sqrt{x}+2+\sqrt{x}-2}{(\sqrt{x}+2)(\sqrt{x}-2)}=\frac{x+2\sqrt{x}}{(\sqrt{x}+2)(\sqrt{x}-2)}=\frac{\sqrt{x}(\sqrt{x}+2)}{(\sqrt{x}-2)(\sqrt{x}+2)}=\frac{\sqrt{x}}{\sqrt{x}-2}\)
Ta có đpcm.
c. \(K=Q(P-1)=\frac{\sqrt{x}-2}{\sqrt{x}-3}.(\frac{\sqrt{x}}{\sqrt{x}-2}-1)=\frac{\sqrt{x}-2}{\sqrt{x}-3}.\frac{2}{\sqrt{x}-2}=\frac{2}{\sqrt{x}-3}\)
$K=m+1$
$\Leftrightarrow \frac{2}{\sqrt{x}-3}=m+1$
$\Leftrightarrow m=\frac{2}{\sqrt{x}-3}-1$
Với $m=0$ (stn nhỏ nhất) thì $\frac{2}{\sqrt{x}-3}-1=m$ có nghiệm $x=25$
Vậy stn $m$ cần tìm là $0$

Ta có: \(AB^2+HC^2=\left(AA'^2+A'B^2\right)+\left(A'H^2+A'C^2\right)\)
\(=\left(AA'^2+A'C^2\right)+\left(A'B^2+A'H^2\right)=AC^2+HB^2\)
Lại có: \(BC^2+HA^2=\left(BB'^2+B'C^2\right)+\left(B'H^2+B'A^2\right)\)
\(=\left(BB'^2+B'A^2\right)+\left(B'C^2+B'H^2\right)=AB^2+HC^2\)
\(\Rightarrow AB^2+HC^2=AC^2+HB^2=BC^2+HA^2\)
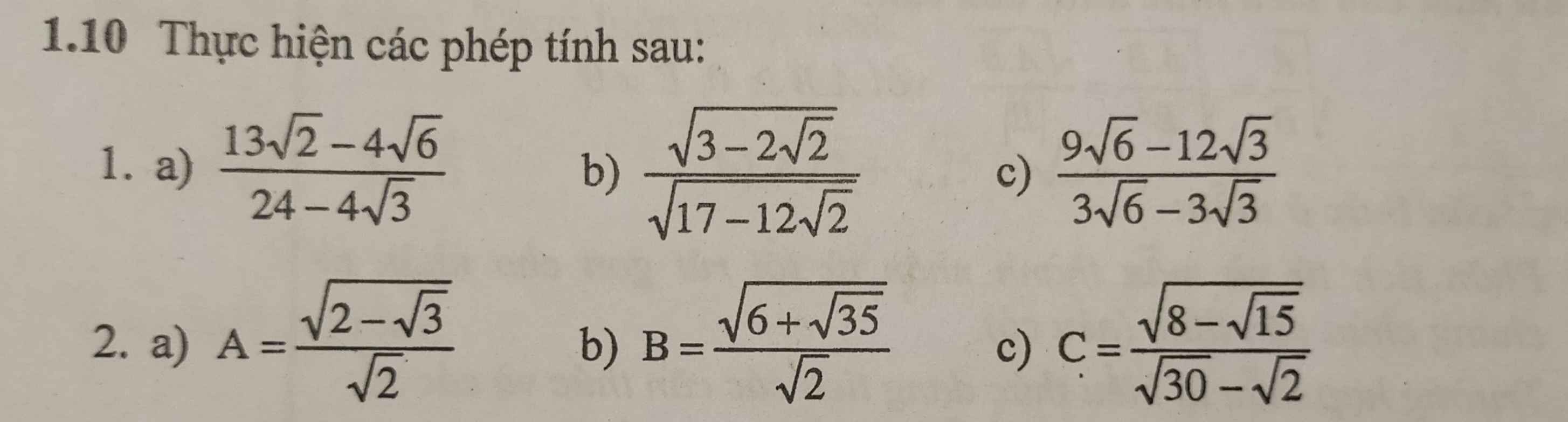

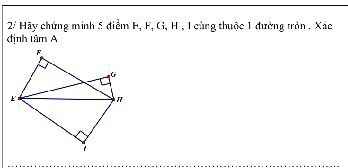 giúp mình với ạ mình cảm ơn nhiều
giúp mình với ạ mình cảm ơn nhiều 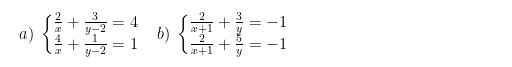




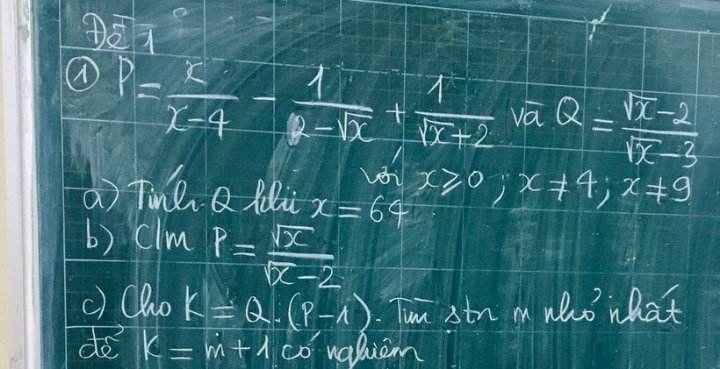 giúp mình câu c với ạ, mình cảm ơn nhiều
giúp mình câu c với ạ, mình cảm ơn nhiều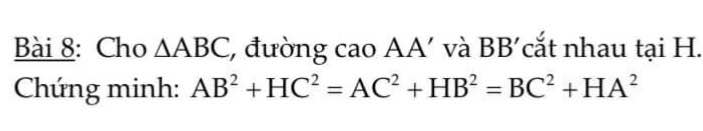
Bài 1:
a: \(\dfrac{13\sqrt{2}-4\sqrt{6}}{24-4\sqrt{3}}=\dfrac{\sqrt{2}\left(13-4\sqrt{3}\right)}{4\sqrt{3}\left(2\sqrt{3}-1\right)}=\dfrac{\sqrt{2}\left(2\sqrt{3}-1\right)}{4\sqrt{3}}=\dfrac{\sqrt{6}\left(2\sqrt{3}-1\right)}{12}\)
b: \(\dfrac{\sqrt{3-2\sqrt{2}}}{\sqrt{17-12\sqrt{2}}}=\dfrac{\sqrt{2}-1}{3-2\sqrt{2}}=\sqrt{2}+1\)