
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.



8: \(x\sqrt{x}-1=\left(\sqrt{x}-1\right)\left(x+\sqrt{x}+1\right)\)
9: \(x\sqrt{x}+1=\left(\sqrt{x}+1\right)\left(x-\sqrt{x}+1\right)\)
10: \(x\sqrt{x}-y\sqrt{y}=\left(\sqrt{x}-\sqrt{y}\right)\left(x+\sqrt{xy}+y\right)\)
11: \(x\sqrt{x}+y\sqrt{y}=\left(\sqrt{x}+\sqrt{y}\right)\left(x-\sqrt{xy}+y\right)\)

Bài 3b:
Giả sử có $a$ hs và mỗi hs dự định trồng $b$ cây
Theo bài ra ta có:
$480=ab(1)$
$480=(a-8)(b+3)$
$\Leftrightarrow 480=ab+3a-8b-24$
$\Leftrightarrow 480=480+3a-8b-24$
$\Leftrightarrow 3a-8b=24(2)$
Từ $(1); (2)\Rightarrow 3a-8.\frac{480}{a}=24$
$\Leftrightarrow 3a-\frac{3840}{a}=24$
$\Leftrightarrow a-\frac{1280}{a}=8$
$\Rightarrow a^2-8a-1280=0$
$\Leftrightarrow (a-40)(a+32)=0$
$\Rightarrow a=40$ (do $a>0$)
Vậy lớp 9A có $40$ hs.

Câu 2: b. \(\sqrt{9x^2-6x+1}=9\)
<=> \(\sqrt{\left(3x-1\right)^2}=9\)
<=> 3x - 1 = 9
<=> 3x = 10
<=> x = \(\dfrac{10}{3}\)

a: Thay m=-5 vào pt, ta được:
\(x^2-x-5=0\)
\(\Delta=\left(-1\right)^2-4\cdot1\cdot\left(-5\right)=21\)
Do đó: Phương trình có hai nghiệm phân biệt là:
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x_1=\dfrac{1-\sqrt{21}}{2}\\x_2=\dfrac{1+\sqrt{21}}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\)
b: \(\Delta=\left(-1\right)^2-4\cdot1\cdot m=-4m+1\)
Để phương trình có hai nghiệm phân biệt thì -4m+1>0
=>-4m>-1
hay m<1/4
Theo đề, ta có: \(\left(m-1\right)^2=9\)
=>m-1=3 hoặc m-1=-3
=>m=4(loại) hoặc m=-2(nhận)
a, Thay m = -5 ta được
\(x^2-x-5=0\)
\(\Delta=1-4\left(-5\right)=1+20=21>0\)
Vậy pt có 2 nghiệm pb
\(x_1=\dfrac{1-\sqrt{21}}{2};x_2=\dfrac{1+\sqrt{21}}{2}\)
b, \(\Delta=1-4m\)Để pt có 2 nghiệm x1 ; x2
=> 1 - 4m >= 0 <=> m =< 1/4
Theo Vi et \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x_1+x_2=1\\x_1x_2=m\end{matrix}\right.\)
Thay vào ta được
\(\left(m-1\right)^2=9\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}m-1=3\\m-1=-3\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}m=4\left(ktm\right)\\m=-2\left(tm\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)

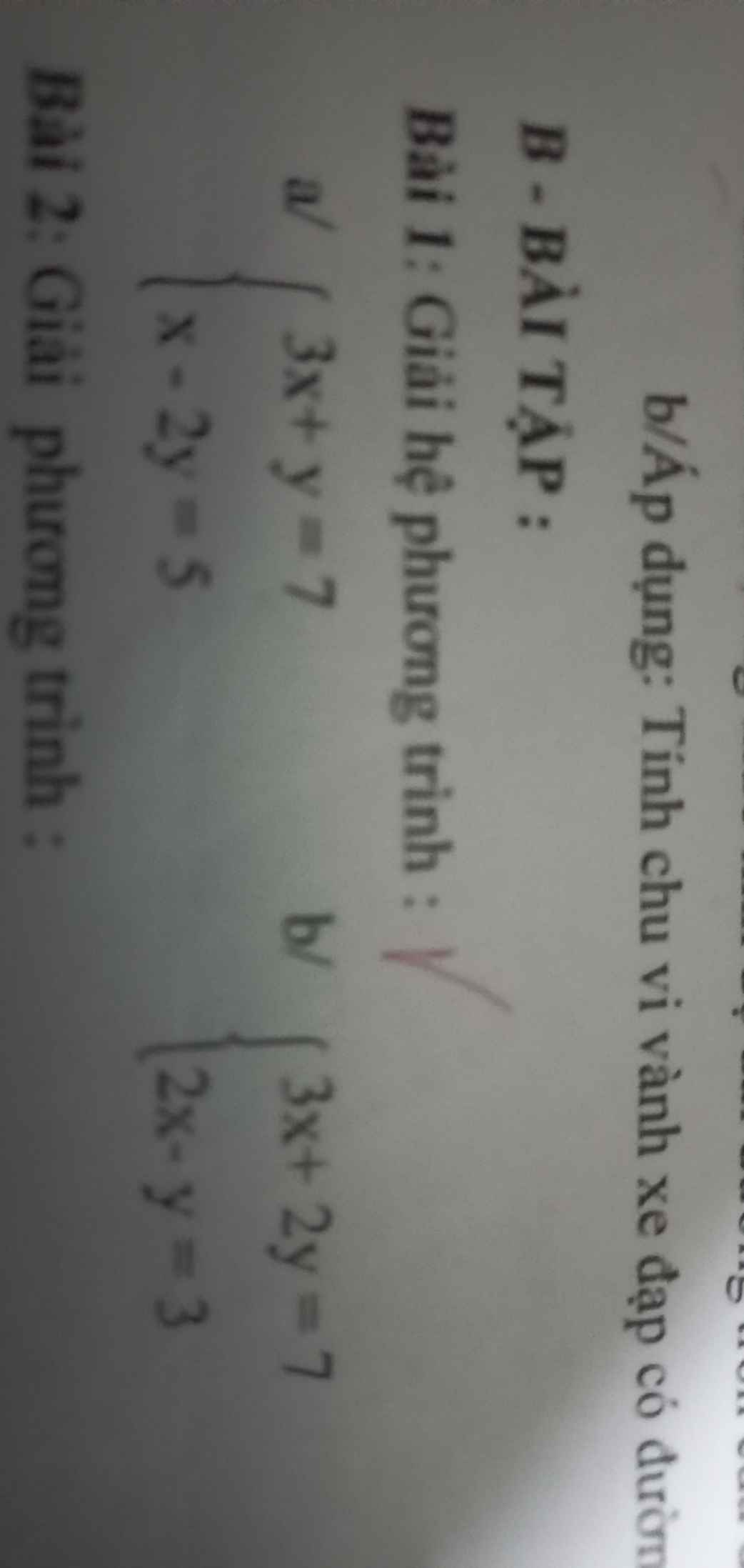






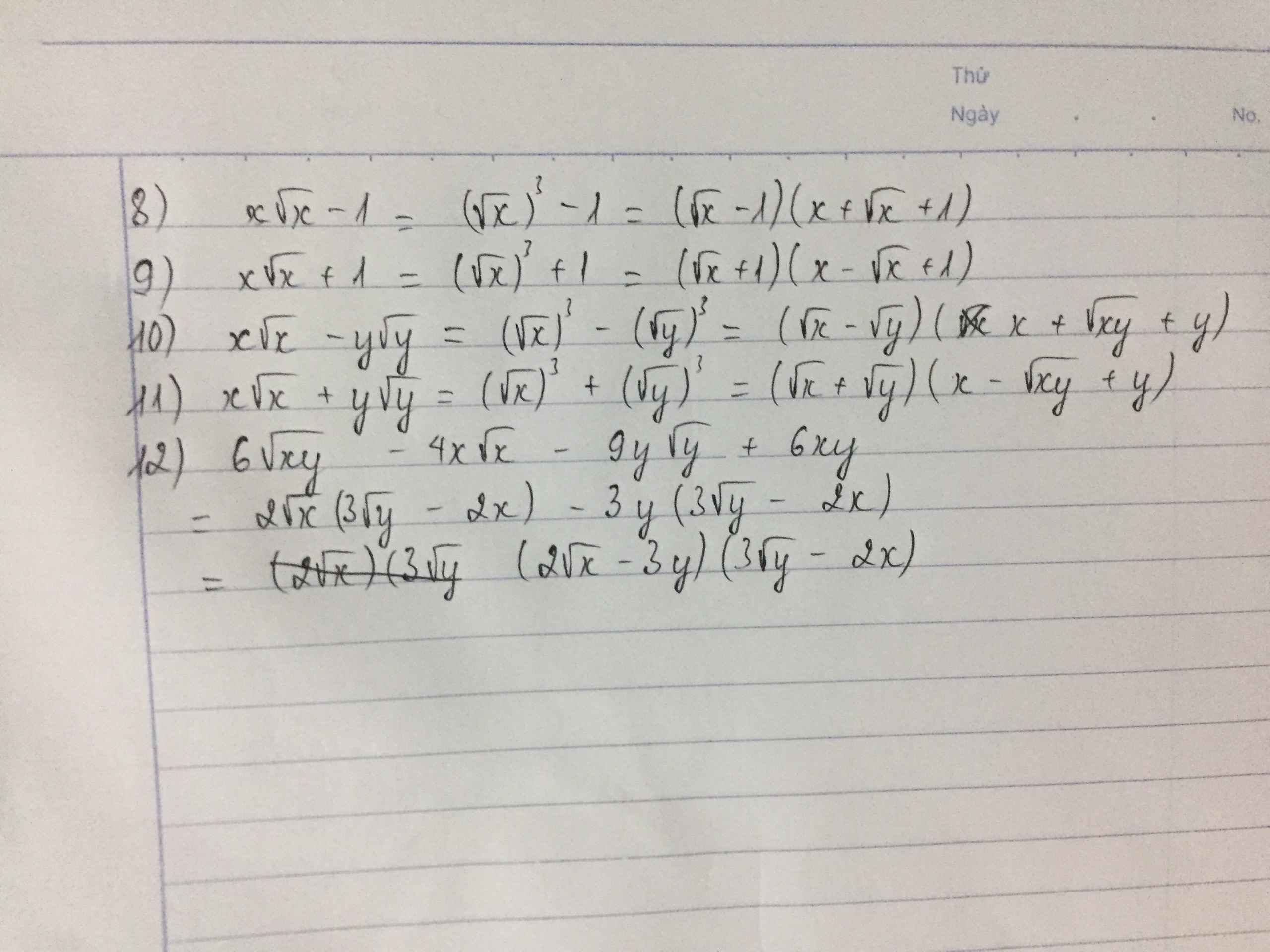

 Giải giúp mình bài 1 bài 2 đi mn
Giải giúp mình bài 1 bài 2 đi mn
 Cho 3 số dương a,b,c thỏa mãn a+b+c=1. CMR:
Cho 3 số dương a,b,c thỏa mãn a+b+c=1. CMR:
a)
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}3x+y=7\left(1\right)\\x-2y=5\left(2\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
lấy (1) . 2 + (2)
<=> 7x = 19 => x = \(\dfrac{19}{7}\)
thay x = \(\dfrac{19}{7}\) vào phương trình (2) ta có
\(\dfrac{19}{7}\) - 2y = 5
<=> 2y = \(\dfrac{-16}{7}\) => y = \(\dfrac{-8}{7}\)
vậy (x;y) = { ( \(\dfrac{19}{7}\);\(\dfrac{-8}{7}\) ) }
b)
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}3x+2y=7\left(1\right)\\2x-y=3\left(2\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
lấy (2).2 + (1)
=> 7x = 13 => x = \(\dfrac{13}{7}\)
thay x = \(\dfrac{13}{7}\) vào phương trình 2 ta có
\(\dfrac{13}{7}\) - 2y = 5
<=> 2y = \(\dfrac{-22}{7}\) => y = \(\dfrac{-11}{7}\)
vậy (x;y) = {(\(\dfrac{13}{7}\);\(\dfrac{-11}{7}\))}