
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


\(D=\dfrac{x^2}{x^2-1}+\dfrac{1}{x^2-x^4}=\dfrac{x^4}{x^2\left(x^2-1\right)}-\dfrac{1}{x^2\left(x^2-1\right)}=\dfrac{x^4-1}{x^2\left(x^2-1\right)}=\dfrac{\left(x^2-1\right)\left(x^2+1\right)}{x^2\left(x^2-1\right)}=\dfrac{x^2+1}{x^2}=1+\dfrac{1}{x^2}\)
do \(x\ne0,\pm1\Rightarrow\dfrac{1}{x^2}>0\Rightarrow1+\dfrac{1}{x^2}>1\Rightarrow D>1\left(đpcm\right)\)
\(D=\dfrac{x^2}{x^2-1}+\dfrac{1}{x^2-x^4}\\ =\dfrac{x^4\left(1-x\right)}{\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)\left(1-x\right)x^2}+\dfrac{x-1}{x^2\left(1-x\right)\left(1+x\right)\left(x-1\right)}\\ =\dfrac{x^4-x^5+x-1}{x^2\left(1-x\right)\left(1+x\right)\left(x-1\right)}\\ =\dfrac{-\left(x-1\right)^2\left(x^2+1\right)\left(x+1\right)}{-x^2\left(x-1\right)^2\left(x+1\right)}\\ =\dfrac{x^2+1}{x^2}>1\left(đpcm\right)\)
(x2 + 1 luôn lớn hơn x2)

Bài 1. (a) Điều kiện: \(x\ne\pm1\).
Ta có: \(A=\left(\dfrac{x-2}{x-1}-\dfrac{x+3}{x+1}+\dfrac{3}{x-1}\right):\left(1-\dfrac{x+3}{x+1}\right)\)
\(=\left(\dfrac{x-2+3}{x-1}-\dfrac{x+3}{x+1}\right):\dfrac{x+1-\left(x+3\right)}{x+1}\)
\(=\left(\dfrac{x+1}{x-1}-\dfrac{x+3}{x+1}\right):\dfrac{x+1-x-3}{x+1}\)
\(=\dfrac{\left(x+1\right)^2-\left(x+3\right)\left(x-1\right)}{\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)}:\dfrac{-2}{x+1}\)
\(=\dfrac{x^2+2x+1-x^2-2x+3}{\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)}\cdot\dfrac{x+1}{-2}\)
\(=\dfrac{4}{\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)}\cdot\dfrac{x+1}{-2}=\dfrac{2}{1-x}\)
Vậy: \(A=\dfrac{2}{1-x}\)
(b) \(A=3\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{2}{1-x}=3\)
\(\Rightarrow1-x=\dfrac{2}{3}\Leftrightarrow x=\dfrac{1}{3}\left(TM\right)\)
Vậy: \(x=\dfrac{1}{3}\)
Bài 2. (a) Phương trình tương đương với:
\(\dfrac{3\left(3x-2\right)}{12}+\dfrac{6\left(x+3\right)}{12}=\dfrac{4\left(x-1\right)}{12}+\dfrac{x+1}{12}\)
\(\Rightarrow3\left(3x-2\right)+6\left(x+3\right)=4\left(x-1\right)+x+1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow9x-6+6x+18=4x-4+x+1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow10x=-15\Leftrightarrow x=-\dfrac{3}{2}\)
Vậy: Phương trình có tập nghiệm \(S=\left\{-\dfrac{3}{2}\right\}\).
(b) Điều kiện: \(x\ne\pm1\). Phương trình tương đương với:
\(\dfrac{2\left(x+1\right)}{\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)}+\dfrac{2\left(x-1\right)}{\left(x+1\right)\left(x-1\right)}=\dfrac{2x^2+2}{\left(x+1\right)\left(x-1\right)}\)
\(\Rightarrow2\left(x+1\right)+2\left(x-1\right)=2x^2+2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x+2+2x-2=2x^2+2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x^2-4x+2=0\Leftrightarrow2\left(x^2-2x+1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2\left(x-1\right)^2=0\Rightarrow x-1=0\Leftrightarrow x=1\left(KTM\right)\)
Vậy: Phương trình có tập nghiệm \(S=\varnothing\)

2:
1: =7x(x-y)-5(x-y)
=(x-y)(7x-5)
2: =(x^2-y^2)-(4x-4y)
=(x-y)(x+y)-4(x-y)
=(x-y)(x+y-4)
3: =(x^2+2xy+y^2)-(2x+2y)+1
=(x+y)^2-2(x+y)+1
=(x+y-1)^2

3:
1: =>15x-9x+6=45-10x+25
=>6x+6=-10x+70
=>16x=64
=>x=4
2: =>x^2+4x-16-16=0
=>x^2+4x-32=0
=>(x+8)(x-4)=0
=>x=4 hoặc x=-8
3: ĐKXĐ: x<>4; x<>-4
\(PT\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{x+4+\left(x+2\right)\left(x-4\right)}{\left(x-4\right)\left(x+4\right)}=\dfrac{5x-4}{\left(x-4\right)\left(x+4\right)}\)
=>x+4+x^2-2x-8=5x-4
=>x^2-x-4=5x-4
=>x^2-6x=0
=>x(x-6)=0
=>x=0 hoặc x=6
4: \(\Leftrightarrow5\left(4x+1\right)-x+2>=3\left(2x-3\right)\)
=>20x+5-x+2>=6x-9
=>19x+7>=6x-9
=>13x>=-16
=>x>=-16/13



f: Ta có: \(\left(5x-1\right)^2-\left(5x-4\right)\left(5x+4\right)=7\)
\(\Leftrightarrow25x^2-10x+1-25x^2+16=7\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-10x=-10\)
hay x=1
b: Ta có: \(\left(x-1\right)\left(x^2+x+1\right)-x\left(x+2\right)\left(x-2\right)=5\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^3-1-x^3+4x=5\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4x=6\)
hay \(x=\dfrac{3}{2}\)

b) \(\left(x-1\right)\left(x^2+x+1\right)-x\left(x+2\right)\left(x-2\right)=5\)
\(x^3-1^3-x\left(x^2-4\right)=5\)
\(x^3-1-\left(x^3-4x\right)=5\)
\(x^3-1-x^3+4x=5\)
\(-1+4x=5\)
\(4x=6\)
\(x=\dfrac{3}{2}\)
\(\left(x-1\right)\left(x^2+x+1\right)-x\left(x+2\right)\left(x-2\right)=5\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^3-1-x^3+4x=5\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4x=6\)
hay \(x=\dfrac{3}{2}\)

 mn giup mik bai 3 nay dc ko aj
mn giup mik bai 3 nay dc ko aj
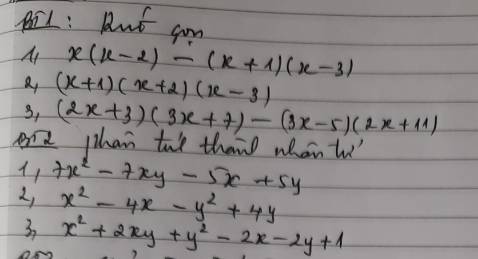



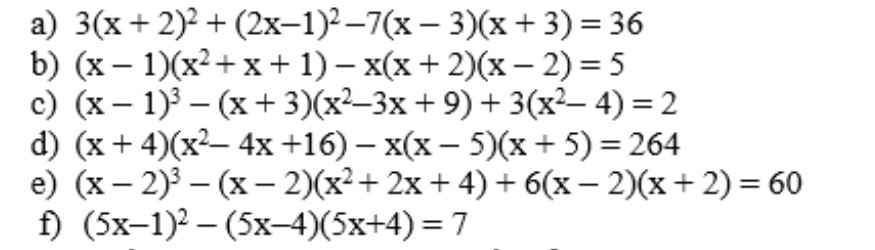
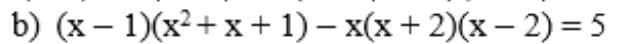
Bài 1:
a: \(\Leftrightarrow\left(3x+2\right)^2-6\left(3x-2\right)=9x^2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow9x^2+12x+4-18x+12=9x^2\)
=>-6x+16=0
=>-6x=-16
=>x=8/3
b: \(\Leftrightarrow3\left(3-x\right)+2\left(5x-1\right)=4\)
=>9-3x+10x-2=4
=>7x+7=4
=>7x=-3
=>x=-3/7
c: \(\Leftrightarrow-3\left(4x+1\right)=2\left(4x-1\right)-6x-8\)
=>\(-12x-3=8x-2-6x-8=2x-10\)
=>-14x=-7
=>x=1/2
d: \(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{5-x}{4x\left(x-2\right)}+\dfrac{7}{8x}=\dfrac{x-1}{2x\left(x-2\right)}+\dfrac{1}{8\left(x-2\right)}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2\left(5-x\right)+7\left(x-2\right)=4\left(x-1\right)+x\)
=>\(10-2x+7x-14=4x-4+x=5x-4\)
=>5x-4=5x-4(luôn đúng)
=>S=R\{0;2}
e: \(\Leftrightarrow x^3+1-x^3+1=\dfrac{3}{x}\)
=>\(2x=3\)
=>x=3/2