
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


Bài 1:
a: \(\Leftrightarrow x^2-5x+6< =0\)
=>(x-2)(x-3)<=0
=>2<=x<=3
b: \(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-6\right)^2< =0\)
=>x=6
c: \(\Leftrightarrow x^2-2x+1>=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-1\right)^2>=0\)
hay \(x\in R\)

ĐK:x\(\ge\)0
Đặt t=x2+3x(t\(\ge\) 0)ta được:
\(\sqrt{t+12}=t\Leftrightarrow t^2=t+12\)
<=>t2-t-12=0
\(\Delta=49\Rightarrow\sqrt{\Delta}=7\)
\(\Delta>0,\text{phương trình có 2 nghiệm phân biệt}\)
\(t_1=4\left(thỏa\right);t_2=-3\left(loại\right)\)
t=4=>x2+3x=4
<=>x2+3x-4=0
\(\Delta=25\Rightarrow\sqrt{\Delta}=5;\Delta>0,pt\text{ có 2 nghiệm phân biệt:}\)
\(x_1=1\left(thỏa\right);x_2=-4\left(loại\right)\)
Vậy S={1}

Chọn C
ĐKXĐ:
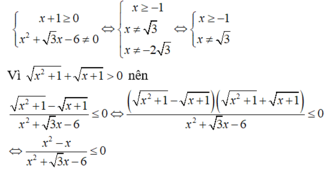
Bảng xét dấu
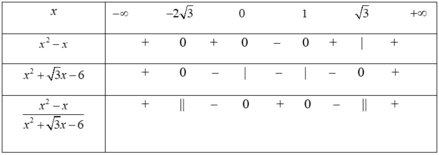
Dựa vào bảng xét dấu và đối chiếu điều kiện, ta có tập nghiệm của bất phương trình đã cho là
![]()

Điều kiện: x + 2 ≥ 0 2 − x ≥ 0 ⇔ x ≥ − 2 x ≤ 2 ⇔ − 2 ≤ x ≤ 2
Đặt: t = 3 x + 2 − 6 2 − x
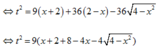
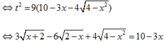
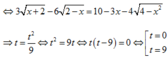
+ Với t = 0 ⇒ 3 x + 2 − 6 2 − x = 0
⇔ 3 x + 2 = 6 2 − x ⇔ x + 2 = 8 − 4 x ⇔ x = 6 5
+ Với t = 9
⇒ 3 x + 2 − 6 2 − x = 9 ⇔ x + 2 = 3 + 2 2 − x
⇔ x + 2 = 0 + 8 − 4 x + 12 2 − x ⇔ 5 x − 15 = 12 2 − x
Điều kiện: 5 x − 15 ≥ 0 ⇔ x ≥ 3 (không thỏa mãn − 2 ≤ x ≤ 2 )
Vậy phương trình có 1 nghiệm duy nhất x = 6 5
Đáp án cần chọn là: C

(2x – 1)(x + 3) – 3x + 1 ≤ (x – 1)(x + 3) + x2 – 5
⇔ 2x2 + 6x - x – 3 – 3x + 1 ≤ x2 + 3x - x – 3 + x2 – 5
⇔ 2x2 + 2x – 2 ≤ 2x2 + 2x – 8
⇔ 6 ≤ 0 (Vô lý).
Vậy BPT vô nghiệm.

\(f\left(x\right)=\dfrac{\left(3x-4\right)\left(2x-3\right)}{\left(x^2-5x+6\right)\left(5-x\right)}>0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{\left(3x-4\right)\left(2x-3\right)}{\left(x-2\right)\left(x-3\right)\left(5-x\right)}>0\)
Bảng xét dấu:
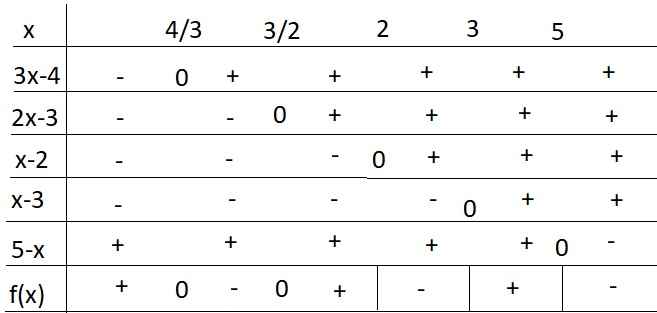
Từ bảng xét dấu ta thấy nghiệm của BPT là: \(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x< 5\\\dfrac{3}{2}< x< 2\\3< x< 5\end{matrix}\right.\)

\(\left(x^2+x+1\right)^2=\left(4x-1\right)^2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x^2+x+1\right)^2-\left(4x-1\right)^2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[\left(x^2+x+1\right)-\left(4x-1\right)\right]\left[\left(x^2+x+1\right)+\left(4x-1\right)\right]=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x^2+x+1-4x+1\right)\left(x^2+x+1+4x-1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x^2-3x+2\right)\left(x^2+5x\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-2\right)\left(x-1\right)x\left(x+5\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x-2=0\\x-1=0\\x+5=0\\x=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=2\\x=1\\x=-5\\x=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy: \(S=\left\{2;1;-5;0\right\}\)

=>\(\dfrac{x^2-3x+6-x^2+3x-3}{\sqrt{x^2-3x+6}-\sqrt{x^2-3x+3}}=3\)
=>căn x^2-3x+6 - căn x^2-3x+3=1
Đặt x^2-3x+3=a
=>căn a+3-căn a=1
=>a+3+a-2căn a(a+3)=1
=>2căn a(a+3)=2a+3-1=2a+2
=>căn a(a+3)=a+1
=>a^2+3a=a^2+2a+1
=>a=1
=>x^2-3x+2=0
=>x=1 hoặc x=2