
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


1:
a: =>3x=6
=>x=2
b: =>4x=16
=>x=4
c: =>4x-6=9-x
=>5x=15
=>x=3
d: =>7x-12=x+6
=>6x=18
=>x=3
2:
a: =>2x<=-8
=>x<=-4
b: =>x+5<0
=>x<-5
c: =>2x>8
=>x>4

a) Ta có: \(x^2-2x-3=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2-3x+x-3=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x\left(x-3\right)+\left(x-3\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-3\right)\left(x+1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x-3=0\\x+1=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=3\\x=-1\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy: \(S_1=\left\{3;-1\right\}\)(1)
Ta có: \(\left(x+1\right)\left(x+3\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x+1=0\\x+3=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=-1\\x=-3\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy: \(S_2=\left\{-3;-1\right\}\)(2)
Từ (1) và (2) suy ra \(S_1\ne S_2\)
hay Hai phương trình \(x^2-2x-3=0\) và \(\left(x+1\right)\left(x+3\right)=0\) không tương đương với nhau

\(a,\dfrac{x-3}{x}=\dfrac{x-3}{x+3}\)\(\left(đk:x\ne0,-3\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{x-3}{x}-\dfrac{x-3}{x+3}=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{\left(x-3\right)\left(x+3\right)-x\left(x-3\right)}{x\left(x+3\right)}=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2-9-x^2+3x=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3x-9=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3x=9\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=3\left(n\right)\)
Vậy \(S=\left\{3\right\}\)
\(b,\dfrac{4x-3}{4}>\dfrac{3x-5}{3}-\dfrac{2x-7}{12}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{4x-3}{4}-\dfrac{3x-5}{3}+\dfrac{2x-7}{12}>0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{3\left(4x-3\right)-4\left(3x-5\right)+2x-7}{12}>0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow12x-9-12x+20+2x-7>0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x+4>0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x>-4\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x>-2\)

c) \(\dfrac{x}{x-2}+\dfrac{x}{x+2}=\dfrac{4x}{x^2-4}.ĐKXĐ:x\ne2;-2\)
<=>\(\dfrac{x\left(x+2\right)}{x^2-4}+\dfrac{x\left(x-2\right)}{x^2-4}=\dfrac{4x}{x^2-4}\)
<=>x2+2x+x2-2x=4x
<=>2x2-4x=0
<=>2x(x-2)=0
<=>\(\left[{}\begin{matrix}2x=0< =>x=0\\x-2=0< =>x=2\left(loại\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy pt trên có nghiệm là S={0}
d) 11x-9=5x+3
<=>11x-5x=9+3
<=>6x=12
<=>x=2
Vậy pt trên có nghiệm là S={2}
e) (2x+3)(3x-4) =0
<=> \(\left[{}\begin{matrix}2x+3=0< =>x=\dfrac{-3}{2}\\3x-4=0< =>x=\dfrac{4}{3}\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy pt trên có tập nghiệm là S={\(\dfrac{-3}{2};\dfrac{4}{3}\)}
a) 5x+9 =2x
<=> 5x-2x=9
<=> 3x=9
<=> x=3
Vậy pt trên có nghiệm là S={3}
b) (x+1)(4x-3)=(2x+5)(x+1)
<=> (x+1)(4x-3)-(2x+5)(x+1)=0
<=>(x+1)(2x-8)=0
<=>\(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x+1=0< =>x=-1\\2x-8=0< =>2x=8< =>x=4\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy pt trên có tập nghiệm là S={-1;4}

a) 8( 3x - 2 ) - 14x = 2( 4 – 7x ) + 15x
⇔ 24x – 16 -14x = 8 – 14x + 15x
⇔ 10x -16 = 8 + x
⇔ 9x = 24
⇔ x = 24/9
b) ( 3x – 1 )( x – 3 ) – 9 + x2 = 0
⇔ (3x -1)( x – 3) + (x - 3)( x + 3) = 0
⇔ (x - 3)(3x - 1 + x - 3) = 0
⇔ (x - 3)(4x - 4) = 0
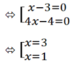
c) |x - 2| = 2x - 3
TH1: x - 2 ≥ 0 ⇔ x ≥ 2
Khi đó: x - 2 = 2x – 3
⇔ 2x – x = -2 + 3
⇔ x = 1 (không TM điều kiện x ≥ 2)
TH2: x – 2 < 0 ⇔ x < 2
Khi đó: x-2 = -(2x – 3)
⇔ x – 2 = -2x + 3
⇔ 3x = 5
⇔ x = 5/3 ( TM điều kiện x < 2)
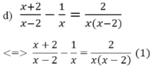
MTC: x(x-2)
ĐKXĐ: x ≠ 0;x ≠ 2

Đối chiếu với ĐKXĐ thì pt có nghiệm x = - 1

a: \(\Leftrightarrow x^2-2x+1-x^2-2x-1=2x-6\)
=>2x-6=-4x
=>6x=6
hay x=1
b: \(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-3\right)\left(x+3\right)-\left(x-3\right)\left(5x+2\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-3\right)\left(x+3-5x-2\right)=0\)
=>(x-3)(-4x+1)=0
=>x=3 hoặc x=1/4
c: \(\Leftrightarrow4x^2+12x+9-3\left(x^2-16\right)-x^2+4x-4=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3x^2+16x+5-3x^2+48=0\)
=>16x+53=0
hay x=-53/16
d: \(\Leftrightarrow x^3+4x^2-9x-36=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x+4\right)\left(x^2-9\right)=0\)
hay \(x\in\left\{-4;3;-3\right\}\)
b)x^2-9=(x-3)(5x+2)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-3\right)\left(x+3\right)-\left(x-3\right)\left(5x+2\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-3\right)\left(x+3-5x-2\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-3\right)\left(1-4x\right)=0\)
\(\Rightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x-3=0\\1-4x=0\end{matrix}\right.\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=0+3\\x=1:4\end{matrix}\right.\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=3\\x=\dfrac{1}{4}\end{matrix}\right.\)

1) 2x4 - 9x3 + 14x2 - 9x + 2 = 0
<=> (2x4 - 4x3) - (5x3 - 10x2) + (4x2 - 8x) - (x - 2) = 0
<=> 2x3(x - 2) - 5x2(x - 2) + 4x(x - 2) - (x - 2) = 0
<=> (2x3 - 5x2 + 4x - 1)(x - 2) = 0
<=> [(2x3 - 2x2) - (3x2 - 3x) + (x - 1)](x - 2) = 0
<=> [2x2(x - 1) - 3x(x - 1) + (x - 1)](x - 2) = 0
<=> (2x2 - 2x - x + 1)(x - 1)(x - 2) = 0
<=> (2x - 1)(x - 1)2(x - 2) = 0
<=> 2x - 1=0
hoặc x - 1 = 0
hoặc x - 2 = 0
<=> x = 1/2
hoặc x = 1
hoặc x = 2
Vậy S = {1/2; 1; 2}
\(x^4-3x^3+2x^2-9x+9=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x^4-2x^3-9x\right)-\left(x^3-2x^2-9\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x\left(x^3-2x^2-9\right)-\left(x^3-2x^2-9\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x^3-2x^2-9\right)\left(x-1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[\left(x^3+x^2+3x\right)-\left(3x^2+3x+9\right)\right]\left(x-1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[x\left(x^2+x+3\right)-3\left(x^2+x+3\right)\right]\left(x-1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x^2+x+3\right)\left(x-3\right)\left(x-1\right)=0\)(1)
Ta thấy \(x^2+x+3=x^2+2.x.\frac{1}{2}+\frac{1}{4}-\frac{1}{4}+3\)
\(=\left(x+\frac{1}{2}\right)^2+\frac{11}{4}\ge\frac{11}{4}>0;\forall x\)
\(\Rightarrow\left(1\right)\)xảy ra \(\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x-3=0\\x-1=0\end{cases}\Leftrightarrow}\orbr{\begin{cases}x=3\\x=1\end{cases}}\)
Vậy \(x\in\left\{3;1\right\}\)
\(x^4-3x^3+2x^2-9x+9=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x^4+9+6x^2\right)-\left(3x^3+9x\right)-4x^2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x^2+3\right)^2-3x\left(x^2+3\right)-4x^2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x^2+3\right)^2-4x\left(x^2+3\right)+x\left(x^2+3\right)-4x^2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x^2+3\right)\left(x^2+3-4x\right)+x\left(x^2+3-4x\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x^2+3-4x\right)\left(x^2+3+x\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-1\right)\left(x-3\right)\left[\left(x+\frac{1}{2}\right)^2+\frac{11}{4}\right]=0\)
Vì \(\left(x^2+\frac{1}{2}\right)^2+\frac{11}{4}>0\)
\(\Rightarrow\left(x-1\right)\left(x-3\right)=0\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x=1\\x=3\end{cases}}\)