
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


\(x-y-5=0\Rightarrow x=y+5\)
Ta có:
\(\left(y+5+y\right)^2+3\left(y+5+y\right)+2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(2y+5\right)^2+3\left(2y+5\right)+2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4y^2+20y+25+6y+15+2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4y^2+26y+42=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(y+3\right)\left(2y+7\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow y=-3;y=-\frac{7}{2}\)
Thay vào tìm x nốt


Bài 1:
Đặt \(\hept{\begin{cases}S=x+y\\P=xy\end{cases}}\) hpt thành:
\(\hept{\begin{cases}S^2-P=3\\S+P=9\end{cases}}\)\(\Leftrightarrow\hept{\begin{cases}S^2-P=3\\S=9-P\end{cases}}\Leftrightarrow\left(9-P\right)^2-P=3\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}P=6\Rightarrow S=3\\P=13\Rightarrow S=-4\end{cases}}\).Thay 2 trường hợp S và P vào ta tìm dc
\(\hept{\begin{cases}x=3\\y=0\end{cases}}\)và\(\hept{\begin{cases}x=0\\y=3\end{cases}}\)
Câu 3: ĐK: \(x\ge0\)
Ta thấy \(x-\sqrt{x-1}=0\Rightarrow x=\sqrt{x-1}\Rightarrow x^2-x+1=0\) (Vô lý), vì thế \(x-\sqrt{x-1}\ne0.\)
Khi đó \(pt\Leftrightarrow\frac{3\left[x^2-\left(x-1\right)\right]}{x+\sqrt{x-1}}=x+\sqrt{x-1}\Rightarrow3\left(x-\sqrt{x-1}\right)=x+\sqrt{x-1}\)
\(\Rightarrow2x-4\sqrt{x-1}=0\)
Đặt \(\sqrt{x-1}=t\Rightarrow x=t^2+1\Rightarrow2\left(t^2+1\right)-4t=0\Rightarrow t=1\Rightarrow x=2\left(tm\right)\)

ĐK: x khác 0
\(\hept{\begin{cases}x\left(x+y\right)+x=3\\x^2\left(x+y\right)^2+x^2=5\end{cases}}\)
Đặt: x(x+y)=u, x=v
Ta có hệ mới :
\(\hept{\begin{cases}u+v=3\\u^2+v^2=5\end{cases}}\)Hệ phương trình đối xứng loại 1, em làm tiếp nhé!

pt (1) <=>5x-2x^2-xy+y^2-y-2=0
giai phuong trinh (1) theo an y ta co:
y² - (x+1)y - (2x² - 5x+2)=0
<=>Δ=(x+1)²+4(2x² - 5x+2)=x²+2x+1+8x²-20y+8=9x²-18x+9
=9(x-1)²
Δ>=0 => phuong trinh co nghiem
<=>y=(x+1+3(x-1))/2 hoac y=(x+1-3(x-1))/2
<=>y=2x-1 hoac y=2-x
* thay y=2x-1 vao pt 2 ta duoc:
x²+(2x-1)²+x+(2x-1)=4
<=>5x²-x-4=0
giai phuong trinh tren ta tim duoc x=1 va y=1 hoac x=-4/5 va y=-13/5
*the y=2-x vao pt 2 ta duoc
x²+(2-x)²+x+(2-x)=4
<=>2x²-4x+2=0
<=>x=1 =>y=1
vay phuong trinh co 2 nghiem (1;1);(-4/5;-13/5)

\(x^2-2x-2-2\sqrt{2x+1}=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2-2x-8-\left(2\sqrt{2x+1}-6\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-4\right)\left(x+2\right)-\frac{4\left(2x+1\right)-36}{2\sqrt{2x+1}+6}=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-4\right)\left(x+2\right)-\frac{8\left(x-4\right)}{2\sqrt{2x+1}+6}=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-4\right)\left(x+2-\frac{8}{2\sqrt{2x+1}+6}\right)=0\)
Thấy: \(x+2-\frac{8}{2\sqrt{2x+1}+6}>0\)
\(\Rightarrow x-4=0\Rightarrow x=4\)

<=>\(\hept{\begin{cases}x^3+y^3=1\\x^2\left(x^3-1\right)+y^2\left(y^3-1\right)=0\end{cases}}\)
<=>\(\hept{\begin{cases}x^3+y^3=1\\x^2y^3+x^3y^2=0\end{cases}}\)
Đặt S=x+y;P=xy
khi đó: \(\hept{\begin{cases}S^3-3SP=1\\P^2S=0\end{cases}}\)
sau đó giải hệ pt . kết wa là (0;1);(1:0)

ĐKXĐ : \(y\ge0\)
P/t (1) \(\Leftrightarrow x^2\left(x-y\right)-\left(x-y\right)=0\) \(\Leftrightarrow\left(x^2-1\right)\left(x-y\right)=0\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x^2-1=0\\x-y=0\end{cases}}\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x=\pm1\\x=y\end{cases}}\)
Xét : \(x=\pm1\) . Với x = 1 và với x = -1 thay vào p/t (2) tìm y rồi đối chiếu ĐK
Xét : \(x=y\) Mà \(y\ge0\) nên \(x\ge0\Rightarrow\left|x\right|=x\)
Khi đó , p/t (2) \(\Leftrightarrow\sqrt{2\left(x^4+1\right)}-5\sqrt{\left|x\right|}+\sqrt{x}+2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\sqrt{2\left(x^4+1\right)}-5\sqrt{x}+\sqrt{x}+2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\sqrt{2\left(x^4+1\right)}-4\sqrt{x}+2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\sqrt{2\left(x^4+1\right)}=4\sqrt{x}-2\) (1)
Vì x >= 0 nên AD BĐT Cô - si ta được : \(x^4+1\ge2x^2\Rightarrow\sqrt{2\left(x^4+1\right)}\ge\sqrt{2.2x^2}=2x\) ( vì x >= 0 ) (2)
Với x >= 0 ta luôn có : \(\left(\sqrt{x}-1\right)^2\ge0\Leftrightarrow x-2\sqrt{x}+1\ge0\Leftrightarrow2x-4\sqrt{x}+2\ge0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4\sqrt{x}-2\le2x\) . (3)
Từ (1) ; (2) và (3) suy ra : \(VT=VP=2x\)
Dấu " = " xảy ra <=> x = 1 (t/m)
Mà x = y suy ra : y = 1 (t/m)
Vậy ...

b) \(\hept{\begin{cases}x^2-4x+3=0\left(1\right)\\x^2+xy+y^2=3\left(2\right)\end{cases}}\)
Từ (1) <=> (x - 1)(x - 3) = 0 \(\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x=1\\x=3\end{cases}}\)
Với x = 3 => (2) <=> 32 + 3y + y2 = 3
<=> y2 + 3y + 6 = 0
<=> \(\left(2y+3\right)^2=-15\)<=> PT vô nghiệm
Với x = 3 => (1) <=> 12 + y + y2 = 3
<=> (y - 1)(y + 2) = 0
<=> \(\orbr{\begin{cases}y=1\\y=-2\end{cases}}\)
=> Hệ có 2 nghiệm (x ; y) = (1;1) ; (1 ; - 2)
2 x - y = 5 x + y + 2 x + 2 y - 5 = 0
Ta đưa về giải hai hệ phương trình:
hoặc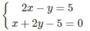
Giải hệ:
Giải hệ:
Vậy hệ phương trình đã cho có hai nghiệm
( x 1 ; y 1 ) = (1; -3) và ( x 2 ; y 2 ) = (3; 1)