
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.



Ta có : |2x - 5| + |4 + x| = 0
Mà : |2x - 5| \(\ge0\forall x\)
|4 + x| \(\ge0\forall x\)
Nên \(\orbr{\begin{cases}\left|2x-5\right|=0\\\left|4+x\right|=0\end{cases}}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}2x-5=0\\4+x=0\end{cases}}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}2x=5\\x=-4\end{cases}}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x=\frac{5}{2}\\x=-4\end{cases}}\)

\(\Delta=4+4.7=32\)
\(\orbr{\begin{cases}x_1=\frac{-2+4\sqrt{2}}{2}=-1+2\sqrt{2}\\x_2=\frac{-2-4\sqrt{2}}{2}=-1-2\sqrt{2}\end{cases}}\)

Ta có: \(\left(3x-1\right)\left(2x+7\right)-\left(x+1\right)\left(6x-5\right)=\left(x+2\right)-\left(x-5\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow6x^2+21x-2x-7-6x^2+5x-6x+5=x+2-x+5\)
\(\Leftrightarrow18x-2=7\)
\(\Leftrightarrow18x=9\)
hay \(x=\dfrac{1}{2}\)

b) Q = 2x2 - 6x => 2Q = 4x2 - 12x => 2Q = (2x)2 - 2 . 2 . 3x + 9 - 9 => 2Q = (2x - 3)2 - 9 \(\ge\)-9 <=> Q \(\ge\)-4,5
Đẳng thức xày ra khi: (2x - 3)2 = 0 => x = 1,5
Vậy giá trị nhỏ nhất của Q là -4,5 khi x = 1,5
c) M = x2 + y2 - x + 6y + 10 => M = x2 + y2 - x + 6y + 0,25 + 9 + 0,75
=> M = (x2 - x + 0,25) + (y2 + 6y + 9) + 0,75
=> M = (x - 0,5)2 + (y + 3)2 + 0,75\(\ge\)0,75
Đẳng thức xảy ra khi: (x - 0,5)2 = 0 và (y + 3)2 = 0 <=> x = 0,5 và y = -3
Vậy giá trị nhỏ nhất của M là 0,75 khi x = 0,5 và y = -3

2:
b: Khi x=-3 thì (1) sẽ là -3(m-1)+2m+5=0
=>-3m+3+2m+5=0
=>8-m=0
=>m=8
c: Để ptvn thì m-1=0
=>m=1

Nếu là câu c
c, Ta có : BD là phân giác \(\widehat{ABC}\)
\(\Rightarrow\dfrac{AD}{DC}=\dfrac{AB}{BC}\left(1\right)\)
Ta có : BK là phân giác \(\widehat{ABH}\)
\(\Rightarrow\dfrac{HK}{AK}=\dfrac{BH}{AB}\left(2\right)\)
Ta có: ΔHBA ~ ΔABC (cmt )
(*nếu chưa c/m tam giác đồng dạng thì hãy c/m, làm r thì khỏi )
\(\Rightarrow\dfrac{HB}{AB}=\dfrac{AB}{AC}\left(3\right)\)
\(\left(1\right)\left(2\right)\left(3\right)\Rightarrow\dfrac{AD}{DC}=\dfrac{HK}{AK}\)
\(\Rightarrow AK.AD=HK.CD\left(đpcm\right)\)




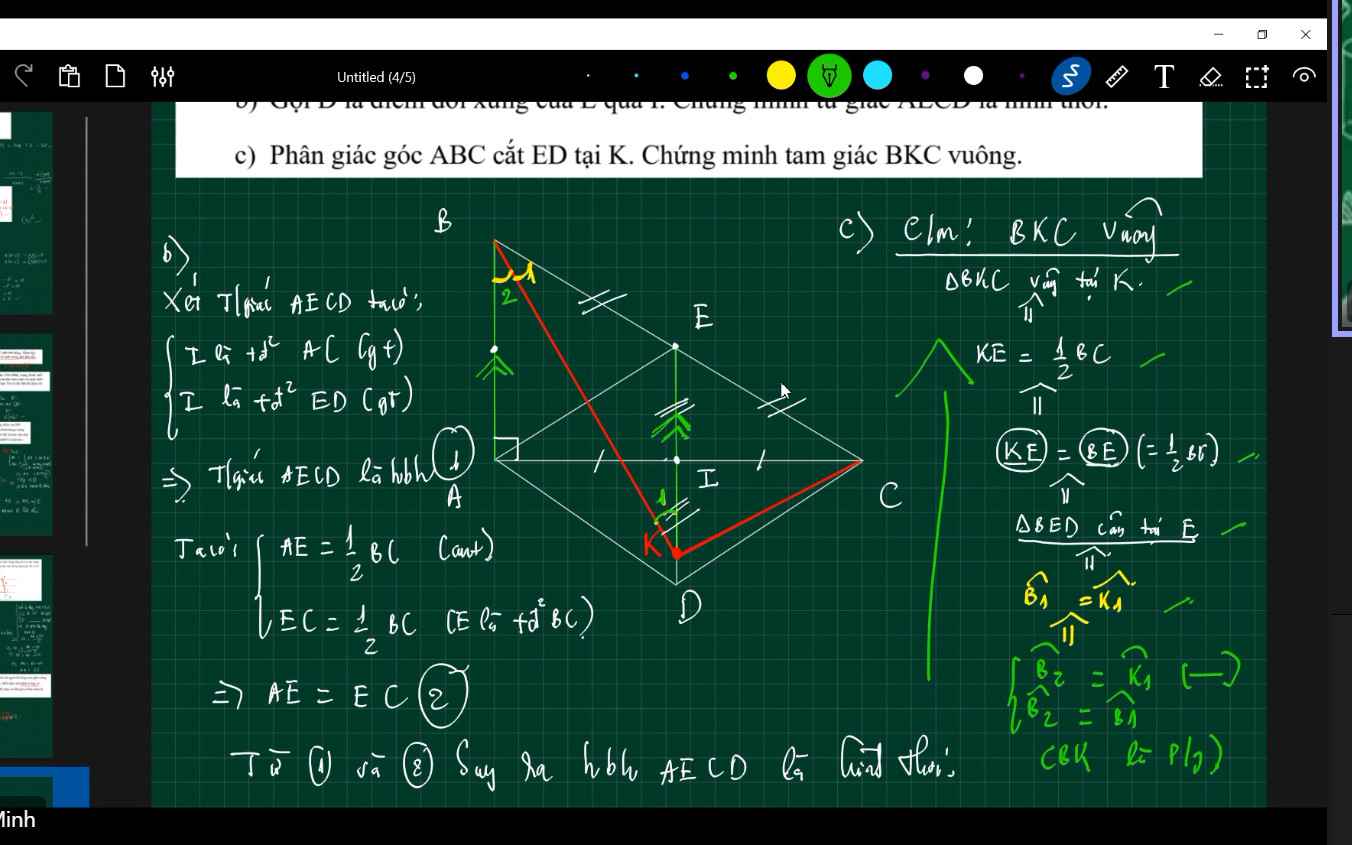
 giải giúp mình câu c với ạ, mình cảm ơnnnnn
giải giúp mình câu c với ạ, mình cảm ơnnnnn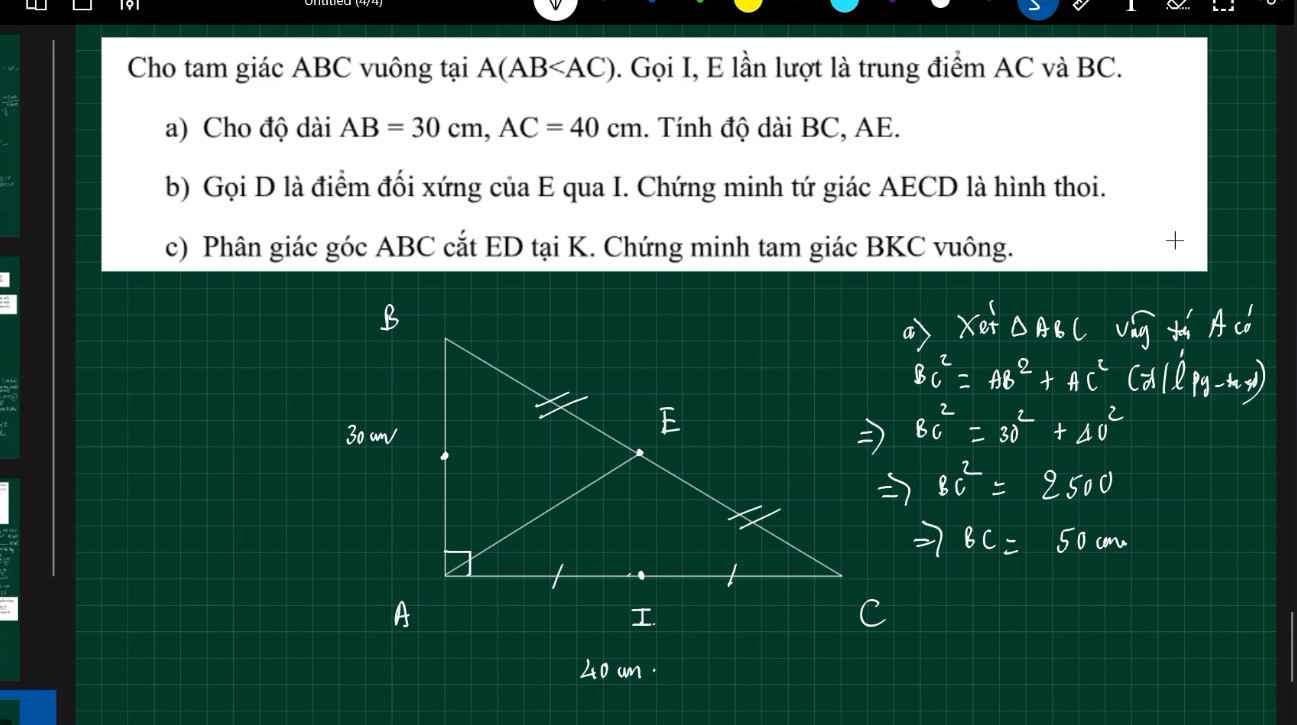
7, ĐKXĐ:\(x\ne2\)
\(\dfrac{1}{x-2}+\dfrac{3-x}{2-x}=-3\\ \Leftrightarrow\dfrac{1}{x-2}+\dfrac{x-3}{x-2}=-3\\ \Leftrightarrow\dfrac{1+x-3}{x-2}=-3\\ \Rightarrow x-2=-3\left(x-2\right)\\ \Leftrightarrow x-2=6-3x\\ \Leftrightarrow x-2-6+3x=0\\ \Leftrightarrow4x-8=0\\ \Leftrightarrow x=2\left(ktm\right)\)
7: \(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{1}{x-2}+\dfrac{x-3}{x-2}=\dfrac{-3\left(x-2\right)}{x-2}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x-2=-3\left(x-2\right)\)
=>x-2=0
hay x=2(loại)
8: \(\Leftrightarrow\left(x+5\right)^2-\left(x-5\right)^2=20\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2+10x+25-x^2+10x-25=20\)
=>20x=20
hay x=1(nhận)