
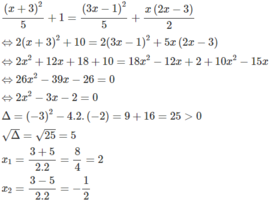
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.

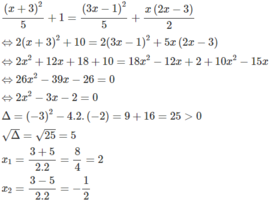

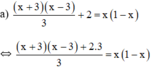
⇔ (x + 3)(x – 3) + 2.3 = 3x(1 – x)
⇔ x 2 − 9 + 6 = 3 x − 3 x 2 ⇔ x 2 − 9 + 6 − 3 x + 3 x 2 = 0 ⇔ 4 x 2 − 3 x − 3 = 0
Có a = 4; b = -3; c = -3 ⇒ Δ = ( - 3 ) 2 – 4 . 4 . ( - 3 ) = 57 > 0
Phương trình có hai nghiệm
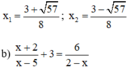
Điều kiện xác định: x ≠ 5; x ≠ 2.
Quy đồng và khử mẫu ta được :
(x + 2)(2 – x) + 3(2 – x)(x – 5) = 6(x – 5)
⇔ 4 − x 2 + 6 x − 3 x 2 − 30 + 15 x = 6 x − 30 ⇔ 4 − x 2 + 6 x − 3 x 2 − 30 + 15 x − 6 x + 30 = 0 ⇔ − 4 x 2 + 15 x + 4 = 0
Có a = -4; b = 15; c = 4 ⇒ Δ = 15 2 – 4 . ( - 4 ) . 4 = 289 > 0
Phương trình có hai nghiệm phân biệt:
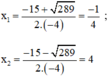
Cả hai giá trị đều thỏa mãn điều kiện.
Vậy phương trình có tập nghiệm 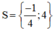
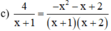
Điều kiện xác định: x ≠ -1; x ≠ -2.
Quy đồng và khử mẫu ta được:
4 ⋅ ( x + 2 ) = − x 2 − x + 2 ⇔ 4 x + 8 = − x 2 − x + 2 ⇔ 4 x + 8 + x 2 + x − 2 = 0 ⇔ x 2 + 5 x + 6 = 0
Có a = 1; b = 5; c = 6 ⇒ Δ = 5 2 – 4 . 1 . 6 = 1 > 0
⇒ Phương trình có hai nghiệm phân biệt:
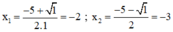
Chỉ có nghiệm x 2 = - 3 thỏa mãn điều kiện xác định.
Vậy phương trình có nghiệm x = -3.

a: ĐKXĐ: \(x\notin\left\{3;-5\right\}\)
\(\dfrac{x+5}{3}-\dfrac{x-3}{5}=\dfrac{5}{x-3}-\dfrac{3}{x+5}\)
=>\(\dfrac{5\left(x+5\right)-3\left(x-3\right)}{15}=\dfrac{5\left(x+5\right)-3\left(x-3\right)}{\left(x-3\right)\left(x+5\right)}\)
=>\(\dfrac{5x+25-3x+9}{15}=\dfrac{5x+25-3x+9}{\left(x-3\right)\left(x+5\right)}\)
=>(x-3)(x+5)=15
=>\(x^2+2x-15-15=0\)
=>\(x^2+2x-30=0\)
=>\(\left(x+1\right)^2=31\)
=>\(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x+1=\sqrt{31}\\x+1=-\sqrt{31}\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow x=-1\pm\sqrt{31}\left(nhận\right)\)
b: ĐKXĐ: \(x\in R\)
\(\sqrt{x^2+x+1}=3-x\)
=>\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x^2+x+1=\left(3-x\right)^2\\x< =3\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x< =3\\x^2-6x+9=x^2+x+1\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x< =3\\-7x=-8\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow x=\dfrac{8}{7}\left(nhận\right)\)
c:
ĐKXĐ: \(x\in R\)
\(x^2-x+\sqrt{x^2-x+24}=18\)
=>\(x^2-x+24+\sqrt{x^2-x+24}=42\)
=>\(\left(\sqrt{x^2-x+24}\right)^2+\left(\sqrt{x^2-x+24}\right)-42=0\)
=>\(\left(\sqrt{x^2-x+24}+7\right)\left(\sqrt{x^2-x+24}-6\right)=0\)
=>\(\sqrt{x^2-x+24}-6=0\)
=>\(x^2-x+24=36\)
=>\(x^2-x-12=0\)
=>(x-4)(x+3)=0
=>\(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x-4=0\\x+3=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=4\left(nhận\right)\\x=-3\left(nhận\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)

e: \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\dfrac{1}{x}-\dfrac{1}{y}=1\\\dfrac{3}{x}+\dfrac{4}{y}=5\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\dfrac{3}{x}-\dfrac{3}{y}=3\\\dfrac{3}{x}+\dfrac{4}{y}=5\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\dfrac{-7}{y}=-2\\\dfrac{1}{x}-\dfrac{1}{y}=1\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}y=\dfrac{7}{2}\\\dfrac{1}{x}=1+\dfrac{2}{7}=\dfrac{9}{7}\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}y=\dfrac{7}{2}\\x=\dfrac{7}{9}\end{matrix}\right.\)

\(1,\sqrt{x+2+4\sqrt{x-2}}=5\left(x\ge2\right)\\ \Leftrightarrow\sqrt{\left(\sqrt{x-2}+4\right)^2}=5\\ \Leftrightarrow\sqrt{x-2}+4=5\\ \Leftrightarrow\sqrt{x-2}=1\\ \Leftrightarrow x-2=1\Leftrightarrow x=3\\ 2,\sqrt{x+3+4\sqrt{x-1}}=2\left(x\ge1\right)\\ \Leftrightarrow\sqrt{\left(\sqrt{x-1}+4\right)^2}=2\\ \Leftrightarrow\sqrt{x-1}+4=2\\ \Leftrightarrow\sqrt{x-1}=-2\\ \Leftrightarrow x\in\varnothing\left(\sqrt{x-1}\ge0\right)\)
\(3,\sqrt{x+\sqrt{2x-1}}=\sqrt{2}\left(x\ge\dfrac{1}{2};x\ne1\right)\\ \Leftrightarrow x+\sqrt{2x-1}=2\\ \Leftrightarrow x-2=-\sqrt{2x-1}\\ \Leftrightarrow x^2-4x+4=2x-1\\ \Leftrightarrow x^2-6x+5=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(x-5\right)\left(x-1\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=5\left(tm\right)\\x=1\left(loại\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(4,\sqrt{x-2+\sqrt{2x-5}}=3\sqrt{2}\left(x\ge\dfrac{5}{2}\right)\\ \Leftrightarrow\sqrt{2x-4+2\sqrt{2x-5}}=6\\ \Leftrightarrow\sqrt{\left(\sqrt{2x-5}+1\right)^2}=6\\ \Leftrightarrow\sqrt{2x-5}+1=6\\ \Leftrightarrow\sqrt{2x-5}=5\\ \Leftrightarrow2x-5=25\Leftrightarrow x=15\left(TM\right)\)

\(3\left(x^2-x+1\right)^2-2\left(x+1\right)^2=5.\)\(\left(x^3+1\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3\left(x^2-x+1\right)^2-2\left(x+1\right)^2=5\left(x+1\right)\left(x^2-x+1\right)\)
Đặt \(x+1=a,x^2-x+1=b\), phương trình trở thành:
\(3b^2-2a^2=5ab\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3b^2-5ab-2a^2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\)\(\left(3b+a\right)\left(b-2a\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[3\left(x^2-x+1\right)+x+1\right]\left[x^2-x+1-2\left(x+1\right)\right]=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(3x^2-2x+4\right)\left(x^2-3x-1\right)=0\)
Vì \(3x^2-2x+4=\left(x-1\right)^2+2x^2+3>0\forall x\)nên:
\(x^2-3x-1=0:\left(3x^2-2x+4\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2-3x-1=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-\frac{3}{2}\right)^2-\frac{13}{4}=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-\frac{3}{2}\right)^2=\frac{13}{4}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x-\frac{3}{2}=\frac{\sqrt{13}}{2}\\x-\frac{3}{2}=\frac{-\sqrt{13}}{2}\end{cases}\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x=\frac{3+\sqrt{13}}{2}\\x=\frac{3-\sqrt{13}}{2}\end{cases}}}\)
Vậy phương trình có tập nghiệm: \(S=\left\{\frac{3\pm\sqrt{13}}{2}\right\}\)
\(2\left(x^2+x+1\right)^2-7\left(x-1\right)^2=13\)\(\left(x^3-1\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2\left(x^2+x+1\right)^2-7\left(x-1\right)^2=13\left(x-1\right)\left(x^2+x+1\right)\)
Đặt \(x-1=a,x^2+x+1=b\), phương trình trở thành:
\(2b^2-7a^2=13ab\)\(x=4\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2b^2-13ab-7a^2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(b-7a\right)\left(a+2b\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[x^2+x+1-7\left(x-1\right)\right]\left[x-1+2\left(x^2+x+1\right)\right]=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x^2-6x+8\right)\left(2x^2+3x+1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-2\right)\left(x-4\right)\left(2x+1\right)\left(x+1\right)=0\)
-Xét các trường hợp sau:
+Với \(x-2=0\Leftrightarrow x=2\)
+Với \(x-4=0\Leftrightarrow x=4\)
+Với \(x+1=0\Leftrightarrow x=-1\)
+Với \(2x+1=0\Leftrightarrow x=-0,5\)
Vậy phương trình có tập nghiệm: \(S=\left\{-1;-0,5;2;4\right\}\)

c) \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}2\left(x-2\right)+3\left(1+y\right)=2\\3\left(x-2\right)-2\left(1+y\right)=-3\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}6\left(x-2\right)+9\left(1+y\right)=6\\6\left(x-2\right)-4\left(1+y\right)=-6\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}13\left(1+y\right)=12\\2\left(x-2\right)+3\left(1+y\right)=2\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{21}{13}\\y=-\dfrac{1}{13}\end{matrix}\right.\)
d) \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\left(x-5\right)\left(y-2\right)=\left(x+2\right)\left(y-1\right)\\\left(x-4\right)\left(y+7\right)=\left(x-3\right)\left(y+4\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}xy-2x-5y+10=xy-x+2y-2\\xy+7x-4y-28=xy+4x-3y-12\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}-x-7y=-12\\3x-y=16\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}-x-7y=-12\\21x-7y=112\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}22x=124\\3x-y=16\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{62}{11}\\y=\dfrac{10}{11}\end{matrix}\right.\)

(a) Điều kiện: \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x+1\ge0\\x-5>0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x\ge-1\\x>5\end{matrix}\right.\Rightarrow x>5\).
Phương trình tương đương: \(\sqrt{x+1}=2\sqrt{x-5}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x+1=4\left(x-5\right)\Leftrightarrow x=7\left(TM\right)\).
Vậy: \(S=\left\{7\right\}.\)
(b) Phương trình tương đương: \(x^2-1=8\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2=9\Leftrightarrow x=\pm3\).
Vậy: \(S=\left\{\pm3\right\}\)
a: ĐKXĐ: x+1>=0 và x-5>0
=>x>5
\(\dfrac{\sqrt{x+1}}{\sqrt{x-5}}=2\)
=>\(\sqrt{\dfrac{x+1}{x-5}}=2\)
=>\(\dfrac{x+1}{x-5}=4\)
=>4x-20=x+1
=>3x=21
=>x=7
b: ĐKXĐ: \(x\in R\)
\(\sqrt[3]{x^2-1}=2\)
=>x^2-1=8
=>x^2=9
=>x=3 hoặc x=-3

Bài 1:
Đặt \(\hept{\begin{cases}S=x+y\\P=xy\end{cases}}\) hpt thành:
\(\hept{\begin{cases}S^2-P=3\\S+P=9\end{cases}}\)\(\Leftrightarrow\hept{\begin{cases}S^2-P=3\\S=9-P\end{cases}}\Leftrightarrow\left(9-P\right)^2-P=3\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}P=6\Rightarrow S=3\\P=13\Rightarrow S=-4\end{cases}}\).Thay 2 trường hợp S và P vào ta tìm dc
\(\hept{\begin{cases}x=3\\y=0\end{cases}}\)và\(\hept{\begin{cases}x=0\\y=3\end{cases}}\)
Câu 3: ĐK: \(x\ge0\)
Ta thấy \(x-\sqrt{x-1}=0\Rightarrow x=\sqrt{x-1}\Rightarrow x^2-x+1=0\) (Vô lý), vì thế \(x-\sqrt{x-1}\ne0.\)
Khi đó \(pt\Leftrightarrow\frac{3\left[x^2-\left(x-1\right)\right]}{x+\sqrt{x-1}}=x+\sqrt{x-1}\Rightarrow3\left(x-\sqrt{x-1}\right)=x+\sqrt{x-1}\)
\(\Rightarrow2x-4\sqrt{x-1}=0\)
Đặt \(\sqrt{x-1}=t\Rightarrow x=t^2+1\Rightarrow2\left(t^2+1\right)-4t=0\Rightarrow t=1\Rightarrow x=2\left(tm\right)\)