
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


cosx.tan3x = sin5x
Điều kiện: cos3x ≠ 0. Khi đó,
(3)⇔ cosx.sin3x = cos3x.sin5x
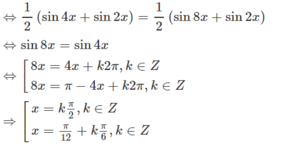
Kết hợp với điều kiện ta được nghiệm của phương trình là:
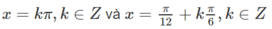

sin 6 x + cos 6 x = 4 cos 2 2 x ⇔ sin 2 x + cos 2 x 3 - 3 sin 2 x . cos 2 x ( sin 2 x + cos 2 x ) = 4 cos 2 2 x
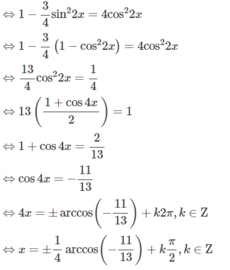

cos 2 x = 3 sin 2 x + 3
Ta thấy cosx = 0 không thỏa mãn phương trình. Với cosx ≠ 0, chia hai vế của phương trình cho cos2x ta được:

cosx.cos2x = 1 + sinx.sin2x
⇔ cosx.cos2x - sinx.sin2x = 1
⇔ cos3x = 1 ⇔ 3x = k2π
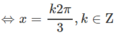

sin 2 x - cos 2 x = cos 4 x ⇔ - cos 2 x = cos 4 x ⇔ 2 cos 3 x . cos x = 0
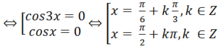
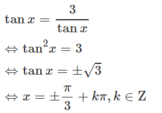
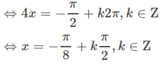
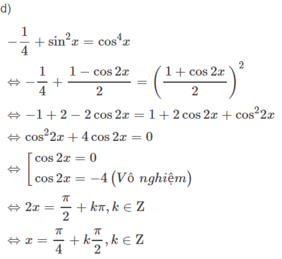
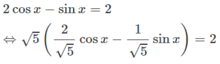


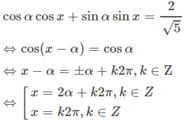
d, \(cosx-cos2x=sin3x\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2sin\dfrac{3x}{2}.sin\dfrac{x}{2}=2sin\dfrac{3x}{2}.cos\dfrac{3x}{2}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow sin\dfrac{3x}{2}.\left(sin\dfrac{x}{2}-cos\dfrac{3x}{2}\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}sin\dfrac{3x}{2}=0\\sin\dfrac{x}{2}=cos\dfrac{3x}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}\dfrac{3x}{2}=k\pi\\cos\left(\dfrac{\pi}{2}-\dfrac{x}{2}\right)=cos\dfrac{3x}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{k2\pi}{3}\\x=\dfrac{\pi}{4}-k\pi\\x=-\dfrac{\pi}{2}+k2\pi\end{matrix}\right.\)
e, \(sinx.cosx+\sqrt{3}sin2x=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{1}{2}sin2x+\sqrt{3}sin2x=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(\sqrt{3}+\dfrac{1}{2}\right)sin2x=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow sin2x=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x=k\pi\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=\dfrac{k\pi}{2}\)