Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


1.: Áp dụng BĐT Cauchy-Schwarz cho 3 số dương
\(a+b+c\ge3\sqrt[3]{abc};\frac{1}{a}+\frac{1}{b}+\frac{1}{c}\ge3\sqrt[3]{\frac{1}{abc}}\)
\(\Rightarrow\left(a+b+c\right)\left(\frac{1}{a}+\frac{1}{b}+\frac{1}{c}\right)\ge3\sqrt[3]{abc}.3\sqrt[3]{\frac{1}{abc}}=9\)

ĐK: a \(\ne\) 0
BPT tương đương
x +\(\frac{x}{a}\)- \(\frac{1}{a}\)- \(\frac{x}{a}\)- \(\frac{1}{a}\)+ (a - 2)x < 0
<=> x - \(\frac{2}{a}\)+ (a - 2) x < 0
<=> (a - 1)x < \(\frac{2}{a}\)
TH1: a = 1: BPT luôn đúng với mọi x
TH2: a > 1: BPT tương đương:
x < \(\frac{2}{a\left(a-1\right)}\)
TH3: a < 1 (a\(\ne\)0) BPT tương đương:
x > \(\frac{2}{a\left(a-1\right)}\)

a, (1-x)(5x+3)= (3x-8)(1-x)
<=> (1-x) (5x+3) - (3x-8)(1-x) =0 <=> (1-x) (2x+11) = 0
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}1-x=0\\2x+11=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=1\\x=-\dfrac{11}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy.........
b, (x-3)(x+4)-2(3x-2)=(x-4)^2
<=> 3x = 24<=> x=8
Vậy .......
c,x^2+ x^3+x+1=0
<=> x^2 (x+1) +(x+1) =0 <=> (x^2 +1)(x+1) =0
<=> x+1 =0 => x=-1
Vậy.......
d, \(\dfrac{x-3}{x+3}-\dfrac{2}{x-3}=\dfrac{3x+1}{9-x^2}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2-6x+9-2x-6=-3x-1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2-5x+4=0\Leftrightarrow\left(x+4\right)\left(x-1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x+4=0\\x-1=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=-4\\x=1\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy...........

a)thay k=0, ta có
\(4x^2-25+0^2+4.0.x=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4x^2-25+0+0=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4x^2-25=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(2x-5\right)\left(2x+5\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\hept{\begin{cases}2x-5=0\\2x+5=0\end{cases}}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\hept{\begin{cases}x=\frac{5}{2}\\x=-\frac{5}{2}\end{cases}}\)
Vậy tập nghiệm của PT là \(S=\left\{\frac{5}{2};-\frac{5}{2}\right\}\)
b) Thay k=-3, ta có:
\(4x^2-25+\left(-3\right)^2+4\left(-3\right)x=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4x^2-25+9-12x=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4x^2-16-12x=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4x^2-16+4x-16x=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(4x^2+4x\right)-\left(16x+16\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4x\left(x+1\right)-16\left(x+1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x+1\right)\left(4x-16\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\hept{\begin{cases}x+1=0\\4x-16=0\end{cases}}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\hept{\begin{cases}x=-1\\x=4\end{cases}}\)
Vậy tập nghiệm của PT là \(S=\left\{-1;4\right\}\)
c) Thay x=-2, ta có:
\(4\left(-2\right)^2-25+k^2+4\left(-2\right)k=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow16-25+k^2-8k=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-9+k^2-8k=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-9+k^2+k-9k=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(k^2+k\right)-\left(9k+9\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow k\left(k+1\right)-9\left(k+1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(k+1\right)\left(k-9\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\hept{\begin{cases}k+1=0\\k-9=0\end{cases}}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\hept{\begin{cases}k=-1\\k=9\end{cases}}\)
Vậy tập nghiệm của PT là \(S=\left\{-1;9\right\}\)

a) Ta có: \(\frac{x+a}{x+2}+\frac{x-2}{x-a}=2\left(1\right)\)
Với a = 4
Thay vào phương trình (t) ta được:
\(\frac{x+2}{x+2}+\frac{x-2}{x-2}=2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\frac{\left(x+2\right)\left(x-2\right)}{\left(x+2\right)\left(x-2\right)}+\frac{\left(x-2\right)\left(x+2\right)}{\left(x+2\right)\left(x-2\right)}=\frac{2\left(x-2\right)\left(x+2\right)}{\left(x-2\right)\left(x+2\right)}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2-4+x^2-4=2\left(x^2-4\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x^2=2x^2-8\)
\(\Leftrightarrow0x=-8\)
Vậy phương trình vô nghiệm
b) Nếu x = -1
\(\Rightarrow\frac{-1+a}{-1+2}+\frac{-1-2}{-1-a}=2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\frac{-1+a}{1}+\frac{-3}{-1-a}=2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\frac{\left(-1+a\right)\left(-1-a\right)}{-1-a}+\frac{-3}{-1-a}=\frac{2\left(-1-a\right)}{-1-a}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow1+a-a-a^2-3=-2-2a\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-a^2+2a=-2-1+3\)
\(\Leftrightarrow a\left(2-a\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}a=0\\2-a=0\end{cases}\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}a=0\\a=2\end{cases}}}\)
Vậy a = {0;2}
NĂM MỚI VUI VẺ

Ta có:
(1) ⇔ 2x2 + x - 10 = 11 ⇔ 2x2 + x - 21 = 0 ⇔ 2x2 - 7x + 6x - 21 = 0
⇔ x(2x - 7) + 3(2x - 7) = 0 ⇔ (2x - 7)(x + 3) = 0
\(\text{⇔}\left[{}\begin{matrix}2x-7=0\\x+3=0\end{matrix}\right.\text{⇔}\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=\frac{7}{2}\\x=-3\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy trong các số 1; -1 ; 2 ; -2 ; \(\frac{5}{2};-\frac{5}{2}\) thì không có số nào là nghiệm của phương trình (1)
Tương tự, ta có:
(2) ⇔ 2x2 - 3x - 5 = -3 ⇔ 2x2 - 3x - 2 = 0 ⇔ 2x2 - 4x + x - 2 = 0
⇔ 2x(x - 2) + (x - 2) = 0 ⇔ (x - 2)(2x + 1) = 0
\(\text{⇔}\left[{}\begin{matrix}x-2=0\\2x+1=0\end{matrix}\right.\text{⇔}\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=2\\x=-\frac{1}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy trong các số trên thì 2 là nghiệm của phương trình.
Trong bài này còn cách là thay từng số vào phương trình, nhưng cách này hơi lâu.
Chúc bạn học tốt@@
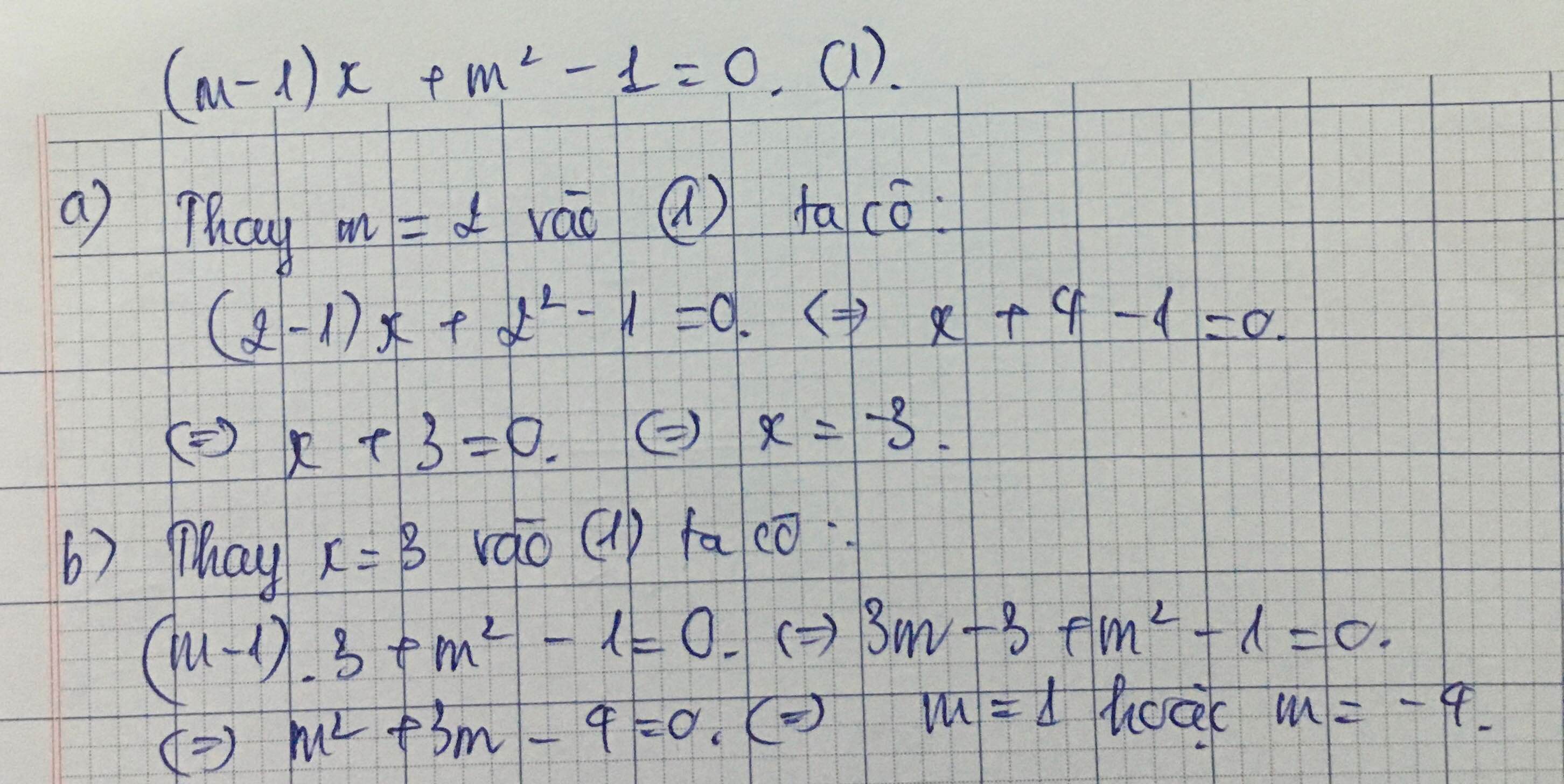

a( ax + 1) = x( a + 2) + 2
⇔ a2x + a - ax- 2x = 2 - a
⇔ x( a2 - a - 2 ) = 2 - a
⇔ x( a2 + a - 2a - 2) = 2 - a
⇔ x[ a( a + 1) -2( a + 1) ] = 2 - a
⇔ x( a + 1)( a - 2) = 2 - a ( *)
+) Với : a # 2 ; a # - 1 , ta có :
( * ) ⇔ x = \(\dfrac{-1}{a+1}\)
+) Với : a = 2 , ta có :
( * ) ⇔ 0x= 0 ( Luôn đúng )
+) Với : a = - 1 , ta có :
( * ) ⇔0x = 3 ( Vô lý )
KL.....
<=>(a^2-a-2)x=2-a
[(a-1/2)^2-(3/2)^2]x=2-a
<=>(a+1)(a-2)x=2-a
a=2 ; =>moi x$R
a=-1 ; vo nghiem
a≠{-1;2}: x=-1/(a+1)