Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.

1/a/\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x+5\right)\left(x+6\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x+5=0\\x+6=0\end{cases}\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x=-5\\x=-6\end{cases}}}\)
Vậy ...................
b/ ĐKXĐ:\(x\ne2;x\ne5\)
.....\(\Rightarrow3x^2-15x-x^2+2x+3x=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x^2-10x=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x\left(x-5\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\hept{\begin{cases}2x=0\\x-5=0\end{cases}\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x=0\left(nhận\right)\\x=5\left(loại\right)\end{cases}}}\)
Vậy ..............
`Answer:`
`1.`
a. \(\left(x+5\right)\left(2x+1\right)-x^2+25=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x+5\right)\left(2x+1\right)-\left(x^2-25\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x+5\right)\left(2x+1\right)-\left(x+5\right)\left(x-5\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x+5\right)\left(2x+1-x+5\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x+5\right)\left(x+6\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x+5=0\\x+6=0\end{cases}\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x=-6\\x=-5\end{cases}}}\)
b. \(\frac{3x}{x-2}-\frac{x}{x-5}+\frac{3x}{\left(x-2\right)\left(x-5\right)}=0\left(ĐKXĐ:x\ne2;x\ne5\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\frac{3x\left(x-5\right)}{\left(x-2\right)\left(x-5\right)}-\frac{x\left(x-2\right)}{\left(x-2\right)\left(x-5\right)}+\frac{3x}{\left(x-2\right)\left(x-5\right)}=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\frac{3x\left(x-5\right)-x\left(x-2\right)+3x}{\left(x-2\right)\left(x-5\right)}=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3x\left(x-5\right)-x\left(x-2\right)+3x=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3x^2-15x-x^2+2x+3x=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x\left(x-5\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}2x=0\\x-5=0\end{cases}\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x=0\\x=5\text{(Không thoả mãn)}\end{cases}}}\)
`2.`
\(ĐKXĐ:x\ne-m-2;x\ne m-2\)
Ta có: \(\frac{x+1}{x+2+m}=\frac{x+1}{x+2-m}\left(1\right)\)
a. Khi `m=-3` phương trình `(1)` sẽ trở thành: \(\frac{x+1}{x-1}=\frac{x+1}{x+5}\left(x\ne1;x\ne-5\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x+1=0\\\frac{1}{x-1}=\frac{1}{x+5}\end{cases}\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x+1=0\\x-1=x+5\end{cases}}\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x=-1\\-1=5\text{(Vô nghiệm)}\end{cases}}}\)
b. Để phương trình `(1)` nhận `x=3` làm nghiệm thì
\(\Leftrightarrow\hept{\begin{cases}\frac{3+1}{3+2-m}=\frac{3+1}{3+2-m}\\3\ne-m-2\\3\ne m-2\end{cases}}\Leftrightarrow\hept{\begin{cases}\frac{4}{5+m}=\frac{4}{5-m}\\m\ne\pm5\end{cases}}\Leftrightarrow\hept{\begin{cases}5+m=5-m\\m\ne\pm5\end{cases}}\Leftrightarrow m=0\)

1)a)(x+5)(2x+1)-x2+25=0
<=>(x+5)(2x+1)-(x-5)(x+5)=0
<=>(x+5)(2x+1-x+5)=0
<=>(x+5)(x+6)=0
<=>x+5=0 hoặc x+6=0
<=>x=-5 hoặc x=-6
Vậy...
b)\(\dfrac{3x}{x-2}-\dfrac{x}{x-5}+\dfrac{3x}{\left(x-2\right)\left(x-5\right)}=0\)
ĐKXĐ:\(x\ne2;x\ne5\)
=>3x2-15x-x2+2x+3x=0
<=>2x2-10x=0
<=>2x(x-5)=0
<=>2x=0 hoặc x-5=0
<=>x=0(TM) hoặc x=5(L)
Vậy...
2)\(\dfrac{x+1}{x+2+m}=\dfrac{x+1}{x+2-m}\)
ĐKXĐ:\(x\ne-m-2;x\ne m-2\)
a)Với m=-3
ĐKXĐ: \(x\ne1;x\ne-5\)
\(\dfrac{x+1}{x-1}=\dfrac{x+1}{x+5}\)
=>(x+1)(x+5)=(x+1)(x-1)
<=>(x+1)(x+5)-(x+1)(x-1)=0
<=>(x+1)(x+5-x+1)=0
<=>6(x+1)=0
<=>x+1=0
<=>x=-1(TM)
Vậy...
b)Với x=3
ĐKXĐ:-m-2\(\ne\)3;m-2\(\ne\)3 hay m\(\ne\)-5;m\(\ne\)5
Thay x=3 vào phương trình ta có:
\(\dfrac{4}{5+m}=\dfrac{4}{5-m}\)
=>4(5-m)=4(5+m)
<=>5-m=5+m
<=>2m=0
<=>m=0(TM)
Vậy m=0 thì phương trình có nghiệm x=3

Bài 9:
Không, vì $x+2=0$ có nghiệm duy nhất $x=-2$ còn $\frac{x}{x+2}=0$ ngay từ đầu đkxđ đã là $x\neq -2$ (cả 2 pt không có cùng tập nghiệm)
Bài 8:
a. Khi $m=2$ thì pt trở thành:
$(2^2-9)x-3=2$
$\Leftrightarrow -5x-3=2$
$\Leftrightarrow -5x=5$
$\Leftrightarrow x=-1$
b.
Khi $m=3$ thì pt trở thành:
$(3^2-9)x-3=3$
$\Leftrightarrow 0x-3=3$
$\Leftrightarrow 0=6$ (vô lý)
c. Khi $m=3$ thì pt trở thành:
$[(-3)^2-9]x-3=-3$
$\Leftrightarrow 0x-3=-3$ (luôn đúng với mọi $x\in\mathbb{R}$)
Vậy pt vô số nghiệm thực.

a: Khi m=1 thì pt sẽ là: x+x-3=6x-6
=>6x-6=2x-3
=>4x=3
=>x=3/4
b: m^2x+m(x-3)=6(x-1)
=>x(m^2+m-6)=-6+3m=3m-6
=>x(m+3)(m-2)=3(m-2)
Để (1) có nghiệm duy nhất thì (m+3)(m-2)<>0
=>m<>-3 và m<>2
=>x=3/(m+3)
\(A=\dfrac{\left(\dfrac{3}{m+3}\right)^2+\dfrac{6}{m+3}+3}{\left(\dfrac{3}{m+3}\right)^2+2}\)
\(=\dfrac{9+6m+18+3m^2+18m+27}{\left(m+3\right)^2}:\dfrac{9+2m^2+12m+18}{\left(m+3\right)^2}\)
\(=\dfrac{3m^2+24m+54}{2m^2+12m+27}>=\dfrac{1}{2}\)
Dấu = xảy ra khi 6m^2+48m+108=2m^2+12m+27
=>4m^2+36m+81=0
=>m=-9/2
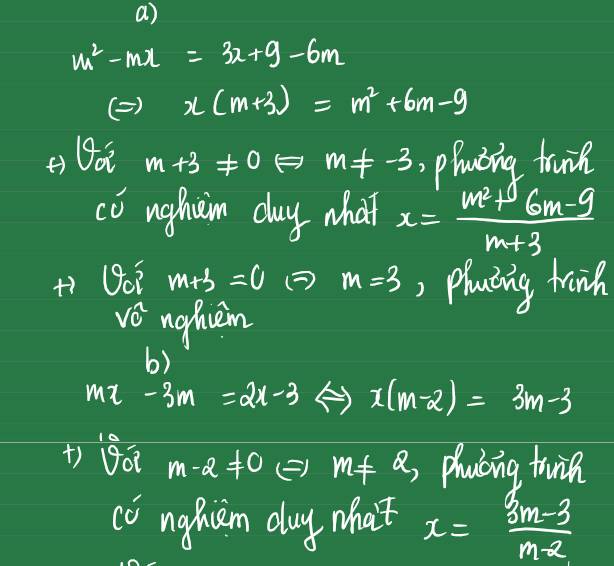
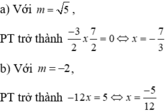
a) Tìm được x = - 1 b) Tìm được x = 17 20