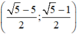Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


\(\frac{1}{x-3}=a,\frac{1}{y-4}=b\)
\(hpt\Leftrightarrow\hept{\begin{cases}a+b=\frac{5}{3}\\4a-3b=\frac{3}{2}\end{cases}\Rightarrow\hept{\begin{cases}a=\frac{13}{14}\\b=\frac{31}{42}\end{cases}\Rightarrow}}\hept{\begin{cases}x=\frac{53}{13}\\y=\frac{166}{31}\end{cases}}\)

Làm mẫu hai câu a, b thôi nha.
a, \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x-\sqrt{3}y=0\\\sqrt{3}x+2y=1+\sqrt{3}\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=\sqrt{3}y\\\sqrt{3}.\sqrt{3}y+2y=1+\sqrt{3}\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=\sqrt{3}y\\5y=1+\sqrt{3}\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{\sqrt{3}+3}{5}\\y=\dfrac{1+\sqrt{3}}{5}\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x\approx0,95\\y\approx0,55\end{matrix}\right.\)
b, \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\sqrt{2}x-\sqrt{5}y=1\\x+\sqrt{5}y=\sqrt{2}\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\sqrt{2}\left(\sqrt{2}-\sqrt{5}y\right)-\sqrt{5}y=1\\x=\sqrt{2}-\sqrt{5}y\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}2-\sqrt{5}\left(\sqrt{2}+1\right)y=1\\x=\sqrt{2}-\sqrt{5}y\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}y=\dfrac{\sqrt{2}-1}{\sqrt{5}}\\x=1\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}y\approx0,19\\x=1\end{matrix}\right.\)

a) \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x-\sqrt{3}y=0\\\sqrt{3}x+2y=1+\sqrt{3}\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\sqrt{3}x-3y=0\\\sqrt{3}x+2y=1+\sqrt{3}\end{matrix}\right.\)
Lấy phương trình dưới trừ phương trình trên thu được: \(5y=1+\sqrt{3}\Rightarrow y=\dfrac{1+\sqrt{3}}{5}\Rightarrow x=\sqrt{3}y=\dfrac{3+\sqrt{3}}{5}\)
b) Cộng hai phương trình lại với nhau thu được:
\(\left(\sqrt{2}+1\right)x=\sqrt{2}+1\Leftrightarrow x=1\Rightarrow y=\dfrac{\sqrt{2}-1}{\sqrt{5}}\)
c) \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\sqrt{2}x+\sqrt{5}y=2\\x+\sqrt{5}y=2\end{matrix}\right.\)
Lấy phương trình trên trừ phương trình dưới:
\(\left(\sqrt{2}-1\right)x=0\Leftrightarrow x=0\Rightarrow y=\dfrac{2-x}{\sqrt{5}}=\dfrac{2}{\sqrt{5}}\)
d) Hướng dẫn. Nhân phương trình đầu với \(\sqrt{2}\) rồi lấy phương trình thu được trừ phương trình dưới.

Đặt m = 1 / x - 3 và n = 1/y - 4
Khi đó ta có hệ m + n = 5/3
4 x x - 3 x n = 3/2
....Bạn tự giải tiếp nhé

\(\int^{3y-2x=1}_{7y-5x=1}\Leftrightarrow\int^{3y-2x=1}_{7y-5x=3y-2x}\Leftrightarrow\int^{3y-2x=1}_{4y=3x}\Leftrightarrow\int^{\frac{9}{4}x-2x=1}_{y=\frac{3}{4}x}\Leftrightarrow\int^{x=4}_{y=3}\)

\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}2x-y=5\\x+2y=5\end{matrix}\right.\\ \Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}y=2x-5\\x+2\left(2x-5\right)=5\end{matrix}\right.\\ \Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}y=2x-5\\x+4x-10=5\end{matrix}\right.\\ \Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}y=2x-5\\5x-10=5\end{matrix}\right.\\ \Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}y=2x-5\\5x=15\end{matrix}\right.\\ \Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}y=2x-5\\x=3\end{matrix}\right.\\ \Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}y=2\cdot3-5\\x=3\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=3\\y=1\end{matrix}\right.\) là nghiệm duy nhất của hệ phương trình.

Trừ 2 vế ta đc : 2y = 8 => y = 4
Thay y = 4 vào x + y = 5 ta đc:
x + 4 = 5 => x = 1
Vậy x = 1 ; y = 4

a ) \(\begin{cases}3x-y=5\\5x+2y=23\end{cases}\)
Từ phương trình \(\left(1\right)\) \(\Leftrightarrow y=3x-5\) \(\left(3\right)\)
Thế \(\left(3\right)\) vào phương trình \(\left(2\right)\) : \(5x+2\left(3x-5\right)=23\)
\(\Leftrightarrow5x+6x-10=23\Leftrightarrow11x=33\Leftrightarrow x=3\)
Từ đó \(y=3.3-5=4\)
Vậy hệ có nghiệm \(\left(x;y\right)=\left(3;4\right)\)
b ) \(\begin{cases}3x+5y=1\\2x-y=-8\end{cases}\)
Từ hệ phương trình \(\left(2\right)\) \(\Leftrightarrow y=3x+8\)
Thế (3) vào (1): \(3x+5\left(2x+8\right)=1\Leftrightarrow3x+10x+40=1\Leftrightarrow13x=-39\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=-3\)
Từ đó \(y=2\left(-3\right)+8=2\)
Vậy hệ có nghiệm \(\left(x;y\right)=\left(-3;2\right)\)
Bài toán giải hệ phương trình bằng phương pháp thế có 2 cách trình bày.
Cách 1:
Từ (1) ta rút ra được x = -y√5 (*)
Thế (*) vào phương trình (2) ta được :
Thay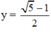 vào (*) ta được:
vào (*) ta được: 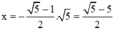
Vậy hệ phương trình có nghiệm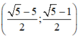
Cách 2 :
Vậy hệ phương trình có nghiệm duy nhất