Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.

Bài toán giải hệ phương trình bằng phương pháp thế có 2 cách trình bày.
Cách 1:
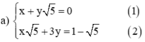
Từ (1) ta rút ra được x = -y√5 (*)
Thế (*) vào phương trình (2) ta được :
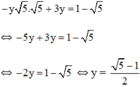
Thay y = 5 - 1 2 vào (*) ta được: x = − 5 − 1 2 ⋅ 5 = 5 − 5 2
Vậy hệ phương trình có nghiệm 5 − 5 2 ; 5 − 1 2
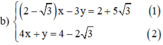
Từ (2) ta rút ra được y = -4x + 4 - 2 √3 (*)
Thế (*) vào phương trình (1) ta được:
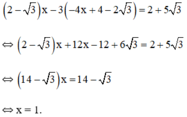
Thay x = 1 vào (*) ta được y = -4.1 + 4 - 2√3 = -2√3
Vậy hệ phương trình có nghiệm duy nhất (1; -2√3)
Cách 2 :
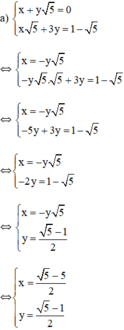
Vậy hệ phương trình có nghiệm duy nhất 5 − 5 2 ; 5 − 1 2
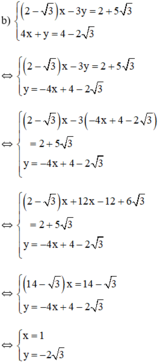
Vậy hệ phương trình có nghiệm duy nhất (1; -2√3)
Kiến thức áp dụng
Giải hệ phương trình 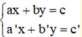 ta làm như sau:
ta làm như sau:
Bước 1: Từ một phương trình (coi là phương trình thứ nhất), ta biểu diễn x theo y (hoặc y theo x) ta được phương trình (*). Sau đó, ta thế (*) vào phương trình thứ hai để được một phương trình mới ( chỉ còn một ẩn).
Bước 2: Dùng phương trình mới ấy thay thế cho phương trình thứ hai, phương trình (*) thay thế cho phương trình thứ nhất của hệ ta được hệ phương trình mới tương đương .
Bước 3: Giải hệ phương trình mới ta tìm được nghiệm của hệ phương trình.

a: \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\dfrac{12}{x-3}-\dfrac{5}{y+2}=63\\\dfrac{8}{x-3}+\dfrac{15}{y+2}=-13\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\dfrac{24}{x-3}-\dfrac{10}{y+2}=126\\\dfrac{24}{x-3}+\dfrac{45}{y+2}=-39\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\dfrac{-55}{y+2}=165\\\dfrac{12}{x-3}-\dfrac{5}{y+2}=63\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}y+2=\dfrac{-1}{3}\\\dfrac{12}{x-3}=48\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}y=-\dfrac{7}{3}\\x=\dfrac{13}{4}\end{matrix}\right.\)

Làm mẫu hai câu a, b thôi nha.
a, \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x-\sqrt{3}y=0\\\sqrt{3}x+2y=1+\sqrt{3}\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=\sqrt{3}y\\\sqrt{3}.\sqrt{3}y+2y=1+\sqrt{3}\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=\sqrt{3}y\\5y=1+\sqrt{3}\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{\sqrt{3}+3}{5}\\y=\dfrac{1+\sqrt{3}}{5}\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x\approx0,95\\y\approx0,55\end{matrix}\right.\)
b, \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\sqrt{2}x-\sqrt{5}y=1\\x+\sqrt{5}y=\sqrt{2}\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\sqrt{2}\left(\sqrt{2}-\sqrt{5}y\right)-\sqrt{5}y=1\\x=\sqrt{2}-\sqrt{5}y\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}2-\sqrt{5}\left(\sqrt{2}+1\right)y=1\\x=\sqrt{2}-\sqrt{5}y\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}y=\dfrac{\sqrt{2}-1}{\sqrt{5}}\\x=1\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}y\approx0,19\\x=1\end{matrix}\right.\)

a) \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x-\sqrt{3}y=0\\\sqrt{3}x+2y=1+\sqrt{3}\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\sqrt{3}x-3y=0\\\sqrt{3}x+2y=1+\sqrt{3}\end{matrix}\right.\)
Lấy phương trình dưới trừ phương trình trên thu được: \(5y=1+\sqrt{3}\Rightarrow y=\dfrac{1+\sqrt{3}}{5}\Rightarrow x=\sqrt{3}y=\dfrac{3+\sqrt{3}}{5}\)
b) Cộng hai phương trình lại với nhau thu được:
\(\left(\sqrt{2}+1\right)x=\sqrt{2}+1\Leftrightarrow x=1\Rightarrow y=\dfrac{\sqrt{2}-1}{\sqrt{5}}\)
c) \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\sqrt{2}x+\sqrt{5}y=2\\x+\sqrt{5}y=2\end{matrix}\right.\)
Lấy phương trình trên trừ phương trình dưới:
\(\left(\sqrt{2}-1\right)x=0\Leftrightarrow x=0\Rightarrow y=\dfrac{2-x}{\sqrt{5}}=\dfrac{2}{\sqrt{5}}\)
d) Hướng dẫn. Nhân phương trình đầu với \(\sqrt{2}\) rồi lấy phương trình thu được trừ phương trình dưới.

\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\left(x-5\right)\left(y-2\right)=\left(x+2\right)\left(y-1\right)\\\left(x-4\right)\left(y+7\right)=\left(x-3\right)\left(y+4\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}xy-2x-5y+10=xy-x+2y-2\\xy+7x-4y-28=xy+4x-3y-12\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x+7y=12\\3x-y=16\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}3x+21y=36\\3x-y=16\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}22y=20\\x+7y=12\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{62}{11}\\y=\dfrac{10}{11}\end{matrix}\right.\)

a) Ta có: \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\sqrt{2}x-y=3\\x+\sqrt{2}y=\sqrt{2}\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\sqrt{2}x-y=3\\\sqrt{2}x+2y=2\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}-3y=1\\x+\sqrt{2}y=\sqrt{2}\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}y=-\dfrac{1}{3}\\x=\sqrt{2}-\sqrt{2}y\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}y=-\dfrac{1}{3}\\x=\sqrt{2}-\sqrt{2}\cdot\dfrac{-1}{3}=\dfrac{4\sqrt{2}}{3}\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy: Hệ phương trình có nghiệm duy nhất là \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{4\sqrt{2}}{3}\\y=-\dfrac{1}{3}\end{matrix}\right.\)
b) Ta có: \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\dfrac{x}{2}-2y=\dfrac{3}{4}\\2x+\dfrac{y}{3}=-\dfrac{1}{3}\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}2x-8y=3\\2x+\dfrac{1}{3}y=-\dfrac{1}{3}\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}-\dfrac{25}{3}y=\dfrac{10}{3}\\2x-8y=3\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}y=-\dfrac{2}{5}\\2x=3+8y=3+8\cdot\dfrac{-2}{5}=-\dfrac{1}{5}\end{matrix}\right.\)
hay \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=-\dfrac{1}{10}\\y=-\dfrac{2}{5}\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy: Hệ phương trình có nghiệm duy nhất là \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=-\dfrac{1}{10}\\y=-\dfrac{2}{5}\end{matrix}\right.\)
c) Ta có: \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\dfrac{2x-3y}{4}-\dfrac{x+y-1}{5}=2x-y-1\\\dfrac{x+y-1}{3}+\dfrac{4x-y-2}{4}=\dfrac{2x-y-3}{6}\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\dfrac{5\left(2x-3y\right)}{20}-\dfrac{4\left(x+y-1\right)}{20}=\dfrac{20\left(2x-y-1\right)}{20}\\\dfrac{4\left(x+y-1\right)}{12}+\dfrac{3\left(4x-y-2\right)}{12}=\dfrac{2\left(2x-y-3\right)}{12}\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}10x-15y-4x-4y+4=40x-20y-20\\4x+4y-4+12x-3y-6=4x-2y-6\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}6x-19y+4-40x+20y+20=0\\16x+y-10-4x+2y+6=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}-34x+y=-24\\12x+3y=4\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}-102x+3y=-72\\12x+3y=4\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}-114x=-76\\12x+3y=4\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{2}{3}\\12\cdot\dfrac{2}{3}+3y=4\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{2}{3}\\3y=4-8=-4\end{matrix}\right.\)
hay \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{2}{3}\\y=-\dfrac{4}{3}\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy: Hệ phương trình có nghiệm duy nhất là \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{2}{3}\\y=-\dfrac{4}{3}\end{matrix}\right.\)

a) Ta có: \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}-x+2y=3\\3x+y=-1\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}-3x+6y=9\\3x+y=-1\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}7y=8\\-x+2y=3\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}y=\dfrac{8}{7}\\-x=3-2y=3-2\cdot\dfrac{8}{7}=\dfrac{5}{7}\end{matrix}\right.\)
hay \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=-\dfrac{5}{7}\\y=\dfrac{8}{7}\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy: Hệ phương trình có nghiệm duy nhất là \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=-\dfrac{5}{7}\\y=\dfrac{8}{7}\end{matrix}\right.\)
b) Ta có: \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}2x+2\sqrt{3}\cdot y=1\\\sqrt{3}x+2y=-5\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}2\sqrt{3}x+6y=\sqrt{3}\\2\sqrt{3}x+4y=-10\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}2y=\sqrt{3}+10\\\sqrt{3}x+2y=-5\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}y=\dfrac{\sqrt{3}+10}{2}\\x\sqrt{3}+2\cdot\dfrac{\sqrt{3}+10}{2}=-5\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}y=\dfrac{\sqrt{3}+10}{2}\\x\sqrt{3}=-5-\sqrt{3}-10=-15-\sqrt{3}\end{matrix}\right.\)
hay \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=-1-5\sqrt{3}\\y=\dfrac{\sqrt{3}+10}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy: Hệ phương trình có nghiệm duy nhất là \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=-1-5\sqrt{3}\\y=\dfrac{\sqrt{3}+10}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\)

=>4x+4y+y=6 và 3x+3y+y=8
=>4x+5y=6 và 3x+4y=8
=>12x+15y=18 và 12x+16y=32
=>-y=-14 và 4x+5y=6
=>y=14 và 4x=6-5y=6-70=-64
=>x=-16 và y=14

a: \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x+4y=-11\\5x-4y=1\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}6x=-10\\x+4y=-11\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{-5}{3}\\y=\dfrac{-11-x}{4}=\dfrac{-11+\dfrac{5}{3}}{4}=-\dfrac{7}{3}\end{matrix}\right.\)
b: \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}2x-y=7\\3x+5y=-22\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}6x-3y=21\\6x+15y=-66\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}-18y=78\\2x-y=7\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}y=\dfrac{-13}{3}\\x=\dfrac{y+7}{2}=\dfrac{4}{3}\end{matrix}\right.\)
Bài toán giải hệ phương trình bằng phương pháp thế có 2 cách trình bày.
Cách 1:
Từ (1) ta rút ra được y = 3 2 x − 11 2 (*)
Thế (*) vào phương trình (2) ta được :
Thay x = 7 vào (*) ta suy ra y = 3 2 ⋅ 7 − 11 2 = 5
Vậy hệ phương trình có nghiệm duy nhất (7 ; 5).
Từ (1) ta rút ra được : y = 3 2 x − 3 (*)
Thế (*) vào phương trình (2) ta được :
Thay x = 3 vào (*) ta suy ra
Vậy hệ phương trình có nghiệm duy nhất (3; 3/2)
Cách 2:
Vậy hệ phương trình có nghiệm duy nhất (7; 5).
Vậy hệ phương trình có nghiệm duy nhất (3; 3/2)
Kiến thức áp dụng
Giải hệ phương trình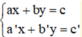 ta làm như sau:
ta làm như sau:
Bước 1: Từ một phương trình (coi là phương trình thứ nhất), ta biểu diễn x theo y (hoặc y theo x) ta được phương trình (*). Sau đó, ta thế (*) vào phương trình thứ hai để được một phương trình mới ( chỉ còn một ẩn).
Bước 2: Dùng phương trình mới ấy thay thế cho phương trình thứ hai, phương trình (*) thay thế cho phương trình thứ nhất của hệ ta được hệ phương trình mới tương đương .
Bước 3: Giải hệ phương trình mới ta tìm được nghiệm của hệ phương trình.