
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


a) Đkxđ: \(x\ne1,x\ne0\)
⇔x+1x−1+2>x−1x⇔2x−1+2>−1x⇔x+1x−1+2>x−1x⇔2x−1+2>−1x
⇔2x−1+1x+2>0⇔2x+x−1+2(x2−x)(x−1)x=2x2+x−1(x−1)(x)>0⇔2x−1+1x+2>0⇔2x+x−1+2(x2−x)(x−1)x=2x2+x−1(x−1)(x)>0
Tử {delta =9}
−1<x<12⇒Tử<0
0<x<1⇒M<0
Nghiệm BPT là
[x<−10<x<12 hoặc x>1

a)
x^2 +1 >0 mọi x
BPT \(\Leftrightarrow x^2+3x-10< 0\) {\(\Delta=9+40=49\)}
\(\Rightarrow-5< x< 2\)
b)
5+x^2 > 0 với mọi x BPT \(\Leftrightarrow20-2x-x^2-5>0\Leftrightarrow x^2+2x-15< 0\){\(\Delta'=1+15=16\)}
\(\Rightarrow-5< x< 3\)

\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{1}{x-1}>\dfrac{1}{x-2}-\dfrac{1}{x+2}=\dfrac{\left(x+2\right)-\left(x-2\right)}{x^2-4}=\dfrac{4}{x^2-4}\)\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{1}{x-1}-\dfrac{4}{x^2-4}>0\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{x^2-4-4x+4}{\left(x-2\right)\left(x-1\right)\left(x+2\right)}>0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow A=\dfrac{x\left(x-2\right)}{\left(x-2\right)\left(x-1\right)\left(x+2\right)}>0\)
Điều kiện tồn tại A
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x\ne2\\x\ne1\\x\ne-2\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Rightarrow A=\dfrac{x}{\left(x-1\right)\left(x+2\right)}\)
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x>0\\\left[{}\begin{matrix}x< -2\\x>1\end{matrix}\right.\end{matrix}\right.\)\(\Rightarrow x>1\)(1)
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x< 0\\-2< x< 1\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Rightarrow-2< x< 0\)(2)
từ (1)&(2)kết luận\(\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}-2< x< 0\\x>1\end{matrix}\right.\)

a) \(4x^2-x+1< 0\)
Tam thức f(x) = 4x2 - x + 1 có hệ số a = 4 > 0 biệt thức ∆ = 12 – 4.4 < 0. Do đó f(x) > 0 ∀x ∈ R.
Bất phương trình 4x2 - x + 1 < 0 vô nghiệm.
b) f(x) = - 3x2 + x + 4 = 0
\(\Delta=1^2-4\left(-3\right).4=49\)
\(x_1=\dfrac{-1+\sqrt{49}}{-3}=-1\)
\(x_2=\dfrac{-1-\sqrt{49}}{-3.2}=\dfrac{4}{3}\)
- 3x2 + x + 4 ≥ 0 <=> - 1 ≤ x ≤ .

a)
<=> f(x) = .
Xét dấu của f(x) ta được tập nghiệm của bất phương trình:
T = ∪ [3; +∞).
b)
<=> f(x) = =
.
f(x) không xác định với x = ± 1.
Xét dấu của f(x) cho tập nghiệm của bất phương trình:
T = (-∞; - 1) ∪ (0; 1) ∪ (1; 3).
c) <=> f(x) =
= .
Tập nghiệm: \(\left(-12;-4\right)\cup\left(-3;0\right)\).

a) 6x^2 -x-2>=0
\(\Delta=1+24=25\)
\(\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x\le\dfrac{1-5}{2.6}=\dfrac{-1}{3}\\x\ge\dfrac{1+5}{2.6}=\dfrac{1}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\)
b)
\(\dfrac{1}{3}x^2+3x+6< 0\Leftrightarrow x^2+9x+18< 0\left\{\Delta=81-4.18=9\right\}\)
\(x_1=\dfrac{-9-3}{2}=-6;x_2=\dfrac{-9+3}{2}=-3\)
\(N_0BPT:\) \(-6< x< -3\)

Ta có: điều kiện xác định của bpt \(x+3-\dfrac{1}{x+7}< -\dfrac{1}{x+7}\) là \(x\ne-7\)
\(\Rightarrow x=-7\) không phải là nghiệm của bpt trên
Lại có: \(x+3< 2\\ \Leftrightarrow x< 2-3\\ \Leftrightarrow x< -1\)
\(\Rightarrow x=-7\) thỏa mãn bpt \(x+3< 2\) \(\left(-7< -1\right)\)
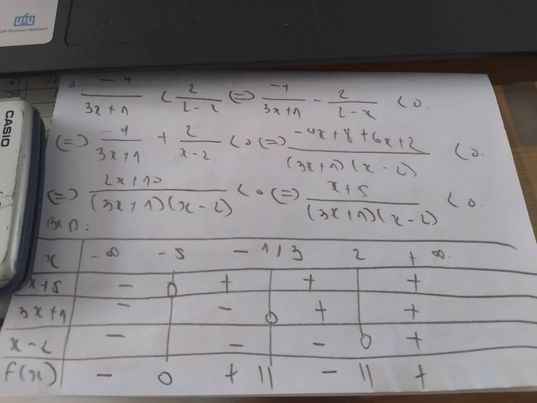

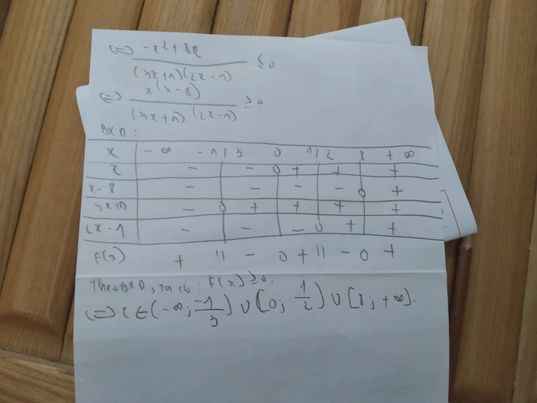
ĐKXĐ:\(x\ne-1\)
\(\dfrac{x-1}{x+1}\le5+x\\ \Leftrightarrow x-1\le\left(x+1\right)\left(5+x\right)\\ \Leftrightarrow x-1\le x^2+6x+5\\ \Leftrightarrow x^2+5x+6\ge0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x\le-3\\x\ge-2\end{matrix}\right.\)