Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.

Rút gọn biểu thức ta có :
\(\left(a-\frac{x^2+a^2}{x+a}\right).\left(\frac{2a}{x}-\frac{4a}{x-a}\right)\)
\(=\frac{a\left(x+a\right)-\left(x^2+a^2\right)}{x+}.\frac{2a\left(x-a\right)-4a.x}{x\left(x-a\right)}\)
\(=\frac{ax+a^2-x^2-a^2}{x+a}.\frac{2ax-2a^2-4ax}{x\left(x-a\right)}\)
\(=\frac{ax-x^2}{x+a}.\frac{-2a^2-2ax}{x\left(x-a\right)}\)
\(=\frac{-\left(x^2-ax\right)}{\left(x+a\right)}.\frac{-\left(2a^2+2ax\right)}{x\left(x-a\right)}\)
\(=\frac{\left(x^2-ax\right).\left(2a^2+2ax\right)}{x\left(x+a\right)\left(x-a\right)}\)
\(=\frac{x\left(x-a\right).2a\left(a+x\right)}{x\left(x+a\right)\left(x-a\right)}\)
\(=2a\)
Với a là một số nguyên thì giá trị biểu thức bằng 2a là một số chẵn.
Chúc bạn học tốt !!!

Rút gọn biểu thức ta có:
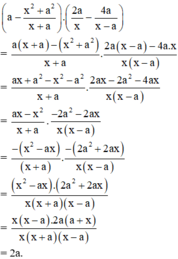
Với a là một số nguyên thì giá trị biểu thức bằng 2a là một số chẵn.

a)Với x \(\ne\)-1
Ta có: x2 + x = 0
=> x(x + 1) = 0
=> \(\orbr{\begin{cases}x=0\\x+1=0\end{cases}}\)
=> \(\orbr{\begin{cases}x=0\\x=-1\left(ktm\right)\end{cases}}\)
Với x = 0 => A = \(\frac{0-3}{0+1}=-3\)
b) Ta có: B = \(\frac{3}{x-3}+\frac{6x}{9-x^3}+\frac{x}{x+3}\)
B = \(\frac{3\left(x+3\right)}{\left(x-3\right)\left(x+3\right)}+\frac{6x}{\left(x-3\right)\left(x+3\right)}+\frac{x\left(x-3\right)}{\left(x+3\right)\left(x-3\right)}\)
B = \(\frac{3x+9+6x+x^2-3x}{\left(x-3\right)\left(x+3\right)}\)
B = \(\frac{x^2+6x+9}{\left(x-3\right)\left(x+3\right)}\)
B = \(\frac{\left(x+3\right)^2}{\left(x-3\right)\left(x+3\right)}\)
B = \(\frac{x+3}{x-3}\)
c) Với x \(\ne\)\(\pm\)3; x \(\ne\)-1
Ta có: P = AB = \(\frac{x-3}{x+1}\cdot\frac{x+3}{x-3}=\frac{x+3}{x+1}=\frac{\left(x+1\right)+2}{x+1}=1+\frac{2}{x+1}\)
Để P \(\in\)Z <=> 2 \(⋮\)x + 1
<=> x + 1 \(\in\)Ư(2) = {1; -1; 2; -2}
<=> x \(\in\){0; -2; 1; -3}

c) Cách 1:
x^4+3x^3-x^2+ax+b x^2+2x-3 x^2+x x^4+2x^3-3x^2 - x^3+2x^2+ax+b x^3+2x^2-3x - (a+3)x+b
Để \(P\left(x\right)⋮Q\left(x\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(a+3\right)x+b=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\hept{\begin{cases}a+3=0\\b=0\end{cases}\Leftrightarrow}\hept{\begin{cases}a=-3\\b=0\end{cases}}\)
Vậy a=-3 và b=0 để \(P\left(x\right)⋮Q\left(x\right)\)
a)
2n^2-n+2 2n+1 n-1 2x^2+n - -2n+2 -2n-1 - 3
Để \(2n^2-n+2⋮2n+1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3⋮2n+1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2n+1\inƯ\left(3\right)=\left\{\pm1;\pm3\right\}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow n\in\left\{0;1;-2;-1\right\}\)
Vậy \(n\in\left\{0;1;-2;-1\right\}\)để \(2n^2-n+2⋮2n+1\)

a) \(ĐKXĐ:\hept{\begin{cases}x\ne2\\x\ne3\end{cases}}\)
\(A=\frac{2x-9}{x^2-5x+6}-\frac{x+3}{x-2}-\frac{2x+4}{3-x}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow A=\frac{2x-9}{\left(x-2\right)\left(x-3\right)}-\frac{x+3}{x-2}+\frac{2\left(x+2\right)}{x-3}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow A=\frac{2x-9-\left(x-3\right)\left(x+3\right)+2\left(x+2\right)\left(x-2\right)}{\left(x-2\right)\left(x-3\right)}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow A=\frac{2x-9-x^2+9+2x^2-8}{\left(x-2\right)\left(x-3\right)}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow A=\frac{x^2+2x-8}{\left(x-2\right)\left(x-3\right)}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow A=\frac{\left(x+4\right)\left(x-2\right)}{\left(x-2\right)\left(x-3\right)}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow A=\frac{x+4}{x-3}\)
b) Để \(A\inℤ\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\frac{x+4}{x-3}\inℤ\)
\(\Leftrightarrow1+\frac{7}{x-3}\inℤ\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x-3\inƯ\left(7\right)=\left\{\pm1;\pm7\right\}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x\in\left\{2;4;-4;10\right\}\)
Vậy để \(A\inℤ\Leftrightarrow x\in\left\{2;4;-4;10\right\}\)
c) Để \(A=\frac{3}{5}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\frac{x+4}{x-3}=\frac{3}{5}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow5x+20=3x-9\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x+29=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=-\frac{29}{2}\)
d) Để \(A< 0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\frac{x+4}{x-3}< 0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow1+\frac{7}{x-3}< 0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\frac{-7}{x-3}< 1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-7< x-3\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x>-4\)
e) Để \(A>0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\frac{x+4}{x-3}>0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow1+\frac{7}{x-3}>0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\frac{-7}{x-3}>1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-7>x-3\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x< -4\)
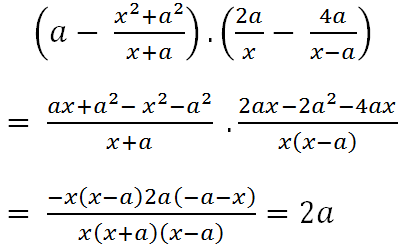
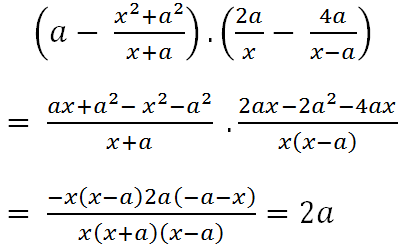 ~~~Học Tốt~~~
~~~Học Tốt~~~
Rút gọn được P = 4a. Do đó P là một số chẵn (vì a nguyên).