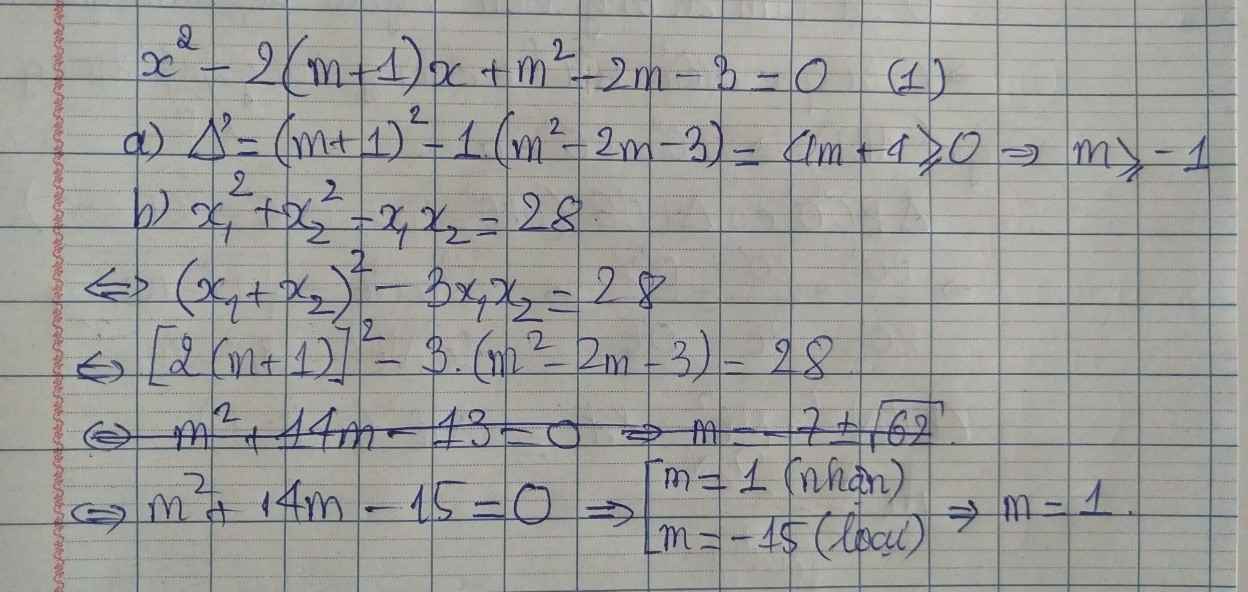Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.

\(\Delta=\left(m+1\right)^2-4.1.2=\left(m+1\right)^2-8\)
Để PT có 2 nghiệm thì:
\(\Delta\ge0\Leftrightarrow\left(m+1\right)^2-8\ge0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(m+1\right)^2\ge8\)
Theo vi ét: \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x_1+x_2=-\left(m+1\right)\\x_1x_2=2\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(x_1^2+x_2^2=x_1^2+2x_1x_2+x_2^2-2x_1x_2=\left(x_1+x_2\right)^2-2x_1x_2\)
\(=\left(m+1\right)^2-2.2=\left(m+1\right)^2-4\)
Mà \(\left(m+1\right)^2\ge8\) nên \(\left(m+1\right)^2-4\ge4\)
\(\Rightarrow min_{x_1^2+x_2^2}=4\) (dấu bằng xảy ra)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(m+1\right)^2=8\)
\(\Leftrightarrow m^2+2m+1=8\\\Leftrightarrow m^2+2m-7=0 \)
\(\Leftrightarrow m=-1\pm2\sqrt{2}\)

Lời giải:
Để PT có 2 nghiệm $x_1,x_2$ thì:
$\Delta'=(m+1)^2-(m^2-1)>0\Leftrightarrow 2m+2>0\Leftrightarrow m>-1$
Áp dụng định lý Viet:
$x_1+x_2=2(m+1)$ và $x_1x_2=m^2-1$
Khi đó, để $x_1^2+x_2^2=x_1x_2+8$
$\Leftrightarrow (x_1+x_2)^2-2x_1x_2=x_1x_2+8$
$\Leftrightarrow (x_1+x_2)^2=3x_1x_2+8$
$\Leftrightarrow 4(m+1)^2=3(m^2-1)+8$
$\Leftrightarrow m^2+8m-1=0$
$\Leftrightarrow m=-4\pm \sqrt{17}$. Vì $m>-1$ nên $m=-4+\sqrt{17}$

\(\Delta=a^2+8>0\Rightarrow\) pt luôn có 2 nghiệm
Theo hệ thức Viet: \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x_1+x_2=a\\x_1x_2=-2\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(N=x_1^2+x_2^2+x_1x_2+2\left(x_1+x_2\right)+4\)
\(=\left(x_1+x_2\right)^2-x_1x_2+2\left(x_1+x_2\right)+4\)
\(=a^2+2+2a+4\)
\(N=a^2+2a+6=\left(a+1\right)^2+5\ge5\)
\(N_{min}=5\) khi \(a=-1\)

a: Δ=(2m-1)^2-4*(-m)
=4m^2-4m+1+4m=4m^2+1>0
=>Phương trình luôn có nghiệm
b: \(A=\left(x_1+x_2\right)^2-2x_1x_2-x_1x_2\)
\(=\left(2m-1\right)^2-3\left(-m\right)\)
=4m^2-4m+1+3m
=4m^2-m+1
=4(m^2-1/4m+1/4)
=4(m^2-2*m*1/8+1/64+15/64)
=4(m-1/8)^2+15/16>=15/16
Dấu = xảy ra khi m=1/8

\(\Delta'=m^2+2m+6=\left(m+1\right)^2+5>0\) ;\(\forall m\Rightarrow\) pt luôn có 2 nghiệm pb với mọi m
Theo hệ thức Viet: \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x_1+x_2=-2m\\x_1x_2=-2m-6\end{matrix}\right.\)
Đặt \(P=x_1^2+x_2^2=\left(x_1+x_2\right)^2-2x_1x_2\)
\(P=\left(-2m\right)^2-2\left(-2m-6\right)=4m^2+4m+12\)
\(P=\left(2m+1\right)^2+11\ge11\)
\(P_{min}=11\) khi \(m=-\dfrac{1}{2}\)

\(\Delta'=\left(m+1\right)^2-2m-10=m^2-9\ge0\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}m\ge3\\m\le-3\end{matrix}\right.\)
Theo hệ thức Viet: \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x_1+x_2=2\left(m+1\right)\\x_1x_2=2m+10\end{matrix}\right.\)
a.
\(P=x_1^2+x_2^2+6x_1x_2=\left(x_1+x_2\right)^2+4x_1x_2\)
\(P=4\left(m+1\right)^2+4\left(2m+10\right)\)
\(P=4m^2+16m+44=\left(4m^2+16m+12\right)+32\)
\(P=4\left(m+1\right)\left(m+3\right)+32\ge32\)
\(P_{min}=32\) khi \(m=-3\)
b.
Theo Viet: \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x_1+x_2=2m+2\\x_1x_2=2m+10\end{matrix}\right.\)
Trừ vế cho vế:
\(x_1+x_2-x_1x_2=-8\)
Đây là hệ thức liên hệ 2 nghiệm ko phụ thuộc m

a: \(\Delta=\left(2m+2\right)^2-4\left(m^2-2m-3\right)\)
\(=4m^2+8m+4-4m^2+8m+12\)
=16m+16
Để phương trình luôn có nghiệm thì 16m+16>=0
hay m>=-1
b: Theo đề, ta có: \(\left(x_1+x_2\right)^2-2x_1x_2-x_1x_2=28\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(2m+2\right)^2-3\left(m^2-2m-3\right)=28\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4m^2+8m+4-3m^2+6m+9=28\)
\(\Leftrightarrow m^2+14m-15=0\)
=>(m+15)(m-1)=0
=>m=1

Δ=(m+1)^2-4(2m-8)
=m^2+2m+1-8m+32
=m^2-6m+33
=(m-3)^2+24>=24
=>Phương trình luôn có hai nghiệm pb
x1^2+x2^2+(x1-2)(x2-2)=11
=>(x1+x2)^2-2x1x2+x1x2-2(x1+x2)+4=11
=>(m+1)^2-(2m-8)-2(m+1)+4=11
=>m^2+2m+1-2m+8-2m-2-7=0
=>m^2-2m-8=0
=>(m-4)(m+2)=0
=>m=4 hoặc m=-2

a, \(\Delta'=\left(-m\right)^2-1\left(-1\right)=m^2+1>0\)
Vậy phương trình đã cho luôn có hai nghiệm phân biệt x1 và x2
b, Theo Vi-ét:\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x_1+x_2=2m\\x_1x_2=-1\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(x^2_1+x^2_2-x_1x_2=7\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(x_1+x_2\right)^2-3x_1x_2=7\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(2m\right)^2-3\left(-1\right)=7\\ \Leftrightarrow4m^2+3=7\\ \Leftrightarrow4m^2=4\\ \Leftrightarrow m^2=1\\ \Leftrightarrow m=\pm1\)

Lời giải:
Để pt có nghiệm thì $\Delta'=4-m\geq 0\Leftrightarrow m\leq 4$
Áp dụng hệ thức Viet, với $x_1,x_2$ là 2 nghiệm của pt thì:
$x_1+x_2=4$
$x_1x_2=m$
Khi đó:
$x_2^2-x_1^2=18$
$\Leftrightarrow (x_2-x_1)(x_2+x_1)=18$
$\Leftrightarrow (x_2-x_1).4=18$
$\Leftrightarrow x_2-x_1=4,5$
$\Rightarrow (x_2-x_1)^2=20,25$
$\Leftrightarrow (x_2+x_1)^2-4x_1x_2=20,25$
$\Leftrightarrow 4^2-4m=20,25$
$\Leftrightarrow m=\frac{-17}{16}$ (tm)