Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.

2, sin4x+cos5=0 <=> cos5x=cos\(\left(\frac{\pi}{2}+4x\right)\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x=\frac{\pi}{2}+k2\pi\\x=-\frac{\pi}{18}+\frac{k2\pi}{9}\end{cases}\left(k\inℤ\right)}\)
ta có \(2\pi>0\Leftrightarrow k< >\frac{1}{4}\)do k nguyên nên nghiệm dương nhỏ nhất trong họ nghiệm \(\frac{\pi}{2}\)khi k=0
\(-\frac{\pi}{18}+\frac{k2\pi}{9}>0\Leftrightarrow k>\frac{1}{4}\)do k nguyên nên nghiệm dương nhỏ nhất trong họ nghiệm \(-\frac{\pi}{18}-\frac{k2\pi}{9}\)là \(\frac{\pi}{6}\)khi k=1
vậy nghiệm dương nhỏ nhất của phương trình là \(\frac{\pi}{6}\)
\(\frac{\pi}{2}+k2\pi< 0\Leftrightarrow k< -\frac{1}{4}\)do k nguyên nên nghiệm âm lớn nhất trong họ nghiệm \(\frac{\pi}{2}+k2\pi\)là \(-\frac{3\pi}{2}\)khi k=-1
\(-\frac{\pi}{18}+\frac{k2\pi}{9}< 0\Leftrightarrow k< \frac{1}{4}\)do k nguyên nên nghiệm âm lớn nhất trong họ nghiệm \(-\frac{\pi}{18}+\frac{k2\pi}{9}\)là \(-\frac{\pi}{18}\)khi k=0
vậy nghiệm âm lớn nhất của phương trình là \(-\frac{\pi}{18}\)

Lời giải:
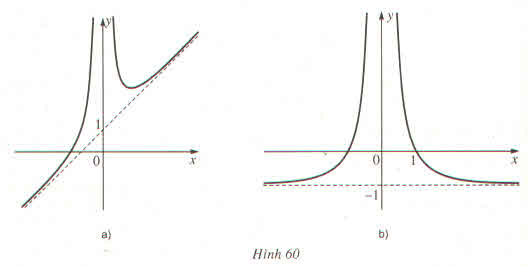
\(\lim\limits_{x\to 1-}f(x)=\lim\limits_{x\to 1-}\left(\frac{1}{x^3-1}-\frac{1}{x-1}\right)=\lim\limits_{x\to 1-}\frac{-x(x+1)}{(x-1)(x^2+x+1)}\)
\(=\lim\limits_{x\to 1-}\frac{x(x+1)}{x^2+x+1}.\lim\limits_{x\to 1-}\frac{1}{1-x}=\frac{2}{3}.(+\infty)=+\infty \)
Đáp án D

ĐK: \(x\ne\frac{k\pi}{2}\)
pt<=> \(8\sin x-\frac{4}{\sin x}=\frac{3}{\cos x}-\frac{3}{\sin x}\)
<=> \(4.\frac{2\sin^2x-1}{\sin x}=3.\frac{\sin x-\cos x}{\sin x.\cos x}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4.\frac{\sin^2x-\cos^2x}{\sin x}=3.\frac{\sin x-\cos x}{\sin x.\cos x}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4.\left(\sin x+\cos x\right)\left(\sin x-\cos x\right)=3\frac{\sin x-\cos x}{\cos x}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}\sin x-\cos x=0\left(1\right)\\4\left(\sin x+\cos x\right)=\frac{3}{\cos x}\left(2\right)\end{cases}}\)
(1) \(\Leftrightarrow\sqrt{2}\sin\left(x+\frac{\pi}{4}\right)=0\) ( tự giải nhé)
(2) \(\Leftrightarrow4\sin x.\cos x+4\cos x.\cos x=3\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2\sin2x+2\cos2x+2=3\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\sin2x+\cos2x=\frac{1}{2}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\sqrt{2}\cos\left(2x+\frac{\pi}{4}\right)=\frac{1}{2}\)Tự giải nhé!

Bạn tự hiểu là giới hạn tiến đến đâu nhé, làm biếng gõ đủ công thức
a. \(\frac{\sqrt{1+x}-1+1-\sqrt[3]{1+x}}{x}=\frac{\frac{x}{\sqrt{1+x}+1}-\frac{x}{1+\sqrt[3]{1+x}+\sqrt[3]{\left(1+x\right)^2}}}{x}=\frac{1}{\sqrt{1+x}+1}-\frac{1}{1+\sqrt[3]{1+x}+\sqrt[3]{\left(1+x\right)^2}}=\frac{1}{2}-\frac{1}{3}=\frac{1}{6}\)
b.
\(\frac{1-x^3-1+x}{\left(1-x\right)^2\left(1+x+x^2\right)}=\frac{x\left(1-x\right)\left(1+x\right)}{\left(1-x\right)^2\left(1+x+x^2\right)}=\frac{x\left(1+x\right)}{\left(1-x\right)\left(1+x+x^2\right)}=\frac{2}{0}=\infty\)
c.
\(=\frac{-2}{\sqrt[3]{\left(2x-1\right)^2}+\sqrt[3]{\left(2x+1\right)^2}+\sqrt[3]{\left(2x-1\right)\left(2x+1\right)}}=\frac{-2}{\infty}=0\)
d.
\(=x\sqrt[3]{3-\frac{1}{x^3}}-x\sqrt{1+\frac{2}{x^2}}=x\left(\sqrt[3]{3-\frac{1}{x^3}}-\sqrt{1+\frac{2}{x^2}}\right)=-\infty\)
e.
\(=\frac{2x^2-8x+8}{\left(x-1\right)\left(x-2\right)\left(x-2\right)\left(x-3\right)}=\frac{2\left(x-2\right)^2}{\left(x-1\right)\left(x-3\right)\left(x-2\right)^2}=\frac{2}{\left(x-1\right)\left(x-3\right)}=\frac{2}{-1}=-2\)
f.
\(=\frac{2x}{x\sqrt{4+x}}=\frac{2}{\sqrt{4+x}}=1\)

Chọn A.
Ta có:
Khi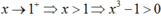
Vậy