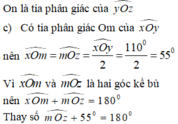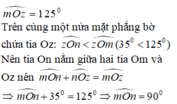Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.

yOz kề bù với xOy
=> yOz + xOy = 180o
=> yOz = 150o
Ot là p/g của xOy => xOt = tOy = xOy/2 = 15o
Om là p/g của yOz => zOm = yOm = yOz/2 = 75o
Vì yOz kề bù với xOy
=> Tia Ox,Oz đối nhau
=> zOm và xOm kề bù
=> zOm + xOm = 180o => xOm = 105o
Vì xOt < xOm ( 15o<105o)
=> Ot nằm giữa Ox, Om
=> xOt + tOm = xOm
=> tOm = 90o
Có xOn + xOm = 105o +75o = 180o
=> xOn và xOm kề bù
=> Om, On đối nhau

Giải:
a) Vì \(x\widehat{O}y\) và \(y\widehat{O}z\) là 2 góc kề bù
\(\Rightarrow x\widehat{O}y+y\widehat{O}z=180^o\)
\(50^o+y\widehat{O}z=180^o\)
\(y\widehat{O}z=180^o-50^o\)
\(y\widehat{O}z=130^o\)
Vì \(y\widehat{O}z=130^o\)
\(\Rightarrow y\widehat{O}z\) là góc tù
b) Vì \(x\widehat{O}y< x\widehat{O}m\left(50^o< 115^o\right)\)
⇒Om ko phải là tia p/g của \(x\widehat{O}y\)
c) Vì On là tia p/g của \(x\widehat{O}y\)
\(\Rightarrow x\widehat{O}n=n\widehat{O}y=\dfrac{x\widehat{O}y}{2}=\dfrac{50^o}{2}=25^o\)
\(\Rightarrow x\widehat{O}y+y\widehat{O}m=x\widehat{O}m\)
\(50^o+y\widehat{O}m=115^o\)
\(y\widehat{O}m=115^o-50^o\)
\(y\widehat{O}m=65^o\)
\(\Rightarrow n\widehat{O}y+y\widehat{O}m=n\widehat{O}m\)
\(25^o+65^o=n\widehat{O}m\)
\(\Rightarrow n\widehat{O}m=90^o\)
Vậy \(n\widehat{O}m=90^o\)
Chúc bạn học tốt!

a) Ta có:
\(\widehat{xOy}< \widehat{xOz}\left(40^o< 150^o\right)\)
\(\Rightarrow Tia\)\(Oy\)nằm giữa hai tia \(Ox\)và \(Oz\)
b) Ta có:
\(\widehat{xOz}=\widehat{zOy}+\widehat{xOy}\)
\(\Rightarrow150^o=\widehat{zOy}+40^o\)
\(\Rightarrow\widehat{zOy}=150^o-40^o=110^o\)
c) Do tia \(Om\)là tia phân giác của \(\widehat{xOy}\)
\(\Rightarrow\widehat{yOm}=\widehat{mOx}=\frac{\widehat{xOy}}{2}=\frac{40^o}{2}=20^o\)
Do tia \(On\)là tia phân giác của \(\widehat{zOy}\)
\(\Rightarrow\widehat{zOn}=\widehat{nOy}=\frac{\widehat{zOy}}{2}=\frac{110^o}{2}=55^o\)
Ta có:
\(\widehat{nOm}=\widehat{nOy}+\widehat{yOm}\)
\(\Rightarrow\widehat{nOm}=55^o+20^o=75^o\)