Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.

\(\text{PT }\left(d_1\right)\text{ giao }Ox:y=0\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{1}{2}x=-2\Leftrightarrow x=-4\Leftrightarrow A\left(-4;0\right)\Leftrightarrow OA=4\left(cm\right)\\ \text{PT }\left(d_2\right)\text{ giao }Ox:y=0\Leftrightarrow x=2\Leftrightarrow B\left(2;0\right)\Leftrightarrow OB=2\left(cm\right)\\ \Leftrightarrow AB=OA+OB=2+4=6\left(cm\right)\\ \text{PT hoành độ giao điểm: }\dfrac{1}{2}x+2=-x+2\Leftrightarrow x=0\Leftrightarrow y=2\Leftrightarrow C\left(0;2\right)\Leftrightarrow OC=2\left(cm\right)\\ \Leftrightarrow S_{ABC}=\dfrac{1}{2}OC\cdot AB=\dfrac{1}{2}\cdot2\cdot6=6\left(cm^2\right)\\ \left\{{}\begin{matrix}AC=\sqrt{2^2+4^2}=2\sqrt{5}\left(pytago\right)\left(cm\right)\\BC=\sqrt{2^2+2^2}=2\sqrt{2}\left(pytago\right)\left(cm\right)\end{matrix}\right.\\ \Leftrightarrow P_{ABC}=AB+BC+CA=2\sqrt{5}+2\sqrt{2}+6\left(cm\right)\)

Giao của (d1) và Ox: \(y_A=0\Rightarrow x_A+1=0\Rightarrow x_A=-1\)
GIao của (d2) và Ox: \(y_B=0\Rightarrow-x_B+1=0\Rightarrow x_B=1\)
Pt hoành độ giao điểm (d1) và (d2):
\(x+1=-x+1\Rightarrow x=0\Rightarrow y=1\)
\(\Rightarrow C\left(0;1\right)\)
Diện tích ABC:
\(S_{ABC}=\dfrac{1}{2}.\left|y_C\right|.\left|x_A-x_B\right|=\dfrac{1}{2}.1.2=1\)
Tọa độ C là:
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x+1=-x+1\\y=x+1\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}2x=0\\y=x+1\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=0\\y=0+1=1\end{matrix}\right.\)
Tọa độ A là:
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}y=0\\x+1=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}y=0\\x=-1\end{matrix}\right.\)
Tọa độ B là:
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}y=0\\-x+1=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}y=0\\-x=-1\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=1\\y=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy: A(-1;0); B(1;0); C(0;1)
\(AB=\sqrt{\left(1+1\right)^2+\left(0-0\right)^2}=2\)
\(AC=\sqrt{\left(0+1\right)^2+\left(1-0\right)^2}=\sqrt{1^2+1^2}=\sqrt{2}\)
\(BC=\sqrt{\left(0-1\right)^2+\left(1-0\right)^2}=\sqrt{1^2+1^2}=\sqrt{2}\)
Xét ΔABC có \(CA^2+CB^2=AB^2\)
nên ΔCAB vuông tại C
=>\(S_{ABC}=\dfrac{1}{2}\cdot CA\cdot CB=\dfrac{1}{2}\cdot\sqrt{2}\cdot\sqrt{2}=1\)

a, HS Tự làm
b, Tìm được C(–2; –3) là tọa độ giao điểm của d 1 và d 2
c, Kẻ OH ⊥ AB (CH ⊥ Ox)
S A B C = 1 2 C H . A B = 9 4 (đvdt)

a: 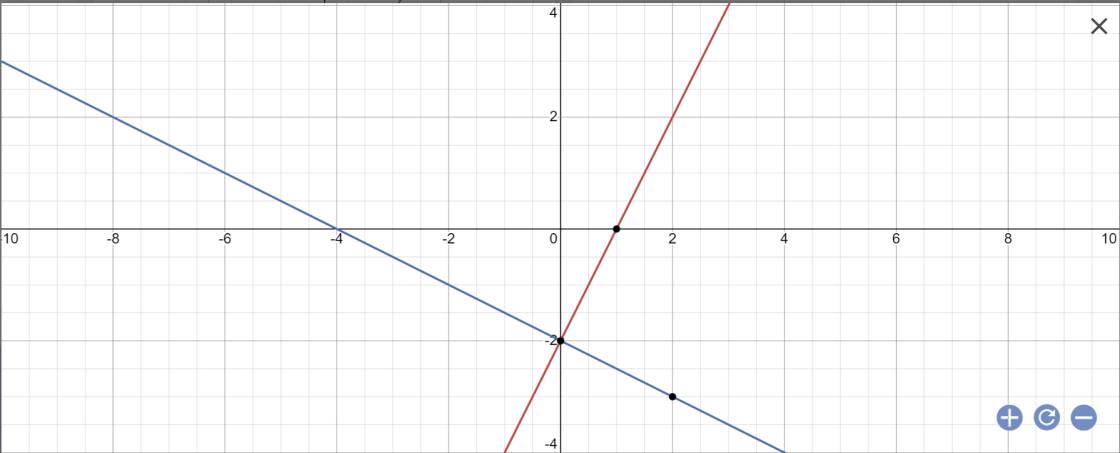
b: Tọa độ A là:
2x-2=-1/2x-2 và y=2x-2
=>x=0 và y=-2
Tọa độ B là:
y=0 và 2x-2=0
=>x=1 và y=0
Tọa độ C là:
y=0 và -1/2x-2=0
=>x=-4; y=0
i: A(0;-2); B(1;0); C(-4;0)
\(\overrightarrow{AB}=\left(1;2\right);\overrightarrow{AC}=\left(-4;2\right)\)
Vì 1*(-4)+2*2=0
nên ΔABC vuông tại A
ii: \(AB=\sqrt{1^2+2^2}=\sqrt{5}\)
\(AC=\sqrt{\left(-4\right)^2+2^2}=2\sqrt{5}\)
\(BC=\sqrt{5+20}=5\left(cm\right)\)
\(C_{ABC}=AB+AC+BC=5+3\sqrt{5}\left(cm\right)\)
\(S_{ABC}=\dfrac{1}{2}\cdot2\sqrt{5}\cdot\sqrt{5}=5\left(cm^2\right)\)
Thay x=-5 vào (d1), ta được:
\(y=\dfrac{1}{5}\cdot\left(-5\right)+1=-1+1=0\)
Vì (d2)//(d3) nên \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}a=-\dfrac{2}{5}\\b\ne-11\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy: (d2): \(y=-\dfrac{2}{5}x+b\)
Thay x=-5 và y=0 vào (d2), ta được:
\(b-\dfrac{2}{5}\cdot\left(-5\right)=0\)
=>b+2=0
=>b=-2
Vậy: (d2): \(y=-\dfrac{2}{5}x-2\)
Tọa độ B là:
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=0\\y=\dfrac{1}{5}\cdot0+1=1\end{matrix}\right.\)
Tọa độ C là:
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=0\\y=-\dfrac{2}{5}\cdot0-2=-2\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy: A(-5;0); B(0;1); C(0;-2)
\(AB=\sqrt{\left(0+5\right)^2+\left(1-0\right)^2}=\sqrt{26}\)
\(AC=\sqrt{\left(0+5\right)^2+\left(-2-0\right)^2}=\sqrt{29}\)
\(BC=\sqrt{\left(0-0\right)^2+\left(-2-1\right)^2}=3\)
Xét ΔABC có \(cosBAC=\dfrac{AB^2+AC^2-BC^2}{2\cdot AB\cdot AC}=\dfrac{26+29-9}{2\cdot\sqrt{26}\cdot\sqrt{29}}=\dfrac{23}{\sqrt{754}}\)
=>\(sinBAC=\sqrt{1-\left(\dfrac{23}{\sqrt{754}}\right)^2}=\dfrac{15}{\sqrt{754}}\)
Diện tích tam giác ABC là:
\(S_{ABC}=\dfrac{1}{2}\cdot AB\cdot AC\cdot sinBAC\)
\(=\dfrac{1}{2}\cdot\dfrac{15}{\sqrt{754}}\cdot\sqrt{26\cdot29}=7,5\)