
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


Ta có BDT luôn đúng \(\left(a-b\right)^2\ge0\) \(\Leftrightarrow a^2+b^2\ge2ab\) \(\Leftrightarrow2\left(a^2+b^2\right)\ge\left(a+b\right)^2\). Do \(a^2+b^2\le2\) nên \(2\left(a^2+b^2\right)\le4\).
Do đó \(\left(a+b\right)^2\le4\) \(\Leftrightarrow-2\le a+b\le2\), suy ra đpcm. ĐTXR \(\Leftrightarrow a=b=1\)

vì a2 và b2 là 2 SCP nên chúng là STN
thử các trường hợp chỉ có 1 và 1 thỏa mãn => a và b đều = 1
=> a + b < 2(a + b)3 vì 2 < 16 (đpcm)


Bài 3:
\(\dfrac{1}{\left(x-y\right)^2}+\dfrac{1}{x^2}+\dfrac{1}{y^2}\ge\dfrac{4}{xy}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2y^2\left(\dfrac{1}{\left(x-y\right)^2}+\dfrac{1}{x^2}+\dfrac{1}{y^2}\right)\ge\dfrac{4}{xy}.x^2y^2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{x^2y^2}{\left(x-y\right)^2}+x^2+y^2\ge4xy\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{x^2y^2}{\left(x-y\right)^2}+x^2-2xy+y^2\ge2xy\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(\dfrac{xy}{x-y}\right)^2+\left(x-y\right)^2\ge2xy\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(\dfrac{xy}{x-y}\right)^2-2xy+\left(x-y\right)^2\ge0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(\dfrac{xy}{x-y}-x+y\right)^2=0\) (luôn đúng)

Áp dụng bất đẳng thức Cauchy ta có :
\(a^2+b^2\ge2\left|ab\right|\)
\(\Rightarrow\left|ab\right|\le1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-1\le\left|ab\right|\le1\)
Ta có : \(a^2+b^2=\left(a+b\right)^2-2ab\)
\(\Rightarrow\left(a+b\right)^2\le2+2ab\le4\)
\(\Rightarrow a+b\le2\)

Áp dụng bất đẳng thức Holder, ta có:
\(\left[\left(\sqrt[3]{a}\right)^3+\left(\sqrt[3]{b}\right)^3+1^3\right].\left(1^3+1^3+1^3\right).\left(1^3+1^3+1^3\right)\ge\left(\sqrt[3]{a}.1.1+\sqrt[3]{b}.1.1+1.1.1\right)^3\)
<=>\(\left(a+b+1\right).9\ge\left(\sqrt[3]{a}+\sqrt[3]{b}+1\right)^3\)
Vì a+b=3
=>\(\left(\sqrt[3]{a}+\sqrt[3]{b}+1\right)^3\le27\)
<=>\(\sqrt[3]{a}+\sqrt[3]{b}+1\le3\)
<=>\(\sqrt[3]{a}+\sqrt[3]{b}\le2\)
Dấu "=" xảy ra khi: a=b=1
=>ĐPCM

dự đoán của chúa Pain a=b=c=1
ta có \(ab^2\le\frac{\left(a+B^2\right)^2}{4}:bc^2\le\frac{\left(b+c^2\right)^2}{4}:ca^2\le\frac{\left(c+a^2\right)^2}{4}.\)
\(ab^2+bc^2+ca^2\le\frac{\left(a^2+2ab+b^2\right)+\left(b^2+2bc+c^2\right)+\left(c^2+2ac+c^2\right)}{4}\)
\(ab^2+bc^2+ca^2\le\frac{1}{2}\left(a^2+b^2+c^2\right)+\frac{1}{2}\left(ab+bc+ca\right)\)
ta có \(xy+yz+zx\le x^2+y^2+z^2\left(cosi\right)\Leftrightarrow ab+bc+ca\le a^2+b^2+c^2=3\)luôn đúng
thay số ta được \(ab^2+bc^2+ca^2\le\frac{3}{2}+\frac{3}{2}=3\)
\(ab^2+bc^2+ca^2-abc\le3-abc\)
có \(abc\ge\frac{\left(a+b+c\right)^3}{27}..."-abc"\ge\rightarrow\le\) ( -abc dấu > thành dấu < cùng dấu thay vào được )
\(ab^2+bc^2+ca^2-abc\le3-\frac{\left(a+b+C\right)^3}{27}\)
ta có \(a^2+1\ge2a\left(cosi\right)\)
\(b^2+1\ge2b\)
\(c^2+1\ge2c\)
\(a^2+b^2+c^2+3\ge2\left(a+b+c\right)\)
có (a^2+b^2+c^2)=3 (gt) \(\Rightarrow3+3\ge2\left(a+b+C\right)\Rightarrow3\ge a+b+C\Rightarrow-3\le-\left(a+b+c\right)\)
cùng dấu < thay vào ta được
\(ab^2+bc^2+ca^2-abc\le3-\frac{\left(3\right)^3}{27}=3-1=2\)
\(\Rightarrow ab^2+bc^2+ca^2-abc\le2\)
cho chúa Pain xin cái tính :)
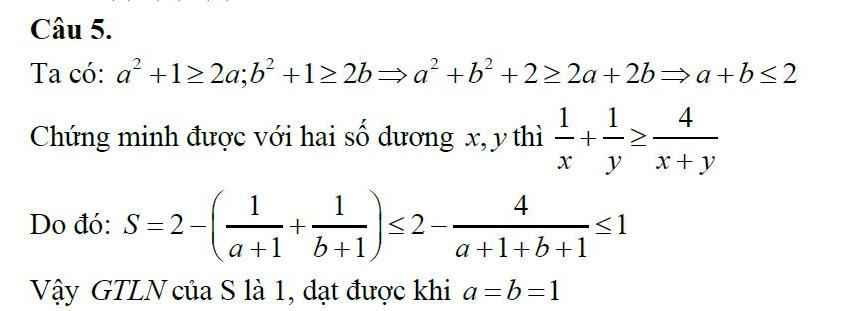
Ta có :
\(a^2+b^2\le2\) ( 1 )
Mặt khác \(2ab\le a^2+b^2\)nên
\(2ab\le a^2+b^2\le2\) ( 2 )
Cộng ( 1 ) với ( 2 ) , \(a^2+b^2+2ab\le4\)\(\Rightarrow\left(a+b\right)^2\le4\)\(\Rightarrow a+b\le2\)
a+b <=2 thế a+b=-3 thì sao???