Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.

a) 8( 3x - 2 ) - 14x = 2( 4 – 7x ) + 15x
⇔ 24x – 16 -14x = 8 – 14x + 15x
⇔ 10x -16 = 8 + x
⇔ 9x = 24
⇔ x = 24/9
b) ( 3x – 1 )( x – 3 ) – 9 + x2 = 0
⇔ (3x -1)( x – 3) + (x - 3)( x + 3) = 0
⇔ (x - 3)(3x - 1 + x - 3) = 0
⇔ (x - 3)(4x - 4) = 0
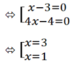
c) |x - 2| = 2x - 3
TH1: x - 2 ≥ 0 ⇔ x ≥ 2
Khi đó: x - 2 = 2x – 3
⇔ 2x – x = -2 + 3
⇔ x = 1 (không TM điều kiện x ≥ 2)
TH2: x – 2 < 0 ⇔ x < 2
Khi đó: x-2 = -(2x – 3)
⇔ x – 2 = -2x + 3
⇔ 3x = 5
⇔ x = 5/3 ( TM điều kiện x < 2)
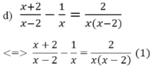
MTC: x(x-2)
ĐKXĐ: x ≠ 0;x ≠ 2

Đối chiếu với ĐKXĐ thì pt có nghiệm x = - 1

\(a.\left(3x+2\right)\left(x^2-1\right)=\left(9x^2-4\right)\left(x+1\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(3x+2\right)\left(x+1\right)\left(x-1\right)=\left(3x-2\right)\left(3x+2\right)\left(x+1\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x-1=3x-2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x=1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=\dfrac{1}{2}\)
c: =>x-3=0
hay x=3
d: \(\Leftrightarrow\left(3x-1\right)\cdot\left(x^2+2-7x+10\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(3x-1\right)\left(x-3\right)\left(x-4\right)=0\)
hay \(x\in\left\{\dfrac{1}{3};3;4\right\}\)

\(\left(3x+2\right)\left(x^2-1\right)=\left(9x^2-4\right)\left(x+1\right).\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(3x+2\right)\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)-\left(3x-2\right)\left(3x+2\right)\left(x+1\right)=0.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(3x+2\right)\left(x+1\right)\left(x-1-3x+2\right)=0.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(3x+2\right)\left(x+1\right)\left(-2x+1\right)=0.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}3x+2=0.\\x+1=0.\\-2x+1=0.\end{matrix}\right.\)\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=-\dfrac{2}{3}.\\x=-1.\\x=\dfrac{1}{2}.\end{matrix}\right.\)
c: =>(x-3)(x2+3x+5)=0
=>x-3=0
hay x=3
d: =>(3x-1)(x2+2-7x+10)=0
=>(3x-1)(x-3)(x-4)=0
hay \(x\in\left\{\dfrac{1}{3};3;4\right\}\)

a: Ta có: \(3x-5\ge2\left(x-6\right)-12\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3x-5\ge2x-24\)
hay \(x\ge-19\)
b: Ta có: \(2\left(5-2x\right)\ge3-x\)
\(\Leftrightarrow10-4x-3+x\ge0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-3x\ge-7\)
hay \(x\le\dfrac{7}{3}\)

a: (3x-2)(4x+5)=0
=>3x-2=0 hoặc 4x+5=0
=>x=2/3 hoặc x=-5/4
b: (2,3x-6,9)(0,1x+2)=0
=>2,3x-6,9=0 hoặc 0,1x+2=0
=>x=3 hoặc x=-20
c: =>(x-3)(2x+5)=0
=>x-3=0 hoặc 2x+5=0
=>x=3 hoặc x=-5/2

Bài 3:
b: \(\Leftrightarrow x^2\left(x+1\right)^2=0\)
hay \(x\in\left\{0;-1\right\}\)
c: \(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-1\right)\left(x^2+x+1\right)=0\)
=>x-1=0
hay x=1
d: \(\Leftrightarrow6x^2-3x-4x+2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(2x-1\right)\left(3x-2\right)=0\)
hay \(x\in\left\{\dfrac{1}{2};\dfrac{2}{3}\right\}\)

a) Ta có: \(3x-1=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3x=1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=\dfrac{1}{3}\)
Vậy: \(S=\left\{\dfrac{1}{3}\right\}\)
b) Ta có: \(5x-2=x+4\)
\(\Leftrightarrow5x-x=4+2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4x=6\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=\dfrac{3}{2}\)
Vậy: \(S=\left\{\dfrac{3}{2}\right\}\)

a) \(2\chi-3=3\left(\chi+1\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2\chi-3=3\chi+3\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2\chi-3\chi=3+3\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\chi=-6\)
Vậy phương trình có tập nghiệm S= \(\left\{-6\right\}\)
\(3\chi-3=2\left(\chi+1\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3\chi-3=2\chi+2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3\chi-2\chi=2+3\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\chi=5\)
Vậy phương trình có tập nghiệm S= \(\left\{5\right\}\)
b) \(\left(3\chi+2\right)\left(4\chi-5\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}3\chi+2=0\\4\chi-5=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}3\chi=-2\\4\chi=5\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}\chi=\dfrac{-2}{3}\\\chi=\dfrac{5}{4}\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy phương trình có tập nghiệm S= \(\left\{\dfrac{-2}{3};\dfrac{5}{4}\right\}\)
\(\left(3\chi+5\right)\left(4\chi-2\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}3\chi+5=0\\4\chi-2=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}3\chi=-5\\4\chi=2\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}\chi=\dfrac{-5}{3}\\\chi=\dfrac{1}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy phương trình có tập nghiệm S= \(\left\{\dfrac{-5}{3};\dfrac{1}{2}\right\}\)
c) \(\left|\chi-7\right|=2\chi+3\)
Trường hợp 1:
Nếu \(\chi-7\ge0\Leftrightarrow\chi\ge7\)
Khi đó:\(\left|\chi-7\right|=2\chi+3\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\chi-7=2\chi+3\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\chi-2\chi=3+7\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\chi=-10\) (KTMĐK)
Trường hợp 2:
Nếu \(\chi-7\le0\Leftrightarrow\chi\le7\)
Khi đó: \(\left|\chi-7\right|=2\chi+3\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-\chi+7=2\chi+3\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-\chi-2\chi=3-7\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-3\chi=-4\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\chi=\dfrac{4}{3}\)(TMĐK)
Vậy phương trình có tập nghiệm S=\(\left\{\dfrac{4}{3}\right\}\)
\(\left|\chi-4\right|=5-3\chi\)
Trường hợp 1:
Nếu \(\chi-4\ge0\Leftrightarrow\chi\ge4\)
Khi đó: \(\left|\chi-4\right|=5-3\chi\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\chi-4=5-3\chi\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\chi+3\chi=5+4\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4\chi=9\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\chi=\dfrac{9}{4}\)(KTMĐK)
Trường hợp 2: Nếu \(\chi-4\le0\Leftrightarrow\chi\le4\)
Khi đó: \(\left|\chi-4\right|=5-3\chi\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-\chi+4=5-3\chi\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-\chi+3\chi=5-4\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2\chi=1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\chi=\dfrac{1}{2}\)(TMĐK)
Vậy phương trình có tập nghiệm S=\(\left\{\dfrac{1}{2}\right\}\)

a) ĐKXĐ: \(x\notin\left\{-1;0\right\}\)
Ta có: \(\dfrac{x+3}{x+1}+\dfrac{x-2}{x}=2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{x\left(x+3\right)}{x\left(x+1\right)}+\dfrac{\left(x+1\right)\left(x-2\right)}{x\left(x+1\right)}=\dfrac{2x\left(x+1\right)}{x\left(x+1\right)}\)
Suy ra: \(x^2+3x+x^2-3x+2=2x^2+2x\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x^2+2-2x^2-2x=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-2x+2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-2x=-2\)
hay x=1(nhận)
Vậy: S={1}
b) ĐKXĐ: \(x\notin\left\{-7;\dfrac{3}{2}\right\}\)
Ta có: \(\dfrac{3x-2}{x+7}=\dfrac{6x+1}{2x-3}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(3x-2\right)\left(2x-3\right)=\left(6x+1\right)\left(x+7\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow6x^2-9x-4x+6=6x^2+42x+x+7\)
\(\Leftrightarrow6x^2-13x+6-6x^2-43x-7=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-56x-1=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-56x=1\)
hay \(x=-\dfrac{1}{56}\)(nhận)
Vậy: \(S=\left\{-\dfrac{1}{56}\right\}\)
c) ĐKXĐ: \(x\ne-\dfrac{2}{3}\)
Ta có: \(\dfrac{5}{3x+2}=2x-1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow5=\left(3x+2\right)\left(2x-1\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow6x^2-3x+4x-2-5=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow6x^2+x-7=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow6x^2-6x+7x-7=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow6x\left(x-1\right)+7\left(x-1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-1\right)\left(6x+7\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x-1=0\\6x+7=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=1\\6x=-7\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=1\left(nhận\right)\\x=-\dfrac{7}{6}\left(nhận\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy: \(S=\left\{1;-\dfrac{7}{6}\right\}\)
d) ĐKXĐ: \(x\ne\dfrac{2}{7}\)
Ta có: \(\left(2x+3\right)\cdot\left(\dfrac{3x+8}{2-7x}+1\right)=\left(x-5\right)\left(\dfrac{3x+8}{2-7x}+1\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(2x+3\right)\cdot\left(\dfrac{3x+8+2-7x}{2-7x}\right)-\left(x-5\right)\left(\dfrac{3x+8+2-7x}{2-7x}\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(2x+3-x+5\right)\cdot\dfrac{-4x+6}{2-7x}=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x+8\right)\cdot\left(-4x+6\right)=0\)(Vì \(2-7x\ne0\forall x\) thỏa mãn ĐKXĐ)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x+8=0\\-4x+6=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=-8\\-4x=-6\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=-8\left(nhận\right)\\x=\dfrac{3}{2}\left(nhận\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy: \(S=\left\{-8;\dfrac{3}{2}\right\}\)
a) \(\left(x+2\right)^2-3x^2=-12\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2+4x+4-3x^2+12=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-2x^2+4x+16=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-2\left(x^2-2x-8\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2-2x-8=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2-4x+2x-8=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x\left(x-4\right)+2\left(x-4\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-4\right)\left(x+2\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x=4\\x=-2\end{cases}}\)
Vậy....
b) \(3x^2-2x-1=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3x^2-3x+x-1=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3x\left(x-1\right)+\left(x-1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-1\right)\left(3x+1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x=1\\x=\frac{-1}{3}\end{cases}}\)
Vậy....
c) \(\frac{7x-3}{x-1}=\frac{2}{3}\)ĐKXĐ : \(x\ne1\)
\(\Rightarrow3\left(7x-3\right)=2\left(x-1\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow21x-9=2x-2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow21x-2x=-2+9\)
\(\Leftrightarrow19x=7\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=\frac{7}{19}\)( thỏa mãn ĐKXĐ )
Vậy....
d) \(\frac{3x-4}{x^2}-\frac{1}{x+1}=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\frac{3x-4}{x^2}=\frac{1}{x+1}\)
\(\Rightarrow\left(x+1\right)\left(3x-4\right)=x^2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3x^2-x-4-x^2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x^2-x-4=0\)
....
Câu 1
Một ô tô đy từ A đến B với vận tốc 35km/h. Khi từ B về A ô tô đy với vận tốc 42km/h vì vậy thời gian về ít hơn thời gian đy là nửa giờ. Tính độ dài quãng đường AB.
Câu 2
Số học sinh của lớp 8a hơn số học sinh của lớp 8b là 5 bạn. Nếu chuyển 10 bạn từ lớp 8a sang lớp 8b thì số học sinh của lớp 8b sẽ gấp rưỡi số học sinh của lớp 8a. Tính số học sinh lúc đầu của mỗi lớp.