Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.

a)
\(C + O_2 \xrightarrow{t^o} CO_2\\ n_{CO_2} = n_{O_2} = \dfrac{6,4}{32} = 0,2(mol)\\ \Rightarrow m_{CO_2} = 0,2.44 = 8,8(gam)\)
b)
\(n_C = \dfrac{6}{12} = 0,5(mol)\\ n_{O_2} =\dfrac{19,2}{32} = 0,6(mol)\\ C + O_2 \xrightarrow{t^o} CO_2\)
\(n_C = 0,5 < n_{O_2} = 0,6 \Rightarrow\) Oxi dư.
\(n_{CO_2} = n_C = 0,5(mol)\\ \Rightarrow m_{CO_2} = 0,5.44 = 22(gam)\)

Câu 1 :
\(2H_2 + O_2 \xrightarrow{t^o} 2H_2O\\ 2Mg + O_2 \xrightarrow{t^o} 2MgO\\ 2Cu + O_2 \xrightarrow{t^o} 2CuO\\ S + O_2 \xrightarrow{t^o} SO_2\\ 4Al + 3O_2 \xrightarrow{t^o} 2Al_2O_3\\ C + O_2 \xrightarrow{t^o} CO_2\\ 4P + 5O_2 \xrightarrow{t^o} 2P_2O_5\)

bài 5:
PTHH: C + O2 -> CO2
a) Số Mol của Oxi là:
ADCT: n= m/M
=>nO2= 6,4/ 32= 0,2 ( mol)
theo PT: nCO2 = nO2 = 0,2 mol
klg của CO2 là:
ADCT: m = n. M
=> mCO2= 0.2 . 12 = 2,4 (g)

1) \(C+O_2\rightarrow CO_2\\
C+CO_2\rightarrow2CO\)
2)
\(pthh:C+O_2\rightarrow CO_2\)
=> số mol bằng nhau
\(n_{O_2}=\dfrac{6,4}{16}=0,4\left(mol\right)\)
áp vào pt trên ta có : nCO2 = 0,4 (mol)
=> \(m_{CO_2}=0,4.44=17,6\left(g\right)\)
=> dCO2/H2 = 44/2 = 22
dCO2/H2 = 44/2 = 22

PTHH: C + O2 \(\underrightarrow{to}\) CO2
a) Khi có 6,4g khí oxi tham gia phản ứng
\(n_{O_2}=\dfrac{6,4}{32}=0,2\left(mol\right)\)
Theo PT: \(n_{CO_2}=n_{O_2}=0,2\left(mol\right)\)
\(\Rightarrow m_{CO_2}=0,2\times44=8,8\left(g\right)\)
b) Khi đốt 6g cacbon trong bình đựng 19,2g khí oxi
\(n_C=\dfrac{6}{12}=0,5\left(mol\right)\)
\(n_{O_2}=\dfrac{19,2}{32}=0,6\left(mol\right)\)
Theo pT: \(n_C=n_{O_2}\)
Theo bài: \(n_C=\dfrac{5}{6}n_{O_2}\)
Vì \(\dfrac{5}{6}< 1\) ⇒ C hết, O2 dư
Theo PT: \(n_{CO_2}=n_C=0,5\left(mol\right)\)
\(\Rightarrow m_{CO_2}=0,5\times44=22\left(g\right)\)
PTHH: \(C+O_2\underrightarrow{t^o}CO_2\)
- khi có 6,4g khí oxi tham gia phản ứng:
\(n_{O_2}=\dfrac{6,4}{32}=0,2\left(mol\right)\)
Theo PT ta có: \(n_{O_2}=n_{CO_2}=0,2\left(mol\right)\)
\(\Rightarrow m_{CO_2}=0,2.44=8,8\left(g\right)\)
- khi đốt 6g cacbon trong bình đựng 19,2g khí oxi:
\(n_C=\dfrac{6}{12}=0,5\left(mol\right)\)
\(n_{O_2}=\dfrac{19,2}{32}=0,6\left(mol\right)\)
Theo PTHH ta có tỉ lệ:
\(\dfrac{0,5}{1}< \dfrac{0,6}{1}\Rightarrow O_2dư\). C phản ứng hết nên ta tính theo \(n_C\)
Theo PT ta có: \(n_C=n_{CO_2}=0,5\left(mol\right)\)
\(\Rightarrow m_{CO_2}=0,5.44=22\left(g\right)\)

PT: C+O2--->CO2
a) n O2=6,4/32=0,2(mol)
n CO2=n O2=0,2(mol)
m CO2=0,2.44=8,8(g)
b) n C=6/12=0,5(mol)
n O2=19,2/32=0,6(mol)
--> O2 dư
n CO2=n C=0,5(mol)
m CO2=0,5.44=22(g)

\(C+O_2\underrightarrow{^{to}}CO_2\)
a) \(n_{O2}=\frac{6,4}{32}=0,2\left(mol\right)\)
\(\Rightarrow n_{CO2}=n_{O2}=0,2\left(mol\right)\)
\(\Rightarrow m_{CO2}=0,2.22,4=8,8\left(g\right)\)
b) \(n_C=\frac{0,3}{12}=0,025\left(mol\right)\)
\(\Rightarrow n_{CO2}=n_C=0,025\left(mol\right)\)
\(\Rightarrow m_{CO2}=0,025.44=1,1\left(g\right)\)
c) \(n_C=0,3\left(mol\right)\)
\(n_{O2}=0,2\left(mol\right)\)
Nên C dư \(\rightarrow\) nCO2 tính theo nO2
\(n_{CO2}=0,2\left(mol\right)\)
\(\Rightarrow m_{CO2}=0,2.44=8,8\left(g\right)\)
d) \(n_C=\frac{6}{12}=0,5\left(mol\right)\)
\(n_{O2}=\frac{19,2}{32}=0,6\left(mol\right)\)
Nên O2 dư
nCO2 được tính theo nC
\(n_{CO2}=0,5\left(mol\right)\)
\(\Rightarrow m_{CO2}=0,5.44=22\left(g\right)\)
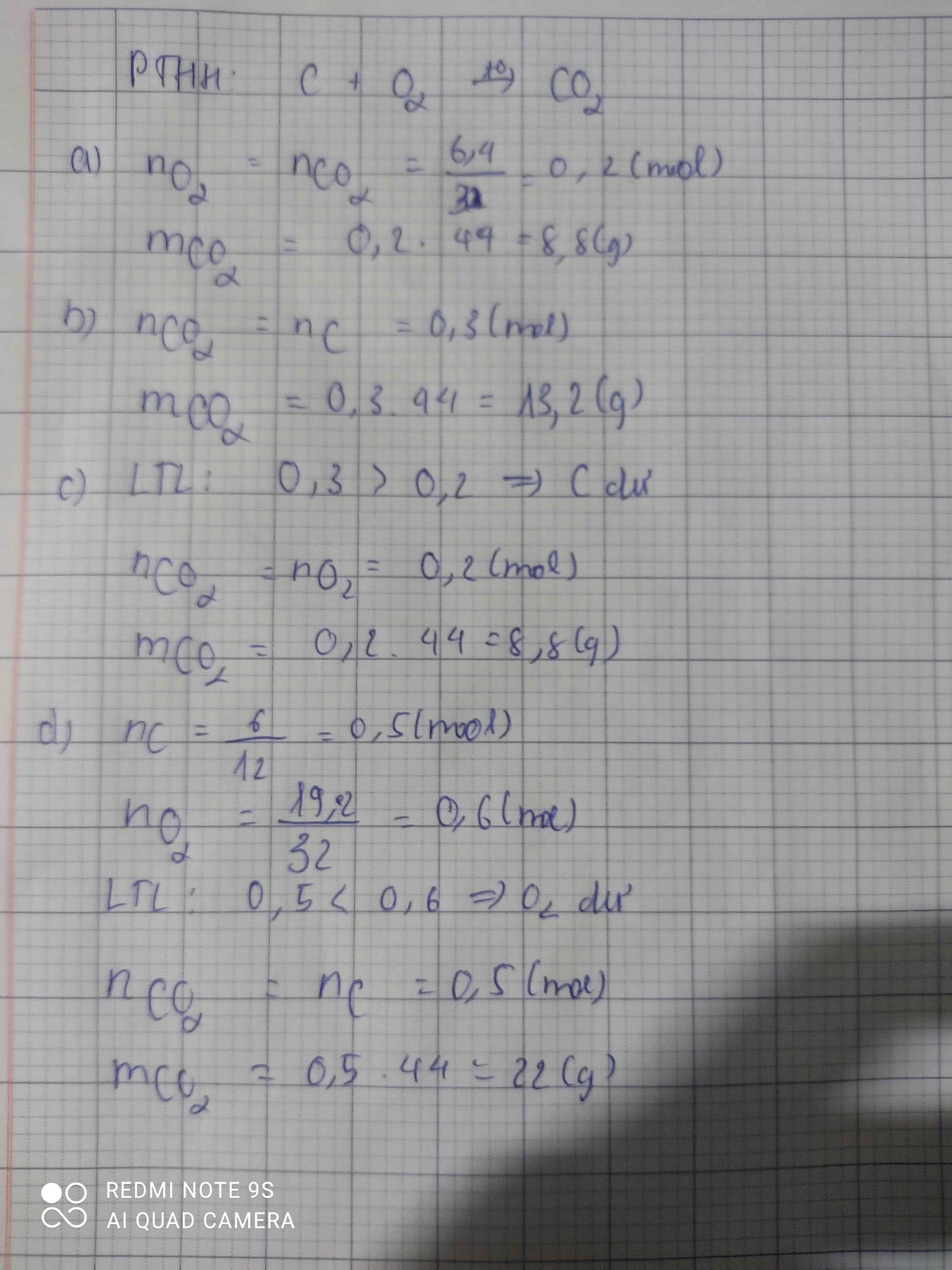
a)C+O2to>CO2
......0,2------0,2 mol
nO2=6,4\32=0,2(mol)
mCO2=0,2.44=8,8(g)
b>
C+O2to>CO2
nC=6\12=0,5(mol)
nO2=19,2\32=0,6(mol)
ta lập tỉ lệ> O2 dư
=>nCO2=nC=0,5(mol)
=>mCO2=0,5.44=22(g)
bạn chắc chứ !!!