Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.

b: \(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x^2-3x-4=2m-1\\x^2-3x-4=-2m+1\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x^2-3x-4-2m+1=0\\x^2-3x-4+2m-1=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x^2-3x-2m+3=0\\x^2-3x+2m-5=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
Để phương trình có bốn nghiệm phân biệt thì \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}9-4\left(-2m+3\right)>0\\9-4\left(2m-5\right)>0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}9+8m-12>0\\9-8m+20>0\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}8m>3\\8m< 29\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{3}{8}< m< \dfrac{29}{8}\)

a: Vì a=-1<0 nên hàm số nghịch biến trên khoảng (2;+∞) và đồng biến trên khoảng (-∞;2]
Bảng biến thiên là:
| x | -∞ | 2 | +∞ |
| y | -∞ | 1 | -∞ |

\(y=\sqrt{\left(2x-1\right)^2}+\sqrt{\left(x-2\right)^2}=\left|2x-1\right|+\left|x-2\right|\)
\(y=\left[{}\begin{matrix}3x-3\left(\text{với }x\ge2\right)\\3-3x\left(\text{với }x\le\dfrac{1}{2}\right)\\x+1\left(\text{với }\dfrac{1}{2}\le x\le2\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
Từ đó ta có đồ thị hàm số như sau:
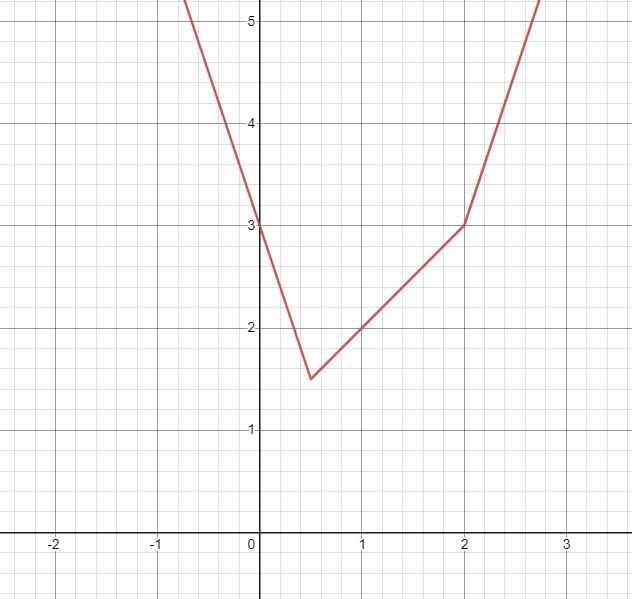
Từ đồ thị ta thấy phương trình \(\sqrt{4x^2-4x+1}+\sqrt{x^2-4x+4}=m\):
- Có đúng 1 nghiệm khi \(m=\dfrac{3}{2}\)
- Có 2 nghiệm phân biệt khi \(m>\dfrac{3}{2}\)
- Vô nghiệm khi \(m< \dfrac{3}{2}\)

Phương trình tương đương
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\left(m-1\right)x+2=\left(m+1\right)\left(x-2\right)\\x\ne2\end{matrix}\right.\)
⇔ \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\left(m-1\right)x+2=\left(m+1\right)x-2m-2\\x\ne2\end{matrix}\right.\)
⇔ \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\left(m-1-m-1\right)x=-2m-4\\x\ne2\end{matrix}\right.\)
⇔ \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}-2x=-2m-4\\x\ne2\end{matrix}\right.\)
⇔ \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=m+2\\x\ne2\end{matrix}\right.\)
Nếu m = 0 thì phương trình vô nghiệm
Nếu m ≠ 0 thì S = {m + 2}

\(PT\Leftrightarrow m^2x-m^2-5mx+m+6x+2=0\\ \Leftrightarrow x\left(m^2-5m+6\right)=m^2-m-2\\ \Leftrightarrow x\left(m-2\right)\left(m-3\right)=\left(m-2\right)\left(m+1\right)\)
Với \(m\ne2;m\ne3\)
\(PT\Leftrightarrow x=\dfrac{\left(m-2\right)\left(m+1\right)}{\left(m-2\right)\left(m-3\right)}=\dfrac{m+1}{m-3}\)
Với \(m=2\Leftrightarrow0x=0\left(vsn\right)\)
Với \(m=3\Leftrightarrow0x=4\left(vn\right)\)
Vậy với \(m\ne2;m\ne3\) thì PT có nghiệm duy nhất \(x=\dfrac{m+1}{m-3}\), với \(m=2\) thì PT có vô số nghiệm và với \(m=3\) thì PT vô nghiệm
f(x)=-x^2+3x+2=2+9/4-(x^2-2.3/2x+9/4) =17/4 -(x-3/2)^2
f(x)<=17/4
f(x)=17/4 -(x-3/2)^2 luôn có 2 nghiệm x1 và x2 => |f(x)| >=0
f(x)<=17/4 => |f(x)| <=17 /4 khi x thuộc (x1;x2)
=>biên luận
nếu 2m-1 =0 => f(x) =2m-1 có 2 nghiệm x1, x2
nếu 2m-1 <0 => f(x) =2m-1 vô nghiệm
nếu 2m-1 =17/4 => f(x) =2m-1 có 3 nghiệm
nếu 2m-1 >17/4 => f(x) =2m-1 có 2 nghiệm
0<nếu 2m-1 <17/4 => f(x) =2m-1 có 4 nghiệm
Bạn tự giải ra m