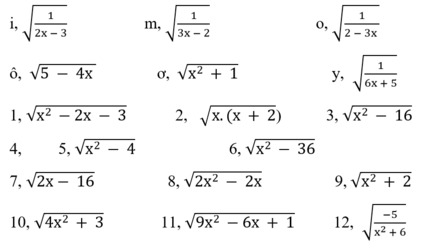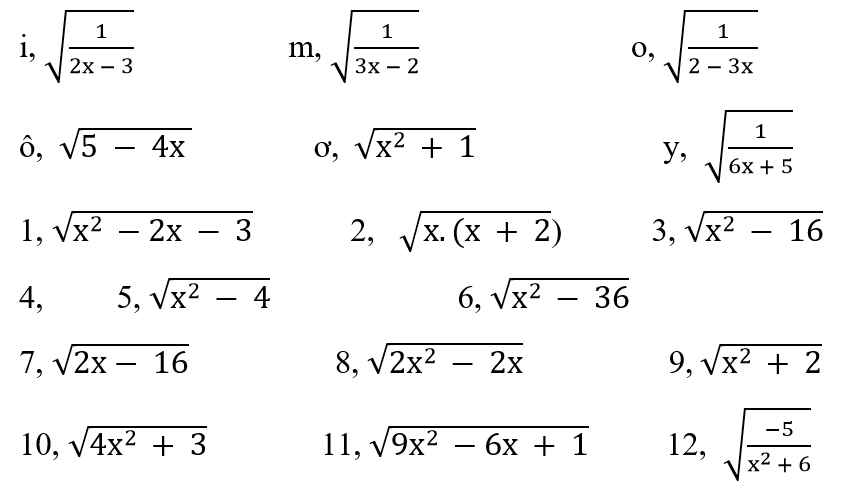Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.

\(A=\sqrt{x^2-4x+25}=\sqrt{\left(x-2\right)^2+21}\)
Ta có : \(\left(x-2\right)^2\ge0\) => \(\left(x-2\right)^2+21\ge21\left(\forall x\right)\) => \(\sqrt{\left(x-2\right)^2+21}\ge\sqrt{21}\left(\forall x\right)\)
Dấu " = " xảy ra \(\Leftrightarrow\) \(\sqrt{\left(x-2\right)^2}=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\) \(x-2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\) x = 2
Vậy giá trị nhỏ nhất của A là : \(\sqrt{21}\) khi x = 2
\(B=\sqrt{x^2-6x+30}=\sqrt{\left(x-3\right)^2+21}\)
Vì \(\sqrt{\left(x-3\right)^2}\ge0\left(\forall x\right)\)=> \(\sqrt{\left(x-3\right)^2+21}\ge\sqrt{21}\left(\forall x\right)\)
Dấu " = " xảy ra \(\Leftrightarrow\) \(\sqrt{\left(x-3\right)^2}=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\) \(x-3=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\) \(x=3\)
Vậy giá trị nhỏ nhất của B là : \(\sqrt{21}\) khi x = 3
\(D=\sqrt{x^2-4x+7}+\sqrt{2}=\sqrt{\left(x-2\right)^2+3}+\sqrt{2}\)
Vì

a/ ĐKXĐ : \(-2x+3\ge0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x\le\dfrac{3}{2}\)
b/ ĐKXĐ : \(3x+4\ge0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x\ge-\dfrac{4}{3}\)
c/ Căn thức \(\sqrt{1+x^2}\) luôn được xác định với mọi x
d/ ĐKXĐ : \(-\dfrac{3}{3x+5}\ge0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3x+5< 0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x< -\dfrac{5}{3}\)
e/ ĐKXĐ : \(\dfrac{2}{x}\ge0\Leftrightarrow x>0\)
P.s : không chắc lắm á!

a) ĐKXĐ: \(x\in R\)
b) ĐKXĐ: \(-2\sqrt{2}+2\le x\le2\sqrt{2}+2\)

1: ĐKXĐ: (x-3)(x+1)>=0
=>x>=3 hoặc x<=-1
2: ĐKXĐ: x(x+2)>=0
=>x>=0 hoặc x<=-2
3: ĐKXĐ: (x-4)(x+4)>=0
=>x>=4 hoặc x<=-4
4: DKXĐ: (x-2)(x+2)>=0
=>x>=2 hoặc x<=-2
6: ĐKXĐ: (x-6)(x+6)>=0
=>x>=6 hoặc x<=-6
7: ĐKXĐ: 2x-16>=0
=>x>=8
8: ĐKXĐ: x(x-1)>=0
=>x>=1 hoặc x<=0