
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.



Bài 3:
a) \(x^4+4\)
\(=x^4+4x^2+4-4x^2\)
\(=\left(x^2+2\right)^2-\left(2x\right)^2\)
\(=\left(x^2-2x+2\right)\left(x^2+2x+2\right)\)
b) \(x^5+x+1\)
\(=x^5+x^4+x^3-x^4-x^3-x^2+x^2+x+1\)
\(=x^3\left(x^2+x+1\right)-x^2\left(x^2+x+1\right)+\left(x^2+x+1\right)\)
\(=\left(x^2+x+1\right)\left(x^3-x^2+1\right)\)
c) \(x^8+x+1\)
\(=x^8+x^7+x^6-x^7-x^6-x^5+x^5+x^4+x^3-x^4-x^3-x^2+x^2+x+1\)
\(=x^6\left(x^2+x+1\right)-x^5\left(x^2+x+1\right)+x^3\left(x^2+x+1\right)-x^2\left(x^2+x+1\right)+\left(x^2+x+1\right)\)
\(=\left(x^2+x+1\right)\left(x^6-x^5+x^3-x^2+1\right)\)
Bài 1:
a) \(\left(x^2-x+1\right)\left(x^2-x+2\right)-12\)
\(=\left(x^2-x\right)^2+3\left(x^2-x\right)+2-12\)
\(=\left(x^2-x\right)^2+5\left(x^2-x\right)-2\left(x^2-x\right)-10\)
\(=\left(x^2-x\right)\left(x^2-x+5\right)-2\left(x^2-x+5\right)\)
\(=\left(x^2-x+5\right)\left(x^2-x-2\right)\)
\(=\left(x-2\right)\left(x+1\right)\left(x^2-x+5\right)\)
b) \(\left(x^2+x\right)^2+4\left(x^2+x\right)-12\)
\(=\left(x^2+x\right)^2+6\left(x^2+x\right)-2\left(x^2+x\right)-12\)
\(=\left(x^2+x+6\right)\left(x^2+x-2\right)\)
\(=\left(x+2\right)\left(x-1\right)\left(x^2+x+6\right)\)
c) \(x^2-6x+8\)
\(=x^2-6x+9-1\)
\(=\left(x-3\right)^2-1\)
\(=\left(x-4\right)\left(x-2\right)\)

Câu 1: Chọn C.
Câu 2: Chọn D.
Câu 3: Chọn A.
Câu 4: Chọn A.
Câu 5: Chọn D (x=13/2).
Câu 6: Chọn A.
Câu 7: Chọn B.
Câu 8: Chọn D.
Câu 9: Chọn a.
Câu 10: Chọn d.

\(A=3x^2-12x+16=3\left(x^2-4x\right)+16\)
\(=3\left(x^2-4x+4-4\right)+16\)
\(=3\left(x^2-4x+4\right)-3.4+16\)
\(=3\left(x-2\right)^2+4\ge4\), với mọi x
Vì \(\left(x-2\right)^2\ge0\) với mọi x
nên \(A=3\left(x-2\right)^2+4\ge3.0+4=4\) với mọi x
dấu "=" xảy ra khi và chỉ khi: \(\left(x-2\right)^2=0\Leftrightarrow x=2\)
Vậy giá tri nhỏ nhất của A là 4 tại x=2

a) x(4x + 2) = 4x2 - 14
⇔ 4x2 + 2x = 4x2 - 14
⇔ 4x2 - 4x2 + 2x = -14
⇔ 2x = -14
⇔ x = -7
Vậy tập nghiệm S = ......
b) (x2 - 9)(2x - 1) = 0
⇔ x2 - 9 = 0 hoặc 2x - 1 = 0
⇔ x2 = 9 hoặc 2x = 1
⇔ x = 3 hoặc -3 hoặc x = \(\dfrac{1}{2}\)
Vậy .......
c) \(\dfrac{3}{x-2}\) + \(\dfrac{4}{x+2}\) = \(\dfrac{x-12}{x^2-4}\)
⇔ \(\dfrac{3}{x-2}\) + \(\dfrac{4}{x+2}\) = \(\dfrac{x-12}{\left(x-2\right)\left(x+2\right)}\)
ĐKXĐ: x - 2 ≠ 0 và x + 2 ≠ 0
⇔ x ≠ 2 và x ≠ -2MSC (mẫu số chung): (x - 2)(x + 2)Quy đồng mẫu hai vế và khử mẫu ta được:3x + 6 + 4x - 8 = x - 12⇔ 3x + 4x - x = 8 - 6 - 12⇔ 6x = -10⇔ x = \(-\dfrac{5}{3}\) (nhận)Vậy ........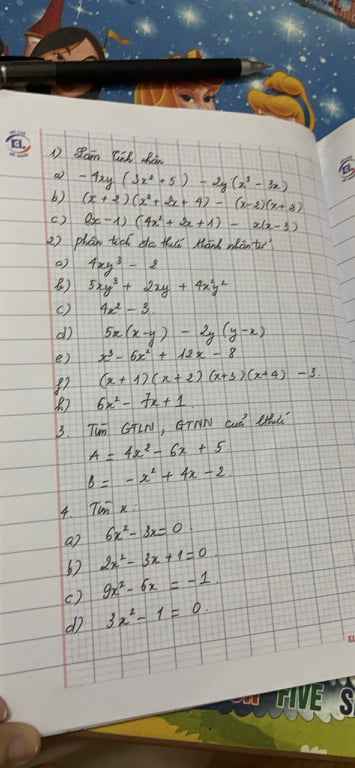
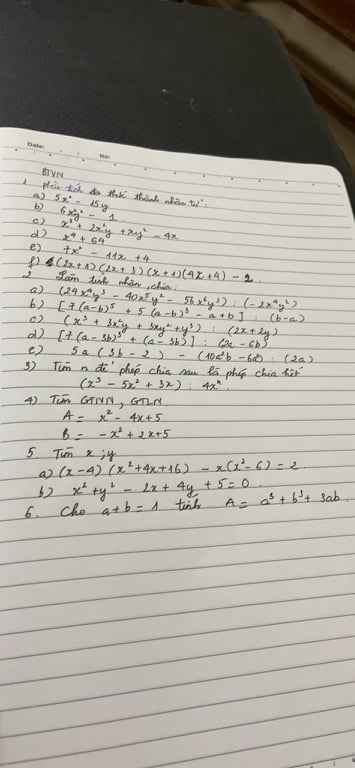
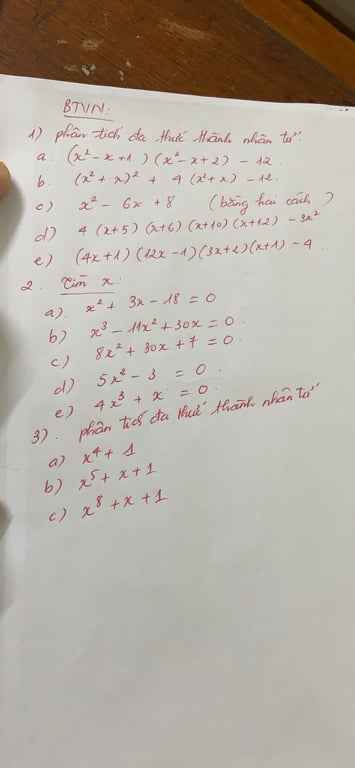



a) 4xy3-2=2(2xy3-1)
b) 5xy3+2xy+4x2y2=xy(5y2+2+4xy)
d) 5x(x-y)-2y(y-x)=(5x+2y)(x-y)
e) x3-6x2+12x-8=(x-2)3
f) (x+1)(x+2)(x+3)(x+4)-3=\(\left[\left(x+1\right)\left(x+4\right)\right]\left[\left(x+2\right)\left(x+3\right)\right]-3\)=\(\left(x^2+5x+4\right)\left(x^2+5x+6\right)-3\)
Đặt x2+5x+5=y
\(\left(x^2+5x+4\right)\left(x^2+5x+6\right)-3\)
= (y-1)(y+1)-3
=y2-1-3
=y2-4
=(y-2)(y+2)
= (x2+5x+5-2)(x2+5x+5+2)
= (x2+5x+3)(x2+5x+7)
h) 6x2-7x+1=(6x2-6x)-(x-1)=6x(x-1)-(x-1)=(6x-1)(x-1)