
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


11)\(\dfrac{3x+1}{x-5}+\dfrac{2x}{x-5}=\dfrac{3x+2x+1}{x-5}=\dfrac{5x+1}{x-5}\)
12)\(\dfrac{4-x^2}{x-3}+\dfrac{2}{x^2-9}=\dfrac{4-x^2}{x-3}+\dfrac{2}{\left(x-3\right)\left(x+3\right)}=\dfrac{\left(4-x^2\right)\left(x+3\right)}{\left(x-3\right)\left(x+3\right)}+\dfrac{2}{\left(x-3\right)\left(x+3\right)}=\dfrac{2+\left(2-x\right)\left(2+x\right)\left(x+3\right)}{\left(x-3\right)\left(x+3\right)}\)
13)
\(\dfrac{3}{4x-2}+\dfrac{2x}{4x^2-1}=\dfrac{3}{2\left(2x-1\right)}+\dfrac{2x}{\left(2x-1\right)\left(2x+1\right)}=\dfrac{3\left(2x+1\right)}{2\left(2x-1\right)\left(2x+1\right)}+\dfrac{2.2x}{2\left(2x-1\right)\left(2x+1\right)}=\dfrac{6x+3+4x}{2\left(2x-1\right)\left(2x+1\right)}=\dfrac{10x+3}{2\left(2x-1\right)\left(2x+1\right)}\)
14)
\(\dfrac{2x+1}{2x-4}+\dfrac{5}{x^2-4}=\dfrac{2x+1}{2\left(x-2\right)}+\dfrac{5}{\left(x-2\right)\left(x+2\right)}=\dfrac{\left(2x+1\right)\left(x+2\right)}{2\left(x-2\right)\left(x+2\right)}+\dfrac{5.2}{2\left(x-2\right)\left(x+2\right)}=\dfrac{2x^2+5x+12}{2\left(x-2\right)\left(x+2\right)}\)

Cách 1: \(5x^2-60x-5600=0\)\(\Leftrightarrow x^2-12x-1120=0\)\(\Leftrightarrow x^2-40x+28x-1120=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x\left(x-40\right)+28\left(x-40\right)=0\)\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-40\right)\left(x+28\right)=0\)\(\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x-40=0\\x+28=0\end{cases}}\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x=40\\x=-28\end{cases}}\)
Vậy \(\orbr{\begin{cases}x=40\\x=-28\end{cases}}\)
Cách 2: \(5x^2-60x-5600=0\)\(\Leftrightarrow x^2-12x-1120=0\)\(\Leftrightarrow x^2-2x.6+6^2-1156=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-6\right)^2-34^2=0\)\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-6-34\right)\left(x-6+34\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-40\right)\left(x+28\right)=0\)\(\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x-40=0\\x+28=0\end{cases}}\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x=40\\x=-28\end{cases}}\)
Vậy \(\orbr{\begin{cases}x=40\\x=-28\end{cases}}\)

DKXD : x khac -1
\(\frac{-x}{x+1}\)+ 3 =\(\frac{2x+3}{x+1}\)
<=> \(\frac{-x}{x+1}\)+\(\frac{3\left(x+1\right)}{x+1}\)= \(\frac{2x+3}{x+1}\)
=> -x + 3x +3 = 2x +3
<=> 2x -2x =3-3
<=> 0x=0
<=> x=0(TMDK)


Đề thiếu ko nhỉ? cộng b^2 nữa chứ
\(\left(a-b\right)\left(a-2b\right)\left(a-3b\right)\left(a-4b\right)+b^2\)
\(=\left[\left(a-b\right)\left(a-4b\right)\right]\left[\left(a-2b\right)\left(a-3b\right)\right]+b^2\)
\(=\left(a^2-4ab-ab+4b^2\right)\left(a^2-3ab-2ab+6b^2\right)+b^2\)
\(=\left(a^2-5ab+4b^2\right)\left(a^2-5ab+6b^2\right)+b^2=\left(a^2-5ab+5b^2\right)^2-b^2+b^2\)
\(=\left(a^2-5ab+b^2\right)^2\rightarrowđpcm\)

Vì P,Q là trung điểm HI,HK nên PQ là đtb tg HIK
Do đó \(PQ=\dfrac{1}{2}IK=9\left(cm\right)\)
xét \(\Delta HIK\) có:
\(HP=IP\)\(\left(gt\right)\)
\(HQ=QK\left(gt\right)\)
\(\Rightarrow PQ\) là đường trung bình
\(\Rightarrow PQ=\dfrac{IK}{2}=\dfrac{18}{2}=9\left(cm\right)\)

Góc C = 180 - 130 = 50
Góc B = 360 - (80+120+50) =110
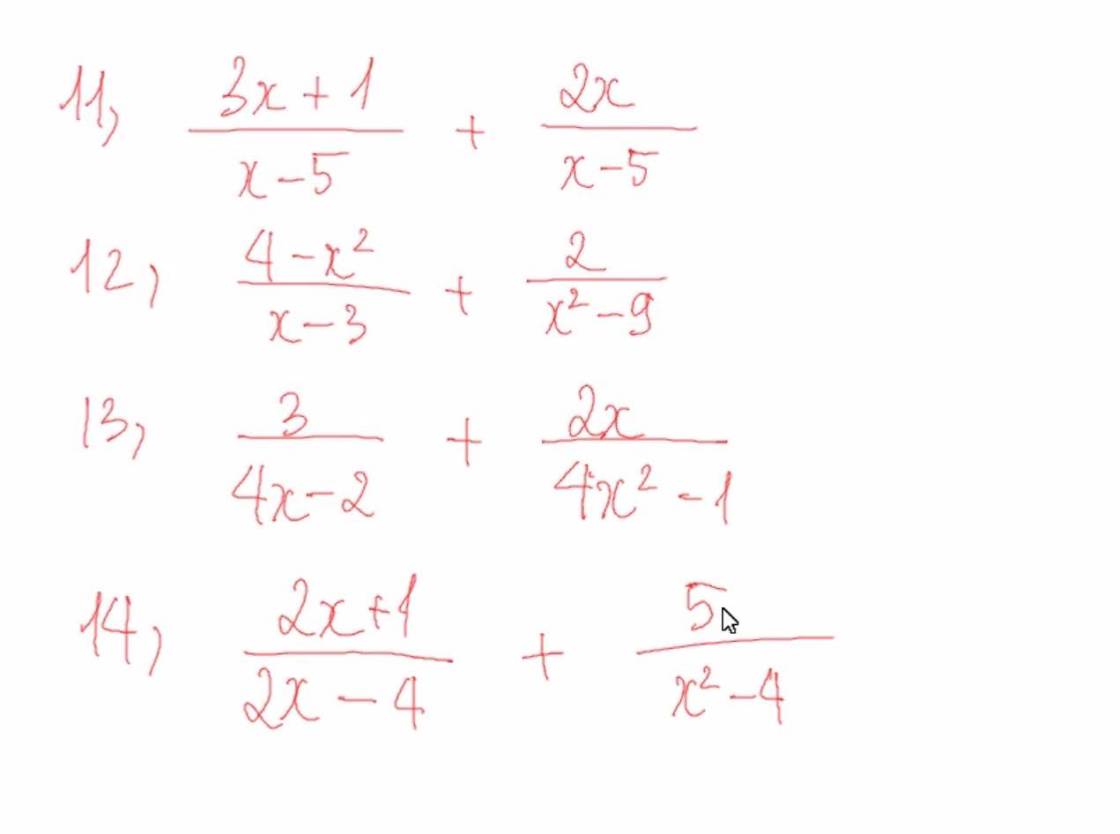
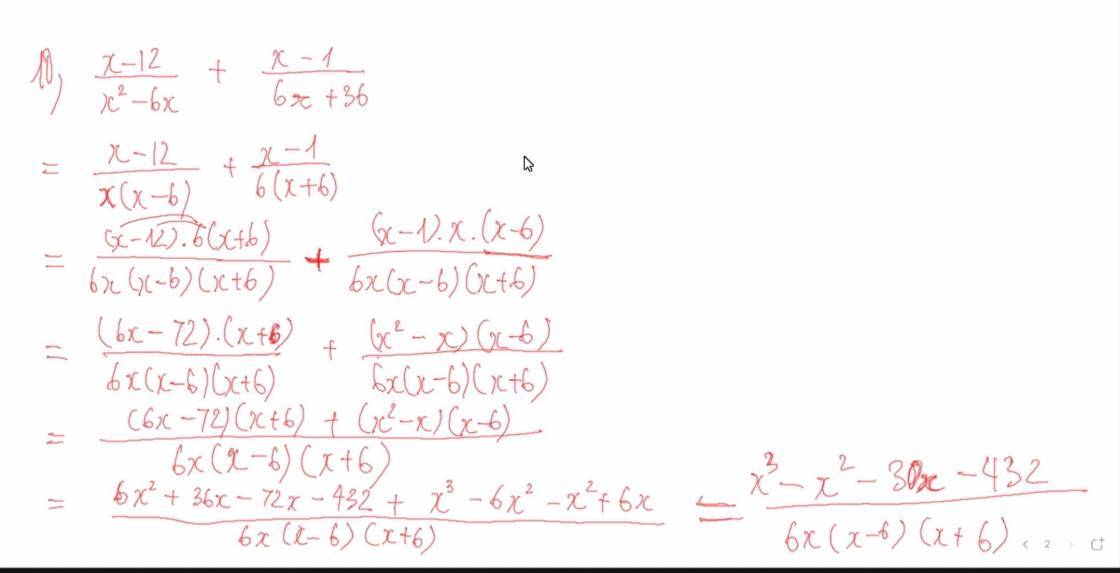

9(x5)2 = 4(x4)2
<=> (3.x5)2 = (2.x4)2
<=> 3x5 = 2x4
<=> 3x5 - 2x4 = 0
<=> x4(3x - 2) = 0
<=> \(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x^4=0\\3x-2=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
<=> \(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=0\\x=\dfrac{2}{3}\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(9x^{10}=4x^8\)
\(9x^{10}-4x^8=0\)
\(x^8\left(9x^2-4\right)=0\)
\(9x^2-4=0\)
\(x^2=\dfrac{4}{9}\)
⇒\(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{2}{3}\\x=-\dfrac{2}{3}\end{matrix}\right.\)