Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.

Câu 1: Lời giải:
a, Đặt \(A=\dfrac{3x+7}{x-1}\).
Ta có: \(A=\dfrac{3x+7}{x-1}=\dfrac{3x-3+10}{x-1}=\dfrac{3x-3}{x-1}+\dfrac{10}{x-1}=3+\dfrac{10}{x-1}\)
Để \(A\in Z\) thì \(\dfrac{10}{x-1}\in Z\Rightarrow10⋮x-1\Leftrightarrow x-1\in U\left(10\right)=\left\{\pm1;\pm2;\pm5;\pm10\right\}\)
Ta có bảng sau:
| \(x-1\) | \(1\) | \(-1\) | \(2\) | \(-2\) | \(5\) | \(-5\) | \(10\) | \(-10\) |
| \(x\) | \(2\) | \(0\) | \(3\) | \(-1\) | \(6\) | \(-4\) | \(11\) | \(-9\) |
Vậy, với \(x\in\left\{-9;-4;-1;0;2;3;6;11\right\}\)thì \(A=\dfrac{3x+7}{x-1}\in Z\).
Câu 3:
a, Ta có: \(-\left(x+1\right)^{2008}\le0\)
\(\Rightarrow P=2010-\left(x+1\right)^{2008}\le2010\)
Dấu " = " khi \(\left(x+1\right)^{2008}=0\Rightarrow x+1=0\Rightarrow x=-1\)
Vậy \(MAX_P=2010\) khi x = -1
b, Ta có: \(-\left|3-x\right|\le0\)
\(\Rightarrow Q=1010-\left|3-x\right|\le1010\)
Dấu " = " khi \(\left|3-x\right|=0\Rightarrow x=3\)
Vậy \(MAX_Q=1010\) khi x = 3
c, Vì \(\left(x-3\right)^2+1\ge0\) nên để C lớn nhất thì \(\left(x-3\right)^2+1\) nhỏ nhất
Ta có: \(\left(x-3\right)^2\ge0\Rightarrow\left(x-3\right)^2+1\ge1\)
\(\Rightarrow C=\dfrac{5}{\left(x-3\right)^2+1}\le\dfrac{5}{1}=5\)
Dấu " = " khi \(\left(x-3\right)^2=0\Rightarrow x=3\)
Vậy \(MAX_C=5\) khi x = 3
d, Do \(\left|x-2\right|+2\ge0\) nên để D lớn nhất thì \(\left|x-2\right|+2\) nhỏ nhất
Ta có: \(\left|x-2\right|\ge0\Rightarrow\left|x-2\right|+2\ge2\)
\(\Rightarrow D=\dfrac{4}{\left|x-2\right|+2}\le\dfrac{4}{2}=2\)
Dấu " = " khi \(\left|x-2\right|=0\Rightarrow x=2\)
Vậy \(MAX_D=2\) khi x = 2

Áp dụng tính chất phân phối, rồi tính giá trị biểu thức.
Chẳng hạn,
Với , thì
ĐS. ; C = 0.
Xem thêm tại: http://loigiaihay.com/bai-77-trang-39-phan-so-hoc-sgk-toan-6-tap-2-c41a5943.html#ixzz4eU1fQCGw

Bài 2.
A = -3/5 + ( -2/5 + 2 )
A = -3/5 + ( -2/5 + 10/5 )
A = -3/5 + 8/5
A = 5/5
A = 1
--------------------------------------------------------
B = 3/7 + ( -1/5 + -3/7 )
B = 3/7 + ( -7/35 + -15/35 )
B = 3/7 + ( -22/35 )
B = 15/35 + ( -22/35 )
B = -1/5
-----------------------------------------------------
C = ( -5/24 + 0,75 + 7/12 ) : ( -2 . 1/8 )
C = ( -5/24 + 3/4 + 7/12 ) : ( -1/4 )
C = 9/8 : ( -1/4 )
C = 9/8 . ( -4 )
C = -9/2
Bài 3 .
a) 4/7 - x = 1/2 . x + 2/7
<=> -x - x = 1/2 - 4/7 + 2/7
<=> -2x = 3/14
<=> x = 3/14 . ( -1/2 )
<=> x = -3/28
Vậy x = -3/28
b) x : 3 1/5 = 1 1/2
<=> x : 16/5 = 3/2
<=> x = 3/2 . 16/5
<=> x = 24/5
Vậy x = 24/5
c) x . 3/4 = -1 5/8
<=> x . 3/4 = -13/8
<=> x = -13/8 . 4/3
<=> x = -13/6
Vậy x = -13/6

Câu 3:
a: \(A=-\left|x-10\right|+2018< =2018\)
Dấu '=' xảy ra khi x=10
\(B=-\left(x+2\right)^2+1999< =1999\)
Dấu '=' xảy ra khi x=-2
b: \(A=\left(2x-8\right)^2+3>=3\)
Dấu '=' xảy ra khi x=4
\(B=\left|x^2-25\right|-2017>=-2017\)
Dấu '=' xảy ra khi x=5 hoặc x=-5

Bài 2:
a: \(\left(x-3\right)^2+1\ge1\)
nên \(A=\dfrac{5}{\left(x-3\right)^2+1}\le5\)
Dấu '=' xảy ra khi x=3
b: \(\left|x-2\right|+2\ge2\)
nên \(B=\dfrac{4}{\left|x-2\right|+2}\le2\)
Dấu '=' xảy ra khi x=2

9) \(\dfrac{x}{4}=\dfrac{9}{x}\)
Theo định nghĩa về hai phân số bằng nhau, ta có:
\(4\cdot9=x^2\\ 36=x^2\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=6\\x=-6\end{matrix}\right.\)
8)
\(x:\dfrac{5}{3}+\dfrac{1}{3}=-\dfrac{2}{5}\\ x:\dfrac{5}{3}=-\dfrac{2}{5}+\dfrac{1}{3}\\ x:\dfrac{5}{3}=-\dfrac{1}{15}\\ x=\dfrac{1}{15}\cdot\dfrac{5}{3}\\ x=\dfrac{1}{9}\)
7)
\(2x-16=40+x\\ 2x-x=40+16\\ x\left(2-1\right)=56\\ x=56\)
6)
\(1\dfrac{1}{2}+x=\dfrac{3}{2}-7\\ \dfrac{3}{2}+x=\dfrac{3}{2}-7\\ \dfrac{3}{2}-\dfrac{3}{2}=-7-x\\ -7-x=0\\ x=-7-0\\ x=-7\)
5)
\(3\dfrac{1}{2}-\dfrac{1}{2}x=\dfrac{2}{3}\\ \dfrac{7}{2}-\dfrac{1}{2}x=\dfrac{2}{3}\\ \dfrac{1}{2}x=\dfrac{7}{2}-\dfrac{2}{3}\\ \dfrac{1}{2}x=\dfrac{17}{6}\\ x=\dfrac{17}{6}:\dfrac{1}{2}\\ x=\dfrac{17}{3}\)
4)
\(x\cdot\left(x+1\right)=0\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=0\\x+1=0\end{matrix}\right.\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=0\\x=-1\end{matrix}\right.\)
3)
\(\left(\dfrac{2x}{5}+2\right):\left(-4\right)=-1\dfrac{1}{2}\\ \left(\dfrac{2x}{5}+2\right):\left(-4\right)=-\dfrac{3}{2}\\ \dfrac{2x}{5}+2=-\dfrac{3}{2}\cdot\left(-4\right)\\ \dfrac{2x}{5}+2=6\\ \dfrac{2x}{5}=6-2\\ \dfrac{2x}{5}=4\\ 2x=4\cdot5\\ 2x=20\\ x=20:2\\ x=10\)
2)
\(\dfrac{1}{3}+\dfrac{1}{2}:x=-0,25\\ \dfrac{1}{3}+\dfrac{1}{2}:x=-\dfrac{1}{4}\\ \dfrac{1}{2}:x=-\dfrac{1}{4}-\dfrac{1}{3}\\ \dfrac{1}{2}:x=-\dfrac{7}{12}\\ x=\dfrac{1}{2}:-\dfrac{7}{12}\\ x=-\dfrac{6}{7}\)
1)
\(\dfrac{4}{3}+x=\dfrac{2}{15}\\ x=\dfrac{2}{15}-\dfrac{4}{3}x=-\dfrac{6}{5}\)
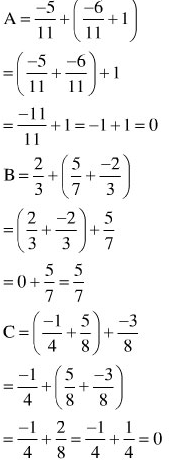
A=\(x.\dfrac{1}{5}+x.\dfrac{2}{3}-x.\dfrac{1}{4}\)
=\(x.\left(\dfrac{1}{5}+\dfrac{2}{3}-\dfrac{1}{4}\right)\)
=\(x.\dfrac{37}{60}\)
Thay x=\(\dfrac{1}{2}\) vào A ta được
A=\(\dfrac{1}{2}.\dfrac{37}{60}=\dfrac{37}{120}\)