
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


đkxđ:
\(x^2-4x+3\ge0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-1\right)\left(x-3\right)\ge0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x-1\ge0\\x-3\ge0\end{matrix}\right.\\\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x-1\le0\\x-3\le0\end{matrix}\right.\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x\ge3\\x\le1\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy đkxđ của biểu thức là \(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x\ge3\\x\le1\end{matrix}\right.\)
đkxđ:
�2−4�+3≥0x2−4x+3≥0
⇔(�−1)(�−3)≥0⇔(x−1)(x−3)≥0
⇔[{�−1≥0�−3≥0{�−1≤0�−3≤0⇔{x−1≥0x−3≥0{x−1≤0x−3≤0
⇔[�≥3�≤1⇔[x≥3x≤1
Vậy đkxđ của biểu thức là [�≥3�≤1[x≥3x≤1

a) ĐK: x ≥ 2
\(\sqrt{3x-6}=3\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3x-6=9\)
<=> 3x = 15
<=> x = 5
Vậy:....
b) ĐK: 5x - 16 ≥ 0
<=> 5x ≥ 16
<=> x ≥ 16/5
\(\sqrt{5x-16}=2\)
<=> 5x - 16 = 4
<=> 5x = 20
<=> x = 4
c) ĐK: \(x^2-4x+3\ne0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-1\right)\left(x-3\right)\ne0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x\ne1\\x\ne3\end{matrix}\right.\)
bình phương hai vế ta được:
a)điều kiện của x:x≥2
3x-6=9 <=> x=5(nhận)
b)ĐK: x≥16/5
5x-16=4 <=>x=4(nhận)
c) ta có: \(\dfrac{2x-3}{\left(x-2\right)^2-1}\)= \(\dfrac{2x-3}{\left(x-3\right)\left(x-1\right)}\)
ĐKXĐ: x≠3 ;x≠1

1) a) Căn thức có nghĩa \(\Leftrightarrow4-2x\ge0\Leftrightarrow2x\le4\Leftrightarrow x\le2\)
b) Thay x = 2 vào biểu thức A, ta được: \(A=\sqrt{4-2.2}=\sqrt{0}=0\)
Thay x = 0 vào biểu thức A, ta được: \(A=\sqrt{4-2.0}=\sqrt{4}=2\)
Thay x = 1 vào biểu thức A, ta được: \(A=\sqrt{4-2.1}=\sqrt{2}\)
Thay x = -6 vào biểu thức A, ta được: \(A=\sqrt{4-2.\left(-6\right)}=\sqrt{16}=4\)
Thay x = -10 vào biểu thức A, ta được: \(A=\sqrt{4-2.\left(-10\right)}=\sqrt{24}=2\sqrt{6}\)
c) \(A=0\Leftrightarrow\sqrt{4-2x}=0\Leftrightarrow4-2x=0\Leftrightarrow x=2\)
\(A=5\Leftrightarrow\sqrt{4-2x}=5\Leftrightarrow4-2x=25\Leftrightarrow x=\frac{-21}{2}\)
\(A=10\Leftrightarrow\sqrt{4-2x}=10\Leftrightarrow4-2x=100\Leftrightarrow x=-48\)

Bài 1 : Điều kiện xác định : \(x\ne\pm1\)
\(K=\left(\frac{x+1}{\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)}-\frac{x-1}{\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)}\right).\frac{x^2-1}{x^2}\)
\(K=\frac{2}{\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)}.\frac{\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)}{x^2}=\frac{2}{x^2}\)
Nhận thấy giá trị của x càng tăng thì giá trị của M càng giảm
mặt khác , giá trị của x lại không giảm quá 0 nên ta không thể nào xác định được giá trị lớn nhất của K

a: ĐKXĐ: (x-1)(x-3)>=0
=>x>=3 hoặc x<=1
b: ĐKXĐ: (x-4)(x-3)>=0
=>x>=4 hoặc x<=3
c: ĐKXĐ: (x-5)(x-4)>=0
=>x>=5 hoặc x<=4

\(ĐK:4x^2-12x+9=\left(2x-3\right)^2\ge0\) (luôn đúng) hay \(ĐK:x\in R\)
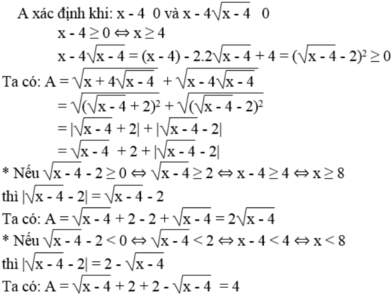
ĐKXĐ: \(x^2-4x+16\ge0\Rightarrow\left(x^2-4x+4\right)+12\ge0\) (luôn đúng)