Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.

Dạng: \(....f'\left(x\right)+...f\left(x\right)=...\)
Ý tưởng luôn là đưa về đạo hàm của tổng sau đó lấy nguyên hàm 2 vế.
Thêm bớt sao cho vế trái biến thành: \(u\left(x\right).f'\left(x\right)+u'\left(x\right).f\left(x\right)\) là được
So sánh nó với vế trái đề bài, dư ra \(u'\left(x\right)\) ở trước \(f\left(x\right)\) nên ta chia nó (vế kia vẫn ko quan tâm)
Được: \(\dfrac{u\left(x\right)}{u'\left(x\right)}.f'\left(x\right)+f\left(x\right)\)
So sánh nó với đề bài, vậy ta cần tìm hàm \(u\left(x\right)\) sao cho:
\(\dfrac{u\left(x\right)}{u'\left(x\right)}=x\left(x+1\right)\)
Nhưng để thế này ko lấy nguyên hàm được, phải nghịch đảo 2 vế:
\(\dfrac{u'\left(x\right)}{u\left(x\right)}=\dfrac{1}{x\left(x+1\right)}\)
Giờ thì lấy nguyên hàm: \(\int\dfrac{u'\left(x\right)}{u\left(x\right)}dx=\int\dfrac{dx}{x\left(x+1\right)}\Leftrightarrow ln\left|u\left(x\right)\right|=ln\left|\dfrac{x}{x+1}\right|+C\)
Tới đây suy được \(u\left(x\right)=\dfrac{x}{x+1}\) \(\Rightarrow\) vế trái cần có dạng:
\(\dfrac{x}{x+1}f'\left(x\right)+\dfrac{1}{\left(x+1\right)^2}f\left(x\right)\)
Nhìn vào đây là xong rồi. Bài toán sẽ được giải như sau:
Chia 2 vế giả thiết cho \(\left(x+1\right)^2\):
\(\Rightarrow\dfrac{x}{x+1}f'\left(x\right)+\dfrac{1}{\left(x+1\right)^2}f\left(x\right)=\dfrac{x}{x+1}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(\dfrac{x}{x+1}+f\left(x\right)\right)'=\dfrac{x}{x+1}\)
Lấy nguyên hàm 2 vế:
\(\Rightarrow\dfrac{x}{x+1}+f\left(x\right)=\int\dfrac{x}{x+1}dx=\int\left(1-\dfrac{1}{x+1}\right)dx=x-ln\left|x+1\right|+C\)
\(\Rightarrow f\left(x\right)=x-\dfrac{x}{x+1}-ln\left|x+1\right|+C=\dfrac{x^2}{x+1}-ln\left|x+1\right|+C\)
Thay \(x=1\)
\(\Rightarrow f\left(1\right)=\dfrac{1}{2}-ln2+C\Rightarrow-2ln2=\dfrac{1}{2}-ln2+C\)
\(\Rightarrow C=-ln2-\dfrac{1}{2}\)
\(\Rightarrow f\left(x\right)=\dfrac{x^2}{x+1}-ln\left|x+1\right|-ln2-\dfrac{1}{2}\)
\(\Rightarrow f\left(2\right)=...\)

Vẫn là đạo hàm của tích
Dễ dàng viết được:
\(\left[f'\left(x\right)\right]^2+f\left(x\right).f''\left(x\right)=\left[f\left(x\right)\right]'.f'\left(x\right)+f\left(x\right).\left[f'\left(x\right)\right]'=\left[f'\left(x\right).f\left(x\right)\right]'\)
Do đó giả thiết biến đổi thành:
\(\left[f'\left(x\right).f\left(x\right)\right]'=15x^4+12x\)
Nguyên hàm 2 vế:
\(f'\left(x\right).f\left(x\right)=\int\left(15x^4+12x\right)dx=3x^5+6x^2+C\)
Thay \(x=0\)
\(\Rightarrow f'\left(0\right).f\left(0\right)=C\Rightarrow C=1\)
\(\Rightarrow f'\left(x\right).f\left(x\right)=3x^5+6x^2+1\)
Tiếp tục nguyên hàm 2 vế:
\(\int f\left(x\right).f'\left(x\right)dx=\int\left(3x^5+6x^2+1\right)dx\) với chú ý \(\int f\left(x\right).f'\left(x\right)dx=\int f\left(x\right).d\left[f\left(x\right)\right]=\dfrac{1}{2}f^2\left(x\right)+C\)
Nên:
\(\Rightarrow\dfrac{1}{2}f^2\left(x\right)=\dfrac{1}{2}x^6+2x^3+x+C\)
Thay \(x=0\Rightarrow C=\dfrac{1}{2}\)
\(\Rightarrow\dfrac{1}{2}f^2\left(x\right)=\dfrac{1}{2}x^6+2x^3+x+\dfrac{1}{2}\)
\(\Rightarrow f^2\left(1\right)\)

Cách làm cơ bản của dạng này:
Cho hàm số y=f(x) liên tục trên R\ {0; -1} thỏa mãn f(1) =-2ln2 và\(x\left(x+1\right)f'\left(x\right)+f\left(x\right)=x^... - Hoc24
https://hoc24.vn/cau-hoi/cho-ham-so-y-fx-lien-tuc-tren-left02right-thoa-man-cac-dieu-kien-f2-1-va-intlimits2-0fleftxrightdxintlimits2-0leftf.3001074942942 giúp luôn câu này nữa ạ

Một trong các nguyên hàm của hàm số \(f\left(x\right)=\cos x+\sin x\) là hàm số \(\sin x-\cos x\) . Từ định lí nếu hàm số f(x) có nguyên hàm F(x) trên khoảng (a,b) thì trên khoảng đó nó có vô số nguyên hàm và hai nguyên hàm bất kì của cùng một hàm cho trên khoảng (a,b) là sai khác nhau một hằng số cộng. suy ra mọi nguyên hàm số đã cho đều có dạng \(F\left(x\right)=\sin x-\cos x+C\), trong đó C là hằng số nào đó.
Để xác định hằng số C ta sử dụng điều kiện F(0)=1
Từ điều kiện này và biểu thức F(x) ta có :
\(\sin0-\cos0+C=1\Rightarrow C=1+\cos0=2\)
Do đó hàm số \(F\left(x\right)=\sin x-\cos x+2\) là nguyên hàm cần tìm
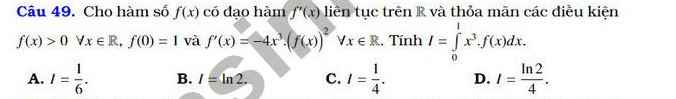
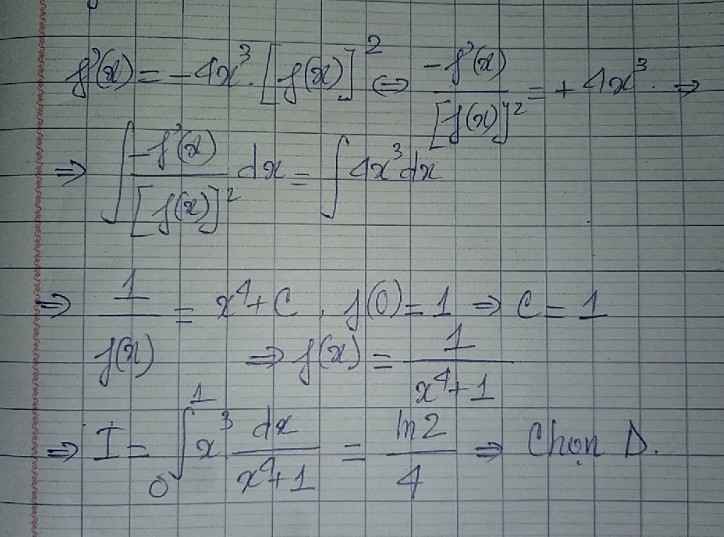




\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{f'\left(x\right)}{f\left(x\right)}+2x=lnx\Rightarrow\dfrac{f'\left(x\right)}{f\left(x\right)}=lnx-2x\)
Lấy nguyên hàm 2 vế:
\(\Rightarrow\int\dfrac{f'\left(x\right)}{f\left(x\right)}dx=\int\left(lnx-2x\right)dx\)
\(\Rightarrow ln\left|f\left(x\right)\right|=x\left(lnx-1\right)-x^2+C\)
Thay \(x=1\)
\(\Rightarrow ln\left|f\left(1\right)\right|=-2+C\Rightarrow C=2\)
\(\Rightarrow ln\left|f\left(x\right)\right|=x\left(lnx-1\right)-x^2+2\)
\(\Rightarrow\left|f\left(x\right)\right|=e^{x\left(lnx-1\right)-x^2+2}\)
\(\Rightarrow\left|f\left(2\right)\right|\)