Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.

a) Xét ΔABH vuông tại H và ΔCAH vuông tại H có
\(\widehat{ABH}=\widehat{CAH}\left(=90^0-\widehat{C}\right)\)
Do đó: ΔABH\(\sim\)ΔCAH(g-g)
Suy ra: \(\dfrac{AH}{CH}=\dfrac{BH}{AH}\)(Các cặp cạnh tương ứng tỉ lệ)
hay \(AH^2=HB\cdot HC\)(đpcm)

i: \(=\dfrac{x+1+x-18+x+2}{x-5}=\dfrac{3x-15}{x-5}=3\)
Bài 1:
\(i,\dfrac{x+1}{x-5}+\dfrac{x-18}{x-5}-\dfrac{x+2}{5-x}=\dfrac{x+1}{x-5}+\dfrac{x-18}{x-5}+\dfrac{x+2}{x-5}=\dfrac{x+1+x-18+x+2}{x-5}=\dfrac{3x-15}{x-5}=\dfrac{3\left(x-5\right)}{x-5}=3\)
\(j,\dfrac{3x\left(x-2\right)}{3x-2}+\dfrac{6x^2}{3x-2}-\dfrac{2\left(2-3x\right)}{2-3x}=\dfrac{3x^2-6x}{3x-2}+\dfrac{6x^2}{3x-2}+\dfrac{4-6x}{3x-2}=\dfrac{3x^2-6x+6x^2+4-6x}{3x-2}=\dfrac{9x^2-12x+4}{3x-2}=\dfrac{\left(3x-2\right)^2}{3x-2}=3x-2\)
\(n,\dfrac{2}{x}+\dfrac{3}{x-1}+\dfrac{1-4x}{x^2-x}=\dfrac{2\left(x-1\right)+3x+1-4x}{x\left(x-1\right)}=\dfrac{2x-2+3x+1-4x}{x\left(x-1\right)}=\dfrac{x-1}{x\left(x-1\right)}=\dfrac{1}{x}\)
Bài 2:
\(j,\dfrac{2}{3x}-\dfrac{1}{2x-2}-\dfrac{x-4}{6x-6x^2}=\dfrac{4\left(x-1\right)}{6x\left(x-1\right)}-\dfrac{3x}{6x\left(x-1\right)}-\dfrac{x-4}{6x\left(1-x\right)}=\dfrac{4x-4-3x+x-4}{6x\left(x-1\right)}=\dfrac{2x-8}{6x\left(x-1\right)}=\dfrac{2\left(x-4\right)}{6x\left(x-1\right)}=\dfrac{x-4}{3x\left(x-1\right)}\)

d) Xét ΔABC có AH là đường cao ứng với cạnh BC(gt)
nên \(S_{ABC}=\dfrac{AH\cdot BC}{2}\)(1)
Ta có: ΔABC vuông tại A(gt)
nên \(S_{ABC}=\dfrac{AB\cdot AC}{2}\)(2)
Từ (1) và (2) suy ra \(AH\cdot BC=AB\cdot AC\)
a) Xét ΔAHB vuông tại H và ΔCAB vuông tại A có
\(\widehat{B}\) chung
Do đó: ΔAHB\(\sim\)ΔCAB(g-g)
Suy ra: \(\dfrac{AB}{CB}=\dfrac{HB}{AB}\)(Các cặp cạnh tương ứng tỉ lệ)
hay \(AB^2=BC\cdot BH\)
b) Xét ΔAHB vuông tại H và ΔCHA vuông tại H có
\(\widehat{BAH}=\widehat{ACH}\left(=90^0-\widehat{B}\right)\)
Do đó:ΔAHB\(\sim\)ΔCHA(g-g)
Suy ra: \(\dfrac{AH}{CH}=\dfrac{HB}{HA}\)(Các cặp cạnh tương ứng tỉ lệ)
hay \(AH^2=HB\cdot HC\)

-Sửa đề: \(\widehat{A}=\widehat{D}=90^0\)
a) -△OAB và △OCD có: \(\widehat{OAB}=\widehat{OCD};\widehat{AOB}=\widehat{COD}\)
\(\Rightarrow\)△OAB∼△OCD (g-g).
b) \(AC^2-BD^2=DC^2-AB^2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow AC^2-DC^2=BD^2-AB^2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow AD^2=AD^2\) (luôn đúng).
c) -△BCD có: OI//DC \(\Rightarrow\dfrac{DC}{OI}=\dfrac{BD}{BO}\Rightarrow\dfrac{DC}{OI}-1=\dfrac{OD}{BO}\)
-△AOB có: AB//DC \(\Rightarrow\dfrac{OD}{BO}=\dfrac{DC}{AB}=\dfrac{DC}{OI}-1\)
\(\Rightarrow\dfrac{DC}{AB}+1=\dfrac{DC}{OI}\Rightarrow\dfrac{DC+AB}{AB}=\dfrac{DC}{OI}\Rightarrow\dfrac{1}{OI}=\dfrac{DC+AB}{DC.AB}=\dfrac{1}{AB}+\dfrac{1}{DC}\)

Ta có : \(\dfrac{a+b}{2}\ge\sqrt{ab}\Leftrightarrow\left(\sqrt{a}-\sqrt{b}\right)^2\ge0\) ( luôn đúng )
Dấu "=" xảy ra khi \(a=b\)
Bài tập :
Có : \(A=\dfrac{1}{x}+\dfrac{1}{y}=\dfrac{x+y}{x}+\dfrac{x+y}{y}=2+\dfrac{x}{y}+\dfrac{y}{x}\) ( do \(x+y=1\) )
Theo BĐT trên có : \(\dfrac{x}{y}+\dfrac{y}{x}\ge2.\sqrt{\dfrac{x}{y}\cdot\dfrac{y}{x}}=2\)
Nên \(A\ge2+2=4\)
Dấu "=" xảy ra \(\Leftrightarrow x=y=\dfrac{1}{2}\)

Ta có : \(\dfrac{a+b}{2}\ge\sqrt{ab}\) (tự cm)
Lại có : \(A=\dfrac{1}{x}+\dfrac{1}{y}=\dfrac{x+y}{xy}\)
Áp dụng BĐT trên ta có : : \(xy\le\left(\dfrac{x+y}{2}\right)^2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow A\ge\dfrac{x+y}{\left(\dfrac{x+y}{2}\right)^2}=\dfrac{1}{\dfrac{1}{2^2}}=4\)
Dấu "=" xảy ra \(\Leftrightarrow x=y=\dfrac{1}{2}\)
Vậy...

Có: A=\(\dfrac{1}{x}+\dfrac{1}{y}\) =\(\dfrac{x+y}{xy}\) =\(\dfrac{1}{xy}\) ( do x+y=1)
Áp dụng bđt \(\dfrac{a+b}{2}\ge\sqrt{ab}\) ,dâú bằng xảy ra khi a=b, ta có:
A=\(\dfrac{1}{x}+\dfrac{1}{y}\) =\(\dfrac{1}{xy}\) ≥ \(\dfrac{2}{x+y}\) =\(\dfrac{2}{1}\) =2 ( x+y=1)
dấu bằng xảy ra khi x=y=0,5.
c/m bđt \(\dfrac{a+b}{2}\ge\sqrt{ab}\) ⇔ a+b ≥ 2\(\sqrt{ab}\)
⇔(a+b)2 ≥ 4ab
⇔a2 +b2 +2ab≥ 4ab
⇔(a-b)2 ≥ 0 (luôn đúng)
dấu bằng xảy ra khi a=b.
\(\dfrac{a+b}{2}\ge\sqrt{ab}\left(\circledast\right)\\ \Leftrightarrow a+b\ge2\sqrt{ab}\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(a+b\right)^2\ge4ab\\ \Leftrightarrow a^2+2ab+b^2-4ab\ge0\\ \Leftrightarrow a^2-2ab+b^2=\left(a-b\right)^2\ge0\left(\text{luôn đúng}\right)\)
Vậy BĐT (*) được chứng minh.
\(A=\dfrac{1}{x}+\dfrac{1}{y}=\dfrac{x+y}{xy}=\dfrac{1}{xy}\)
__________________________________
\(\dfrac{x+y}{2}\ge\sqrt{xy}\\ \Rightarrow\sqrt{xy}\le\dfrac{1}{2}\\ \Rightarrow xy\le\dfrac{1}{4}\\ \Rightarrow A=\dfrac{1}{xy}\ge\dfrac{1}{\dfrac{1}{4}}=4\)
Vậy GTNN của A = 4
Dấu "=" xảy ra \(\Leftrightarrow x=y=\dfrac{1}{2}\)

k,\(\dfrac{x}{3}-\dfrac{2x+1}{2}=\dfrac{x}{6}-x\)
giúp mk câu k nhé đề bài như trên
b: \(\Leftrightarrow4x+8-9=4x-4\)
=>-1=-4(loại)
d: \(\Leftrightarrow3\left(x-2\right)+2\left(x+1\right)=8x\)
=>8x=3x-6+2x+2=5x-4
=>3x=-4
=>x=-4/3
f: \(\Leftrightarrow3\left(x+2\right)+4\left(2x-3\right)=2\left(x-12\right)\)
=>3x+6+8x-12=2x-24
=>11x-6=2x-24
=>9x=-18
=>x=-2


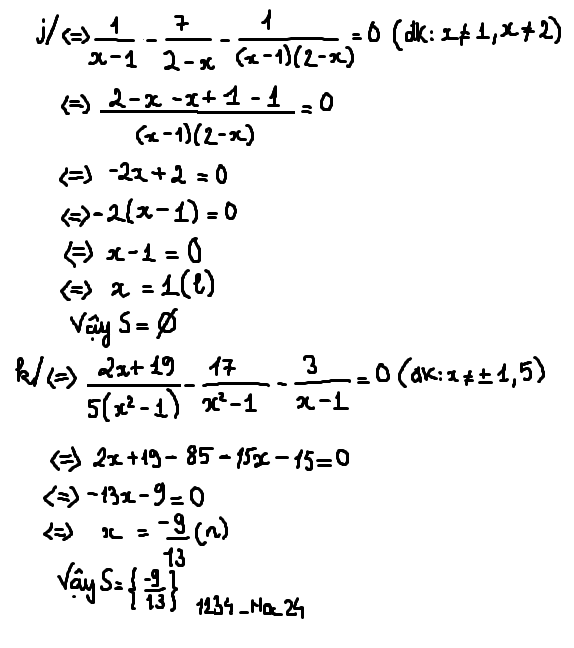

Hệ thức lượng
Áp dụng định lí 4 của hệ thức lượng