phân tích đa thức x2+ax+b thành nhân tử
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


a: \(=4xy\left(1-5x^2y\right)\)
b: \(=\left(x-y\right)\left(x+y\right)+3\left(x-y\right)=\left(x-y\right)\left(x+y+3\right)\)
c: \(=x\left(x-a\right)+y\left(x-a\right)=\left(x-a\right)\left(x+y\right)\)
d: \(=\left(x+2y\right)^2-36=\left(x+2y+6\right)\left(x+2y-6\right)\)
Bài 2 : Phân tích các đa thức sau thành nhân tử :
a) x2 - ( m + n )x + mn
b) ax + by + a - bx - ay - b

\(a,=x^2-mx-nx+mn=x\left(x-m\right)-n\left(x-m\right)=\left(x-n\right)\left(x-m\right)\\ b,=a\left(x-y\right)-b\left(x-y\right)+\left(a-b\right)\\ =\left(x-y\right)\left(a-b\right)+\left(a-b\right)=\left(a-b\right)\left(x-y+1\right)\)
b: \(=a\left(x-y\right)-b\left(x-y\right)+a-b\)
\(=\left(x-y+1\right)\left(a-b\right)\)

\(a,=x\left(x-2\right)\\ b,=2b\left(x-3y\right)+a\left(x-3y\right)=\left(a+2b\right)\left(x-3y\right)\\ c,=x\left(x^2+2xy+y^2-4\right)=x\left[\left(x+y\right)^2-4\right]=x\left(x+y+2\right)\left(x+y-2\right)\\ d,=4-\left(x+y\right)^2=\left(2-x-y\right)\left(2+x+y\right)\\ đ,=5\left(x-y\right)\left(x+y\right)+3\left(x+y\right)^2=\left(x+y\right)\left(5x-5y+3x+3y\right)\\ =\left(x+y\right)\left(8x-2y\right)=2\left(4x-y\right)\left(x+y\right)\\ e,=3x\left(2xy-3\right)\\ b,=x\left(4x^2-4xy+y^2-4\right)=x\left[\left(2x-y\right)^2-4\right]=x\left(2x-y-2\right)\left(2x-y+2\right)\\ f,=\left(x+y\right)^2-z^2=\left(x+y-z\right)\left(x+y+z\right)\)

b) x3 – x2 – 5x + 125
= (x3 + 125) - (x2 + 5x)
= (x + 5)(x2 - 5x + 25) - x(x + 5)
= (x + 5)(x2 - 5x + 25 - x)
= (x + 5)(x2 - 6x + 25)

b) 4 – x2 – 2xy – y2 = 4 – (x2 + 2xy + y2) = 4 – (x + y)2
= (2 + x + y)(2 – x – y)

Cách 1: Tách một hạng tử thành tổng hai hạng tử để xuất hiện nhân tử chung.
a) x2 – 3x + 2
= x2 – x – 2x + 2 (Tách –3x = – x – 2x)
= (x2 – x) – (2x – 2)
= x(x – 1) – 2(x – 1) (Có x – 1 là nhân tử chung)
= (x – 1)(x – 2)
Hoặc: x2 – 3x + 2
= x2 – 3x – 4 + 6 (Tách 2 = – 4 + 6)
= x2 – 4 – 3x + 6
= (x2 – 22) – 3(x – 2)
= (x – 2)(x + 2) – 3.(x – 2) (Xuất hiện nhân tử chung x – 2)
= (x – 2)(x + 2 – 3) = (x – 2)(x – 1)
b) x2 + x – 6
= x2 + 3x – 2x – 6 (Tách x = 3x – 2x)
= x(x + 3) – 2(x + 3) (có x + 3 là nhân tử chung)
= (x + 3)(x – 2)
c) x2 + 5x + 6 (Tách 5x = 2x + 3x)
= x2 + 2x + 3x + 6
= x(x + 2) + 3(x + 2) (Có x + 2 là nhân tử chung)
= (x + 2)(x + 3)
Cách 2: Đưa về hằng đẳng thức (1) hoặc (2)
a) x2 – 3x + 2
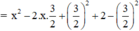
(Vì có x2 và 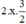 nên ta thêm bớt
nên ta thêm bớt 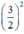 để xuất hiện HĐT)
để xuất hiện HĐT)
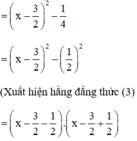
= (x – 2)(x – 1)
b) x2 + x - 6

= (x – 2)(x + 3).
c) x2 + 5x + 6

= (x + 2)(x + 3).

\(x^2+ax+b\)
\(=\left(x^2+\frac{2ax}{2}+\frac{a^2}{4}\right)+b-\frac{a^2}{4}\)
\(=\left(x+\frac{a}{2}\right)^2-\left(\frac{a^2}{4}-b\right)\)
Với điều kiện: \(\frac{a^2}{4}-b\ge0\)thì phân tích được
\(=\left(x+\frac{a}{2}+\sqrt{\frac{a^2}{4}-b}\right)\left(x+\frac{a}{2}-\sqrt{\frac{a^2}{4}-b}\right)\)