giải hộ mình bài này với
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


Bài 5 hình 1: (tự vẽ hình nhé bạn)
a) Xét ΔABD và ΔACB ta có:
\(\widehat{BAD}\)= \(\widehat{BAC}\) (góc chung)
\(\widehat{ABD}\)= \(\widehat{ACB}\) (gt)
=> ΔABD ~ ΔACB (g-g)
=> \(\dfrac{AB}{AC}\) = \(\dfrac{BD}{CB}\) = \(\dfrac{AD}{AB}\) (tsđd)
b) Ta có: \(\dfrac{AB}{AC}\) = \(\dfrac{AD}{AB}\) (cm a)
=> \(AB^2\) = AD.AC
=> \(2^2\) = AD.4
=> AD = 1 (cm)
Ta có: AC = AD + DC (D thuộc AC)
=> 4 = 1 + DC
=> DC = 3 (cm)
c) Xét ΔABH và ΔADE ta có:
\(\widehat{AHB}\) = \(\widehat{AED}\) (=\(90^0\))
\(\widehat{ADB}\) = \(\widehat{ABH}\) (ΔABD ~ ΔACB)
=> ΔABH ~ ΔADE
=> \(\dfrac{AB}{AD}\) = \(\dfrac{AH}{AE}\) = \(\dfrac{BH}{DE}\) (tsdd)
Ta có: \(\dfrac{S_{ABH}}{S_{ADE}}\) = \(\left(\dfrac{AB}{AD}\right)^2\)= \(\left(\dfrac{2}{1}\right)^2\)= 4
=> đpcm
Tiếp bài 5 hình 2 (tự vẽ hình)
a) Xét ΔABC vuông tại A ta có:
\(BC^2\) = \(AB^2\) + \(AC^2\)
\(BC^2\) = \(21^2\) + \(28^2\)
BC = 35 (cm)
b) Xét ΔABC và ΔHBA ta có:
\(\widehat{BAC}\) = \(\widehat{AHB}\) ( =\(90^0\))
\(\widehat{ABC}\) = \(\widehat{ABH}\) (góc chung)
=> ΔABC ~ ΔHBA (g-g)
=> \(\dfrac{AB}{BH}\) = \(\dfrac{BC}{AB}\) (tsdd)
=> \(AB^2\) = BH.BC
=> \(21^2\) = 35.BH
=> BH = 12,6 (cm)
c) Xét ΔABC ta có:
BD là đường p/g (gt)
=> \(\dfrac{AD}{DC}\) = \(\dfrac{AB}{BC}\) (t/c đường p/g)
Xét ΔABH ta có:
BE là đường p/g (gt)
=> \(\dfrac{HE}{AE}\) = \(\dfrac{BH}{AB}\) (t/c đường p/g)
Mà: \(\dfrac{AB}{BC}\) = \(\dfrac{BH}{AB}\) (cm b)
=> đpcm
d) Ta có: \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\widehat{HBE}+\widehat{BEH}=90^0\\\widehat{ABD}+\widehat{ADB=90^0}\\\widehat{HBE}=\widehat{ABD}\end{matrix}\right.\)
=> \(\widehat{BEH}=\widehat{ADB}\)
Mà \(\widehat{BEH}=\widehat{AED}\) (2 góc dd)
Nên \(\widehat{ADB}=\widehat{AED}\)
=> đpcm

| Vượn cổ | Người tối cổ | Người tinh khôn | |
| Thời gian xuất hiện | khoảng 6 triệu năm trước | 4 triệu nằm trước đây | khoảng 4 vạn nằm trước đây |
Cấu tạo cơ thể
| - Có thể đi, đứng bằng 2 chân | - Đi, đứng bằng hai chân. - Trán thấp và bợt ra sau, u mày nổi cao, hộp sọ đã lớn hơn và hình thành trung tâm phát tiếng nói trong não. | - Như con người ngày nay |
| Địa điểm xuất hiện | ở Đông Phi,Tây Á, Việt Nam | ở Đông Phi, Gia va, Bắc kinh, Thanh Hóa | ở hầu hết các châu lục |


\(Tacó:\left\{{}\begin{matrix}2Z+N=34\\N-Z=1\end{matrix}\right.\\ \Rightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}Z=11=P=E\\N=12\end{matrix}\right.\)

Bài 1 :
a) \(sin4x=sin\dfrac{\pi}{5}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}4x=\dfrac{\pi}{5}+k2\pi\\4x=\pi-\dfrac{\pi}{5}+k2\pi\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{\pi}{20}+k\dfrac{\pi}{2}\\x=\dfrac{\pi}{5}+k\dfrac{\pi}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\)
e) \(2sin\dfrac{x}{2}+\sqrt[]{3}=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow sin\dfrac{x}{2}=-\dfrac{\sqrt[]{3}}{2}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow sin\dfrac{x}{2}=sin\left(-\dfrac{\pi}{3}\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}\dfrac{x}{2}=-\dfrac{\pi}{3}+k2\pi\\\dfrac{x}{2}=\pi+\dfrac{\pi}{3}+k2\pi\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=-\dfrac{2\pi}{3}+k2\pi\\x=\dfrac{8\pi}{3}+k2\pi\end{matrix}\right.\)
m) \(\sqrt[]{3}tan2x-3=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow tan2x=\sqrt[]{3}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow tan2x=tan\dfrac{\pi}{3}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x=\dfrac{\pi}{3}+k\pi\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=\dfrac{\pi}{6}+\dfrac{k\pi}{2}\)

1 because
2 as long as
3 although
4 so that
5 although
6 even if
7 until
8 while
9 because
10 Although

\(M=\left(\dfrac{\sqrt{x}}{\left(\sqrt{x}-2\right)\left(\sqrt{x}+2\right)}+\dfrac{\sqrt{x}+2}{\left(\sqrt{x}-2\right)\left(\sqrt{x}+2\right)}\right).\dfrac{\sqrt{x}-2}{2}\)
\(=\dfrac{2\left(\sqrt{x}+1\right)\left(\sqrt{x}-2\right)}{2\left(\sqrt{x}-2\right)\left(\sqrt{x}+2\right)}=\dfrac{\sqrt{x}+1}{\sqrt{x}+2}\)
2. Ta có:
\(\sqrt{x}>0\Rightarrow\dfrac{\sqrt{x}+1}{\sqrt{x}+2}>0\) hay \(M>0\)
Lại có: \(M=\dfrac{\sqrt{x}+2-1}{\sqrt{x}+2}=1-\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{x}+2}< 1\)
\(\Rightarrow0< M< 1\Rightarrow M>M^2\)
1) Ta có: \(M=\left(\dfrac{\sqrt{x}}{x-4}+\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{x}-2}\right)\cdot\dfrac{\sqrt{x}-2}{2}\)
\(=\dfrac{\sqrt{x}+\sqrt{x}+2}{\left(\sqrt{x}-2\right)\left(\sqrt{x}+2\right)}\cdot\dfrac{\sqrt{x}-2}{2}\)
\(=\dfrac{2\sqrt{x}+2}{2\left(\sqrt{x}+2\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{\sqrt{x}+1}{\sqrt{x}+2}\)

Sửa đề là : 4.6 (g)
\(n_{H_2}=\dfrac{2.24}{22.4}=0.1\left(mol\right)\)
\(A+H_2O\rightarrow AOH+\dfrac{1}{2}H_2\)
\(0.2...............................0.1\)
\(M_A=\dfrac{4.6}{0.2}=23\left(\dfrac{g}{mol}\right)\)
\(A:Na\)
Đề này C1 em sửa thành 4,6 gam kim loại như bạn dưới, C2 em sửa thành 22,4 lít H2

\(P=\left[\dfrac{a+3\sqrt{a}+2}{\left(\sqrt{a}+2\right)\left(\sqrt{a}-1\right)}-\dfrac{a+\sqrt{a}}{a-1}\right]:\left(\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{a}+1}+\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{a}-1}\right)\) (đk:\(a\ge0;a\ne1\))
\(=\left[\dfrac{\left(\sqrt{a}+1\right)\left(\sqrt{a}+2\right)}{\left(\sqrt{a}+2\right)\left(\sqrt{a}-1\right)}-\dfrac{\sqrt{a}\left(\sqrt{a}+1\right)}{\left(\sqrt{a}+1\right)\left(\sqrt{a}-1\right)}\right]:\dfrac{\sqrt{a}-1+\sqrt{a}+1}{\left(\sqrt{a}-1\right)\left(\sqrt{a}+1\right)}\)
\(=\left(\dfrac{\sqrt{a}+1}{\sqrt{a}-1}-\dfrac{\sqrt{a}}{\sqrt{a}-1}\right).\dfrac{\left(\sqrt{a}-1\right)\left(\sqrt{a}+1\right)}{2\sqrt{a}}\)
\(=\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{a}-1}.\dfrac{\left(\sqrt{a}-1\right)\left(\sqrt{a}+1\right)}{2\sqrt{a}}=\dfrac{\sqrt{a}+1}{2\sqrt{a}}\)
2) \(\dfrac{1}{P}\ge\dfrac{\sqrt{a}+9}{8}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{2\sqrt{a}}{\sqrt{a}+1}\ge\dfrac{\sqrt{a}+9}{8}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow16\sqrt{a}\ge\left(\sqrt{a}+9\right)\left(\sqrt{a}+1\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow a-6\sqrt{a}+9\le0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(\sqrt{a}-3\right)^2\le0\)
Dấu "=" xảy ra khi \(\sqrt{a}-3=0\Leftrightarrow a=9\) (tm)
Vậy...
1) ĐKXĐ: \(a\ge0;a\ne1\)
\(P=\left[\dfrac{a+\sqrt{a}+2\sqrt{a}+2}{\left(\sqrt{a}+2\right).\left(\sqrt{a}-1\right)}-\dfrac{\sqrt{a}.\left(\sqrt{a}+1\right)}{\left(\sqrt{a}-1\right).\left(\sqrt{a}+1\right)}\right]\)\(:\left[\dfrac{\sqrt{a}-1+\sqrt{a}+1}{\left(\sqrt{a}-1\right).\left(\sqrt{a}+1\right)}\right]\)
\(\Leftrightarrow P=\left[\dfrac{\sqrt{a}.\left(\sqrt{a}+1\right)+2.\left(\sqrt{a}+1\right)}{\left(\sqrt{a}+2\right).\left(\sqrt{a}-1\right)}-\dfrac{\sqrt{a}}{\sqrt{a}-1}\right]\)\(:\dfrac{2\sqrt{a}}{\left(\sqrt{a}-1\right).\left(\sqrt{a}+1\right)}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow P=\left[\dfrac{\left(\sqrt{a}+2\right).\left(\sqrt{a}+1\right)}{\left(\sqrt{a}+2\right).\left(\sqrt{a}-1\right)}-\dfrac{\sqrt{a}}{\sqrt{a}-1}\right].\dfrac{\left(\sqrt{a}-1\right).\left(\sqrt{a}+1\right)}{2\sqrt{a}}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow P=\dfrac{\sqrt{a}+1-\sqrt{a}}{\sqrt{a}-1}.\dfrac{\left(\sqrt{a}-1\right).\left(\sqrt{a}+1\right)}{2\sqrt{a}}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow P=\dfrac{\sqrt{a}+1}{2\sqrt{a}}\)
2) Có : \(\dfrac{1}{P}\ge\dfrac{\sqrt{a}+9}{8}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{2\sqrt{a}}{\sqrt{a}+1}\ge\dfrac{\sqrt{a}+9}{8}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{2\sqrt{a}}{\sqrt{a}+1}-\dfrac{\sqrt{a}+9}{8}\ge0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{16\sqrt{a}-\left(\sqrt{a}+9\right).\left(\sqrt{a}+1\right)}{8.\left(\sqrt{a}+1\right)}\ge0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{16\sqrt{a}-a-10\sqrt{a}-9}{8.\left(\sqrt{a}+1\right)}\ge0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{-\left(a-6\sqrt{a}+9\right)}{8.\left(\sqrt{a}+1\right)}\ge0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{\left(\sqrt{a}-3\right)^2}{8.\left(\sqrt{a}+1\right)}\le0\)
Vì \(\sqrt{a}\ge0\Rightarrow8.\left(\sqrt{a}+1\right)>0\) mà \(\left(\sqrt{a}-3\right)^2\) \(\ge0\)
\(\Rightarrow\) \(\dfrac{\left(\sqrt{a}-3\right)^2}{8.\left(\sqrt{a}+1\right)}=0\) \(\Rightarrow\left(\sqrt{a}-3\right)^2=0\) \(\Leftrightarrow\sqrt{a}-3=0\Leftrightarrow\sqrt{a}=3\Leftrightarrow a=9\)
Vậy để\(\dfrac{1}{P}\ge\dfrac{\sqrt{a}+9}{8}\) thì \(a=9\)
 giải hộ mình mấy bài này vs ạ !
giải hộ mình mấy bài này vs ạ !


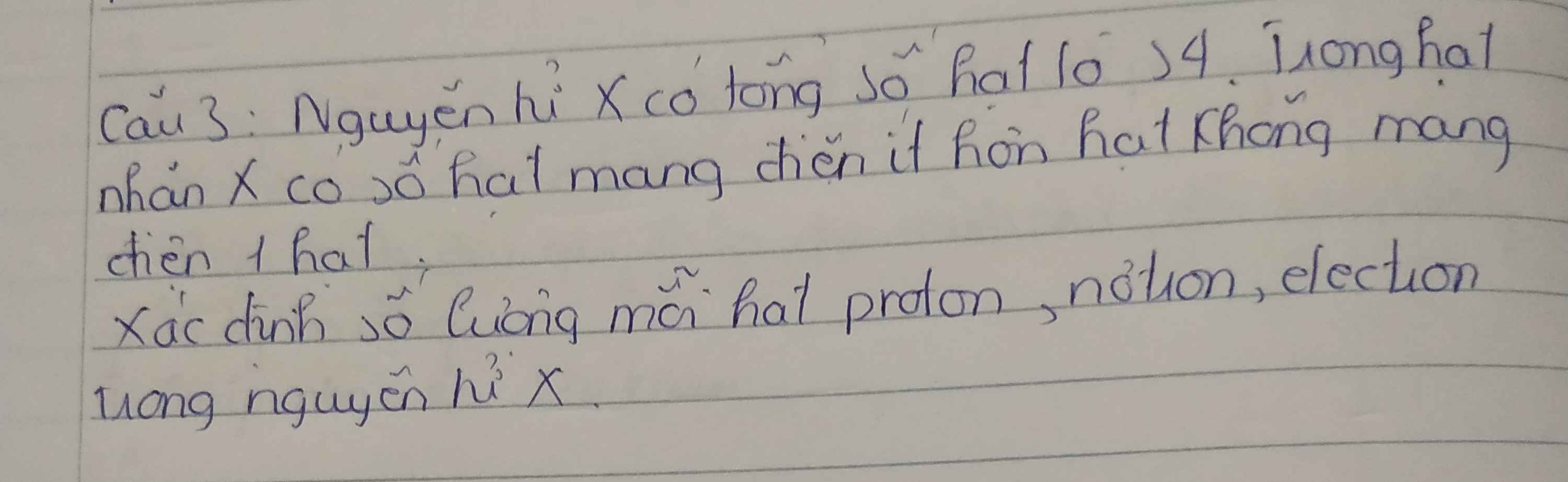
 Giải bài này hộ mình với!!!
Giải bài này hộ mình với!!!
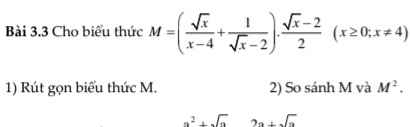


Quy tắc phát âm /s/
Nếu từ có kết thúc là c, s, x, z, ss, ch, sh, ge thì S được phát âm là /iz/
Nếu từ có kết thúc là p, t, k, f, th thì S được phát âm là /s/
Nếu từ có kết thúc là d, g, l, m, n, ng, r, v, y thì S được phát âm là /z/
Công thức phát âm nha