Điều kiện xác định của hàm số y = log 2 ( x - 1 ) là
A. x ≠ 1
B. x > 1
C. x < 1
D. ∀ x ∈ R
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.

![]()

Điều kiện xác định: \(x^2-2x+1>0\)
Mà \(x^2-2x+1=\left(x-1\right)^2\ge0\forall x\in R\)
\(\Rightarrow x-1\ne0\\ \Leftrightarrow x\ne1\)
Vậy D = \(R/\left\{1\right\}\) ⇒ Chọn B.

a, Điều kiện: \(2^x\ne3\Rightarrow x\ne log_23\)
Vậy D = R \ \(log_23\)
b, Điều kiện: \(25-5^x\ge0\Rightarrow5^x\le5^2\Rightarrow x\le2\)
Vậy D = \((-\infty;2]\)
c, Điều kiện: \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x>0\\lnx\ne1\end{matrix}\right.\Rightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x>0\\x\ne e\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy D = \(\left(0;+\infty\right)\backslash\left\{e\right\}\)
d, Điều kiện: \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x>0\\1-log_3x\ge0\end{matrix}\right.\Rightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x>0\\log_3x\le1\end{matrix}\right.\Rightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x>0\\x\le3\end{matrix}\right.\Rightarrow0< x\le3\)
Vậy D = \((0;3]\)

Chẳng hạn 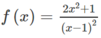 .
.
Dễ dàng kiểm tra được rằng f(x) thoả mãn các điều kiện đã nêu

Chọn D. Bởi vì hàm số ln x luôn luôn dương nên chắc chắn sẽ đồng biến trên TXĐ của nó

ĐKXĐ:
a.
\(x^2-16>0\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x>4\\x< -4\end{matrix}\right.\)
b.
\(x^2-2x+1>0\Rightarrow\left(x-1\right)^2>0\Rightarrow x\ne1\)
c.
\(\left(2-x\right)\left(x+1\right)>0\Rightarrow-1< x< 2\)
d.
\(\left(x^2-1\right)\left(x+5\right)>0\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}-5< x< -1\\x>1\end{matrix}\right.\)

Vì \(\dfrac{1}{e}\simeq0,368< 1\)
\(\Rightarrow y=log_{\dfrac{1}{e}}\left(x\right)\) nghịch biến trên D = \(\left(0;+\infty\right)\)
Chọn C.
0<1/e<1
=>\(log_{\dfrac{1}{e}}\left(x\right)\) nghịch biến
=>C

\(a,D=R\\ b,2x-3>0\\ \Rightarrow x>\dfrac{3}{2}\\ \Rightarrow D=(\dfrac{3}{2};+\infty)\\ c,-x^2+4>0\\ \Rightarrow x^2< 4\\ \Leftrightarrow-2< x< 2\\ \Rightarrow D=\left(-2;2\right)\)

Bài 1:
a: f(0)=1
f(2)=-3x2+1=-6+1=-5
f(-2)=-3x2+1=-5
f(-1/2)=-3x1/2+1=-3/2+1=-1/2
b: f(x)=-3
=>-3|x|+1=-3
=>-3|x|=-4
=>|x|=4/3
=>x=4/3 hoặc x=-4/3