Giả sử hàm số f có đạo hàm cấp n trên R thỏa mãn f 1 - x + x 2 f ' ' x = 2 x với mọi x ∈ R . Tính tích phân I = ∫ 0 1 xf ' x dx .
A. I = 1
B. I = 2
C. I = 1/3
D. I = 2/3
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.

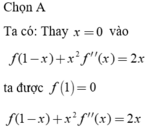
![]()
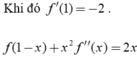
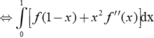
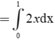
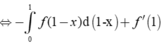
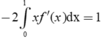
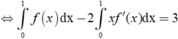
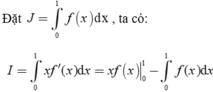
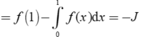
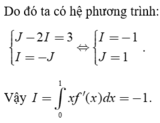

f ( 1 - x ) + x 2 f ' ' ( x ) = 2 x 1
Thay x=0 vào (1) ta được f(1)=0
Đạo hàm hai vế của (1) ta có - f ' ( 1 - x ) + 2 x f ' ' ( x ) + x 2 f ' ' ' ( x ) = 2 2
Thay x=0 vào (2) ta được f'(1)=2
Mặt khác, lấy tích phân hai vế cận từ 0 đến 1 của (1) ta có:
∫ 0 1 f ( 1 - x ) d x + ∫ 0 1 x 2 f ' ' ( x ) d x = ∫ 0 1 2 x d x
⇔ - ∫ 0 1 f ( 1 - x ) d ( 1 - x ) + f ' ( 1 ) - 2 ∫ 0 1 x f ' ( x ) d x = 1 ⇔ ∫ 0 1 f ( x ) d x - 2 ∫ 0 1 x f ' ( x ) d x = 3
Đặt ∫ 1 f ( x ) d x = I 1 . Vì
∫ 0 1 x f ' ( x ) d x = f ( 1 ) - ∫ 0 1 f ( x ) d x = - ∫ 0 1 f ( x ) d x
nên ta có hệ: I 1 - 2 I = 3 I = - I 1 ⇔ I 1 = 1 I = - 1
Vậy I=-1
Chọn đáp án B.

Chọn A.
Phương pháp:
Sử dụng công thức tính đạo hàm của tích
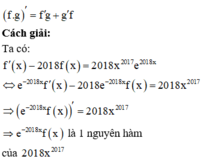
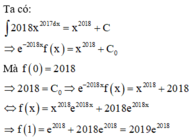

\(f\left(0\right)=-1\Rightarrow f'\left(0\right)+2=0\Leftrightarrow f'\left(0\right)=-2\)
\(\int\limits^1_0f\left(x\right)dx=\int\limits^1_0\dfrac{f'\left(x\right)-x.e^{3x}}{2}dx=\dfrac{1}{2}\int\limits^1_0f'\left(x\right)dx-\dfrac{1}{2}\int\limits^1_0x.e^{3x}dx=\dfrac{1}{2}f\left(x\right)|^1_0-\dfrac{1}{2}\int\limits^1_0xe^{3x}dx\)
\(I_1=\int xe^{3x}dx\)
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}u=x\\dv=e^{3x}dx\end{matrix}\right.\Rightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}du=dx\\v=\dfrac{1}{3}e^{3x}\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Rightarrow I_1=\dfrac{1}{3}xe^{3x}-\dfrac{1}{3}\int e^{3x}dx=\dfrac{1}{3}xe^{3x}-\dfrac{1}{9}e^{3x}\)
\(\Rightarrow I=\dfrac{1}{2}f\left(1\right)-\dfrac{1}{2}f\left(0\right)-\dfrac{1}{2}\left(\dfrac{1}{3}xe^{3x}-\dfrac{1}{9}e^{3x}\right)|^1_0\)
Èo, tắc chỗ f(1) rồi, vậy đành phải biến đổi để tìm f(x) luôn vậy, hmm
Thử nhân 2 vế với \(e^{2x}\) xem nào:
\(e^{2x}f'\left(x\right)-2e^{2x}f\left(x\right)=x.e^{5x}\Leftrightarrow\left(e^{2x}.f\left(x\right)\right)'=x.e^{5x}\)
Lay nguyen ham 2 ve:
\(e^{2x}.f\left(x\right)=\int x.e^{5x}dx\)
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=u\\dv=e^{5x}dx\end{matrix}\right.\Rightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}dx=du\\v=\dfrac{1}{5}e^{5x}\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Rightarrow e^{2x}.f\left(x\right)=\int x.e^{5x}dx=\dfrac{1}{5}x.e^{5x}-\dfrac{1}{5}\int e^{5x}dx=\dfrac{1}{5}xe^{5x}-\dfrac{1}{25}e^{5x}+C\)
\(f\left(0\right)=-1\Leftrightarrow f\left(0\right)=-\dfrac{1}{25}+C=-1\Leftrightarrow C=-\dfrac{24}{25}\)
\(\Rightarrow f\left(x\right)=\dfrac{\dfrac{1}{5}xe^{5x}-\dfrac{1}{25}e^{5x}-\dfrac{24}{25}}{e^{2x}}\)
Vậy là xong rồi \(\Rightarrow f\left(1\right)=...\) , thay vô \(I=\dfrac{1}{2}f\left(1\right)-\dfrac{1}{2}.\left(-1\right)-\dfrac{1}{2}\left(\dfrac{1}{3}xe^{3x}-\dfrac{1}{9}e^{3x}\right)|^1_0\) là được nha :)
Nguyên tắc:
\(g\left(x\right).f'\left(x\right)+h\left(x\right).f\left(x\right)=p\left(x\right)\)
Đầu tiên luôn biến đổi để \(f'\left(x\right)\) đứng riêng biệt 1 mình:
\(\Rightarrow f'\left(x\right)+\dfrac{h\left(x\right)}{g\left(x\right)}.f\left(x\right)=\dfrac{p\left(x\right)}{g\left(x\right)}\) (1)
Cần thêm/bớt, nhân/chia sao cho biến về dạng:
\(\left[u\left(x\right).f\left(x\right)\right]'=q\left(x\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow f'\left(x\right).u\left(x\right)+u'\left(x\right).f\left(x\right)=q\left(x\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow f'\left(x\right)+\dfrac{u'\left(x\right)}{u\left(x\right)}.f\left(x\right)=\dfrac{q\left(x\right)}{u\left(x\right)}\)
Chỉ quan tâm vế trái, khi đó ta sẽ thấy hàm đằng trước \(f\left(x\right)\) chính là \(\dfrac{u'\left(x\right)}{u\left(x\right)}\)
Đồng nhất \(\Rightarrow\dfrac{u'\left(x\right)}{u\left(x\right)}=-2\)
Lấy nguyên hàm 2 vế \(\Rightarrow ln\left|u\left(x\right)\right|=-2x\Rightarrow u\left(x\right)=e^{-2x}\)
Do đó, ở bài toán ban đầu ta cần nhân 2 vế của (1) với \(u\left(x\right)=e^{-2x}\) nghĩa là:
\(f'\left(x\right)-2f\left(x\right)=x.e^{3x}\Leftrightarrow e^{-2x}.f'\left(x\right)-2e^{-2x}.f\left(x\right)=x.e^x\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[e^{-2x}.f\left(x\right)\right]'=x.e^x\)
Nguyên hàm 2 vế: \(\Rightarrow e^{-2x}.f\left(x\right)=\left(x-1\right)e^x+C\)
Thay \(x=0\Rightarrow1.f\left(0\right)=-1+C\Rightarrow C=0\)
\(\Rightarrow e^{-2x}.f\left(x\right)=\left(x-1\right)e^x\Rightarrow f\left(x\right)=\left(x-1\right)e^{3x}\)
\(\Rightarrow I=\int\limits^1_0\left(x-1\right)e^{3x}dx=...\)