Cho log 9 x = log 12 y = log 16 ( x + 3 y ) . Tính giá trị x y
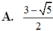
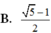
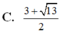
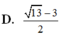
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


a) Với \(x = 1\) thì \(y = {\log _2}1 = 0\)
Với \(x = 2\) thì \(y = {\log _2}2 = 1\)
Với \(x = 4\) thì \(y = {\log _2}4 = 2\)
b) Biểu thức \(y = {\log _2}x\) có nghĩa khi x > 0.

Đáp án B
Ta có log(x + 2y) = log x + log y
<=> log 2 (x+2y) = log 2xy
<=> 2 (x+2y) = 2xy (*).
Đ ặ t a = x > 0 b = 2 y > 0 , khi đó
* ⇔ 2 a + b = a b
và P = a 2 1 + b + b 2 1 + a ≥ a + b 2 a + b + 2
Lại có a b ≤ a + b 2 4 ⇒ 2 a + b ≤ a + b 2 4 ⇔ a + b ≥ 8 .
Đặt t = a + b, do đó
P ≥ f t = t 2 t + 2 .
X é t h à m s ố f t = t 2 t + 2 t r ê n [ 8 ; + ∞ )
c ó f ' t = t 2 + 2 t t + 2 2 > 0 ; ∀ ≥ 8
Suy ra f(t) là hàm số đồng biến trên [ 8 ; + ∞ )
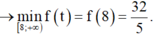
Vậy gía trị nhỏ nhất của biểu thức P là 32 5 .

a) \(log_216=4\)
b) \(log_3\dfrac{1}{27}=-3\)
c) \(log1000=3\)
d) \(9^{log_312}=144\)

ĐKXĐ: \(x\ne y\)
\(log_xy=\frac{1}{log_xy}\Leftrightarrow log_x^2y=1\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}log_xy=1\\log_xy=-1\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=y\left(l\right)\\x=\frac{1}{y}\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(log_x\left(x-\frac{1}{x}\right)=log_{x^{-1}}\left(x+\frac{1}{x}\right)\Leftrightarrow log_x\left(x-\frac{1}{x}\right)=-log_x\left(x+\frac{1}{x}\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow log_x\left(x-\frac{1}{x}\right)\left(x+\frac{1}{x}\right)=0\Leftrightarrow\left(x-\frac{1}{x}\right)\left(x+\frac{1}{x}\right)=1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2-\frac{1}{x^2}=1\Leftrightarrow x^4-x^2-1=0\Rightarrow x^2=\frac{1+\sqrt{5}}{2}\Rightarrow y^2=\frac{1}{x^2}=\frac{-1+\sqrt{5}}{2}\)
\(\Rightarrow x^2+xy+y^2=\frac{1+\sqrt{5}}{2}+1+\frac{-1+\sqrt{5}}{2}=\sqrt{5}+1\)

Khoảng giá trị của x mà đồ thị hàm số \(y=log_2x\) nằm phía trên đường thẳng y = 2 là \(\left(4;+\infty\right)\)
\(\Rightarrow\) Tập nghiệm của bất phương trình \(log_2x>2\) là \(\left(4;+\infty\right)\)

\(log_xy=log_yx=\frac{1}{log_xy}\Rightarrow\left(log_xy\right)^2=1\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}log_xy=1\\log_xy=-1\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=y\\x=\frac{1}{y}\end{matrix}\right.\)
Do \(log_x\left(x-y\right)\) tồn tại \(\Rightarrow x-y\ne0\Rightarrow x\ne y\Rightarrow x=\frac{1}{y}\)
\(log_x\left(x-y\right)=log_y\left(x+1\right)\Leftrightarrow log_x\left(x-\frac{1}{x}\right)=-log_x\left(x+1\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow log_x\left[\left(x-\frac{1}{x}\right)\left(x+1\right)\right]=0\Leftrightarrow\left(x-\frac{1}{x}\right)\left(x+1\right)=1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x^2-1\right)\left(x+1\right)=x\Leftrightarrow x^3+x^2-2x-1=0\)
Pt này nghiệm xấu, đề bài có vấn đề

a:
| x | 0,5 | 1 | 2 | 4 | 8 |
| \(y\) | -1 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 |
b:
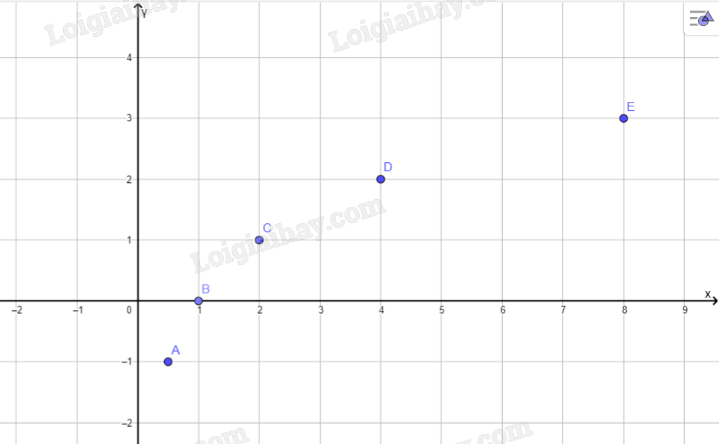
c: Tọa độ giao điểm của hàm số với trục hoành là B(2;0)
Đồ thị hàm số này ko cắt trục tung
d:
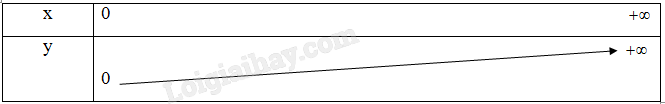
\(\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow0^+}log_2x=0\)
\(\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow+\infty}\left(log_2x\right)=+\infty\)
=>Hàm số này đồng biến trên TXĐ của nó là D=[0;+vô cực)