Rút gọn rồi tính giá trị các biểu thức sau: 1 + 3 m m - 2 m 2 - 4 m + 4 t ạ i m = 1 , 5
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.

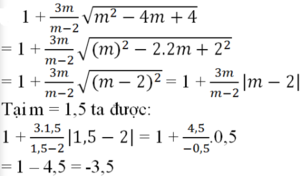

a)
Thay ta được:
.
b) Điều kiện:
+) , ta được: .
+) , ta được: .
Với . Thay vào biểu thức ta có:
Vậy giá trị biểu thức tại là .
c)
+) Với , ta được: .
+) Với , ta được: .
Vì . Thay vào biểu thức ta có: .
Vậy giá trị của biểu thức tại là .
d)
+) Với , ta có: .
+) Với , ta có: .
Vì . Thay vào biểu thức , ta có: .
Giá trị của biểu thức tại là .

Bài 1 :
a) \(M=\dfrac{1}{2}x^2y.\left(-4\right)y\)
\(\Rightarrow M=-2x^2y^2\)
Khi \(x=\sqrt[]{2};y=\sqrt[]{3}\)
\(\Rightarrow M=-2.\left(\sqrt[]{2}\right)^2.\left(\sqrt[]{3}\right)^2\)
\(\Rightarrow M=-2.2.3=-12\)
b) \(N=xy.\sqrt[]{5x^2}\)
\(\Rightarrow N=xy.\left|x\right|\sqrt[]{5}\)
\(\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}N=xy.x\sqrt[]{5}\left(x\ge0\right)\\N=xy.\left(-x\right)\sqrt[]{5}\left(x< 0\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}N=x^2y\sqrt[]{5}\left(x\ge0\right)\\N=-x^2y\sqrt[]{5}\left(x< 0\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
Khi \(x=-2< 0;y=\sqrt[]{5}\)
\(\Rightarrow N=-x^2y\sqrt[]{5}=-\left(-2\right)^2.\sqrt[]{5}.\sqrt[]{5}=-4.5=-20\)
2:
Tổng của 4 đơn thức là;
\(A=11x^2y^3+\dfrac{10}{7}x^2y^3-\dfrac{3}{7}x^2y^3-12x^2y^3=0\)
=>Khi x=-6 và y=15 thì A=0

a: \(M=\dfrac{\sqrt{x}}{\sqrt{x}-2}-\dfrac{4\sqrt{x}-4}{\sqrt{x}\left(\sqrt{x}-2\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{x-4\sqrt{x}+4}{\sqrt{x}\left(\sqrt{x}-2\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{\left(\sqrt{x}-2\right)^2}{\sqrt{x}\left(\sqrt{x}-2\right)}=\dfrac{\sqrt{x}-2}{\sqrt{x}}\)
b: Khi \(x=3+2\sqrt{2}=\left(\sqrt{2}+1\right)^2\) thì
\(M=\dfrac{\sqrt{\left(\sqrt{2}+1\right)^2}-2}{\sqrt{\left(\sqrt{2}+1\right)^2}}=\dfrac{\sqrt{2}+1-2}{\sqrt{2}+1}\)
\(=\dfrac{\sqrt{2}-1}{\sqrt{2}+1}=\left(\sqrt{2}-1\right)^2=3-2\sqrt{2}\)
c: M>0
=>\(\dfrac{\sqrt{x}-2}{\sqrt{x}}>0\)
mà \(\sqrt{x}>0\)
nên \(\sqrt{x}-2>0\)
=>\(\sqrt{x}>2\)
=>x>4

M xác định
\(\Leftrightarrow\hept{\begin{cases}x-1\ne0\\x^2-x\ne0\end{cases}\Leftrightarrow}\hept{\begin{cases}x\ne1\\x\left(x-1\right)\ne0\end{cases}\Leftrightarrow\hept{\begin{cases}x\ne1\\x\ne0;x\ne1\end{cases}}\Leftrightarrow}\hept{\begin{cases}x\ne1\\x\ne0\end{cases}}\)
Vậy ĐKXĐ của M là \(\hept{\begin{cases}x\ne1\\x\ne0\end{cases}}\)
\(M=\frac{3}{x-1}+\frac{1}{x^2-x}=\frac{3}{x-1}+\frac{1}{x\left(x-1\right)}=\frac{3x}{x\left(x-1\right)}+\frac{1}{x\left(x-1\right)}=\frac{3x+1}{x\left(x-1\right)}\)
Thay x=5 ta có:
\(M=\frac{3.5+1}{5\left(5-1\right)}=\frac{15+1}{5.4}=\frac{16}{20}=\frac{4}{5}\)
Vậy \(M=5\)tại x=5
\(M=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\frac{3x+1}{x\left(x-1\right)}=0\Leftrightarrow3x+1=0\Leftrightarrow x=-\frac{1}{3}\)( thỏa mãn đkxđ)
Vậy với \(x=-\frac{1}{3}\)thì \(M=0\)
\(M=-1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\frac{3x+1}{x\left(x-1\right)}=-1\Leftrightarrow3x+1=-x^2+x\Leftrightarrow x^2+2x+1=0\Leftrightarrow\left(x+1\right)^2=0\Leftrightarrow x=-1\)
Vậy với \(x=-1\)thì \(M=-1\)