Với giá trị nào của tham số m thì bất phương trình m + 1 x - m 2 - m + 2 > 0 có tập nghiệm là 0 ; + ∞ ?
A. m<-2
B. m=1
C. m>1
D. m<-2
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.




Đáp án A
Phương pháp: Chia cả 2 vế cho 3x, đặt  , tìm điều kiện của t.
, tìm điều kiện của t.
Đưa về bất phương trình dạng ![]()
Cách giải :
![]()

Ta có 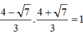
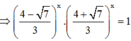
Đặt 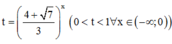 , khi đó phương trình trở thành
, khi đó phương trình trở thành
![]()
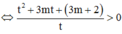
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Ta có: 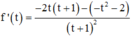
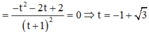
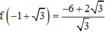
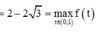
Vậy 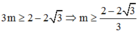

2: \(\text{Δ}=1^2-4\cdot\left(-1\right)\cdot\left(-m\right)=1-4m\)
Để bất phương trình vô nghiệm thì \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}1-4m< 0\\-1< 0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow m>\dfrac{1}{4}\)

a/ Xét pt :
\(x^2-2\left(m-1\right)+2m-5=0\)
\(\Delta'=\left(m-1\right)^2-\left(2m-5\right)=m^2-2m+1-2m+5=m^2-4m+6=\left(m-2\right)^2+2>0\forall m\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\) pt luôn có 2 nghiệm pb với mọi m
b/ Phương trình cớ 2 nghiệm trái dấu
\(\Leftrightarrow2m-5< 0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow m< \dfrac{5}{2}\)
c/ Theo định lí Vi - et ta có :
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x_1+x_2=2\left(m-1\right)\\x_1.x_2=2m-5\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(A=x_1^2+x_2^2\)
\(=\left(x_1+x_2\right)^2-2x_1.x_2\)
\(=4\left(m-1\right)^2-2\left(2m-5\right)\)
\(=4m^2-8m+4-4m+10\)
\(=4m^2-12m+14=4\left(m^2-3m+\dfrac{9}{4}\right)+5=4\left(m-\dfrac{3}{2}\right)^2+5\ge5\)
\(A_{min}=5\Leftrightarrow m=\dfrac{3}{2}\)
1, \(\Delta'=\left(m-1\right)^2-\left(2m-5\right)=m^2-4m+6=\left(m-2\right)^2+2>0\)
Vậy pt luôn có 2 nghiệm pb với mọi m
2, Vì pt có 2 nghiệm trái dấu
\(x_1x_2=\dfrac{c}{a}=2m-5< 0\Leftrightarrow m< \dfrac{5}{2}\)
3, Theo Vi et \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x_1+x_2=2\left(m-1\right)\\x_1x_2=2m-5\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(A=\left(x_1+x_2\right)^2-2x_1x_2=4\left(m-1\right)^2-2\left(2m-5\right)\)
\(=4m^2-12m+14=4m^2-2.2m.3+9+6\)
\(=\left(2m-3\right)^2+6\ge6\forall m\)
Dấu ''='' xảy ra khi m = 3/2
Vậy với m = 3/2 thì A đạt GTNN tại 6

a) Thay m=1 vào phương trình, ta được:
\(x^2-6\cdot x+5=0\)
a=1; b=-6; c=5
Vì a+b+c=0 nên phương trình có hai nghiệm phân biệt là:
\(x_1=1;x_2=\dfrac{c}{a}=\dfrac{5}{1}=5\)
b) Ta có: \(x^2-\left(m+5\right)x-m+6=0\)
a=1; b=-m-5; c=-m+6
\(\Delta=b^2-4ac\)
\(=\left(-m-5\right)^2-4\cdot1\cdot\left(-m+6\right)\)
\(=\left(m+5\right)^2-4\left(-m+6\right)\)
\(=m^2+10m+25+4m-24\)
\(=m^2+14m+1\)
\(=m^2+14m+49-48\)
\(=\left(m+7\right)^2-48\)
Để phương trình có hai nghiệm phân biệt thì \(\left(m+7\right)^2\ge48\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}m+7\ge4\sqrt{3}\\m+7\le-4\sqrt{3}\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}m\ge4\sqrt{3}-7\\m\le-4\sqrt{3}-7\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vì x1,x2 là hai nghiệm của phương trình (1) nên ta có:
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x_1^2-\left(m+5\right)x_1-m+6=0\\x_2^2-\left(m+5\right)x_2-m+6=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x_1^2=\left(m+5\right)x_1+m-6\\x_2^2=\left(m+5\right)x_2+m-6\end{matrix}\right.\)
Ta có: \(x_1^2+x_1\cdot x_2^2=24\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(m+5\right)x_1+m-6+x_1\cdot\left[\left(m+5\right)x_2+m-6\right]=24\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(m+5\right)x_1+m-6+\left(m+5\right)\cdot x_1x_2+x_1\left(m-6\right)=24\)
Xin lỗi bạn, đến đây mình thua
a, khi m=1
\(=>x^2-6x+5=0\)
\(=>a+b+c=0=>\left[{}\begin{matrix}x1=1\\x2=5\end{matrix}\right.\)
b,\(\Delta=\left[-\left(m+5\right)\right]^2-4\left(-m+6\right)=m^2+10m+25+4m-24\)
\(=m^2+14m+1=m^2+2.7m+49-48\)\(=\left(m+7\right)^2-48\)
pt (1) có nghiệm \(< =>\left(m+7\right)^2-48\ge0\)
\(< =>\left[{}\begin{matrix}m\ge-7+4\sqrt{3}\\m\le-7-4\sqrt{3}\end{matrix}\right.\)
theo vi ét \(=>\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x1+x2=m+5\\x1x2=-m+6\end{matrix}\right.\)
tui nghĩ là đề thế này \(x1^2x2+x1x2^2=24=>x1x2\left(x1+x2\right)=24\)
\(=>\left(6-m\right)\left(m+5\right)=24\)
\(< =>-m^2-5m+6m+30-24=0\)
\(< =>-m^2+m+6=0\)
\(\Delta=1^2-4\left(-1\right).6=25>0\)
\(=>\left[{}\begin{matrix}m1=\dfrac{-1+\sqrt{25}}{2\left(-1\right)}=-2\left(loai\right)\\m2=\dfrac{-1-\sqrt{25}}{2\left(-1\right)}=3\left(tm\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)

Đáp án B
Đặt t = 2x > 1
PT
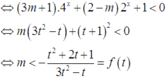
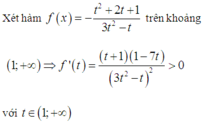
Dựa vào bảng biến thiên, suy ra m < -2