Cho ∫ 1 2 d x x 2 + 5 x + 6 = a ln 2 + b ln 3 + c ln 5 với a, b, c là các số nguyên. Mệnh đề nào dưới đây đúng?
A. a+b+c = 4
B. a+b+c = 3
C. a+b+c=2
D. a+b+c = 6
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.

a) Bất phương trình đã cho tương đương với hệ sau:
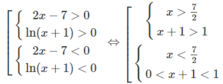
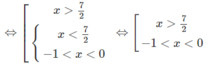
Vậy tập nghiệm là (−1;0) ∪ (7/2; + ∞ )
b) Tương tự câu a), tập nghiệm là (1/10; 5)
c) Đặt t = log 2 x , ta có bất phương trình 2 t 3 + 5 t 2 + t – 2 ≥ 0 hay (t + 2)(2 t 2 + t − 1) ≥ 0 có nghiệm −2 ≤ t ≤ −1 hoặc t ≥ 1/2
Suy ra 1/4 ≤ x ≤ 1/2 hoặc x ≥ 2
Vậy tập nghiệm của bất phương trình đã cho là: [1/4; 1/2] ∪ [ 2 ; + ∞ )
d) Bất phương trình đã cho tương đương với hệ:
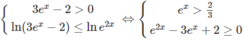
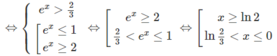
Vậy tập nghiệm là (ln(2/3); 0] ∪ [ln2; + ∞ )

a) \(\int\dfrac{2dx}{x^2-5x}=\int\left(\dfrac{-2}{5x}+\dfrac{2}{5\left(x-5\right)}\right)dx=-\dfrac{2}{5}ln\left|x\right|+\dfrac{2}{5}ln\left|x-5\right|+C\)
\(\Rightarrow A=-\dfrac{2}{5};B=\dfrac{2}{5}\Rightarrow2A-3B=-2\)
b) \(\int\dfrac{x^3-1}{x+1}dx=\int\dfrac{x^3+1-2}{x+1}dx=\int\left(x^2-x+1-\dfrac{2}{x+1}\right)dx=\dfrac{1}{3}x^3-\dfrac{1}{2}x^2+x-2ln\left|x+1\right|+C\)
\(\Rightarrow A=\dfrac{1}{3};B=\dfrac{1}{2};E=-2\Rightarrow A-B+E=-\dfrac{13}{6}\)

a) Điều kiện: \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}4x+2>0\\x-1>0\\x>0\end{matrix}\right.\)
Hay là: \(x>1\)
Khi đó biến đổi pương trình như sau:
\(\ln\dfrac{4x+2}{x-1}=\ln x\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{4x+2}{x-1}=x\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4x+2=x\left(x-1\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2-5x-2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x_1=\dfrac{5+\sqrt{33}}{2}\\x_2=\dfrac{5-\sqrt{33}}{2}\left(loại\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy nghiệm của phương trình là: \(x=\dfrac{5+\sqrt{33}}{2}\)
b) Điều kiện: \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}3x+1>0\\x>0\end{matrix}\right.\)
Hay là: \(x>0\)
Biến đổi phương trình như sau:
\(\log_2\left(3x+1\right)\log_3x-2\log_2\left(3x+1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\log_2\left(3x+1\right)\left(\log_3x-2\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}\log_2\left(3x+1\right)=0\\\log_3x=2\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}3x+1=2^0\\x=3^2\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=0\left(loại\right)\\x=9\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy nghiệm là x = 9.

\(a,y'=8x^3-9x^2+10x\\ \Rightarrow y''=24x^2-18x+10\\ b,y'=\dfrac{2}{\left(3-x\right)^2}\\ \Rightarrow y''=\dfrac{4}{\left(3-x\right)^3}\)
\(c,y'=2cos2xcosx-sin2xsinx\\ \Rightarrow y''=-5sin\left(2x\right)cos\left(x\right)-4cos\left(2x\right)sin\left(x\right)\\ d,y'=-2e^{-2x+3}\\ \Rightarrow y''=4e^{-2x+3}\)

`a)TXĐ:R\\{1;1/3}`
`y'=[-4(6x-4)]/[(3x^2-4x+1)^5]`
`b)TXĐ:R`
`y'=2x. 3^[x^2-1] ln 3-e^[-x+1]`
`c)TXĐ: (4;+oo)`
`y'=[2x-4]/[x^2-4x]+2/[(2x-1).ln 3]`
`d)TXĐ:(0;+oo)`
`y'=ln x+2/[(x+1)^2].2^[[x-1]/[x+1]].ln 2`
`e)TXĐ:(-oo;-1)uu(1;+oo)`
`y'=-7x^[-8]-[2x]/[x^2-1]`
Lời giải:
a.
$y'=-4(3x^2-4x+1)^{-5}(3x^2-4x+1)'$
$=-4(3x^2-4x+1)^{-5}(6x-4)$
$=-8(3x-2)(3x^2-4x+1)^{-5}$
b.
$y'=(3^{x^2-1})'+(e^{-x+1})'$
$=(x^2-1)'3^{x^2-1}\ln 3 + (-x+1)'e^{-x+1}$
$=2x.3^{x^2-1}.\ln 3 -e^{-x+1}$
c.
$y'=\frac{(x^2-4x)'}{x^2-4x}+\frac{(2x-1)'}{(2x-1)\ln 3}$
$=\frac{2x-4}{x^2-4x}+\frac{2}{(2x-1)\ln 3}$
d.
\(y'=(x\ln x)'+(2^{\frac{x-1}{x+1}})'=x(\ln x)'+x'\ln x+(\frac{x-1}{x+1})'.2^{\frac{x-1}{x+1}}\ln 2\)
\(=x.\frac{1}{x}+\ln x+\frac{2}{(x+1)^2}.2^{\frac{x-1}{x+1}}\ln 2\\ =1+\ln x+\frac{2^{\frac{2x}{x+1}}\ln 2}{(x+1)^2}\)
e.
\(y'=-7x^{-8}-\frac{(x^2-1)'}{x^2-1}=-7x^{-8}-\frac{2x}{x^2-1}\)

d) Điều kiện \(\begin{cases}x\ne0\\\log_2\left|x\right|\ge0\end{cases}\)\(\Leftrightarrow\left|x\right|\ge\)1
Phương trình đã cho tương đương với :
\(\log_2\left|x\right|^{\frac{1}{2}}-4\sqrt{\log_{2^2}\left|x\right|}-5=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\frac{1}{2}\log_2\left|x\right|-4\sqrt{\frac{1}{4}\log_2\left|x\right|}-5=0\)
Đặt \(t=\sqrt{\frac{1}{2}\log_2\left|x\right|}\) \(\left(t\ge0\right)\) thì phương trình trở thành :
\(t^2-4t-5=0\) hay t=-1 V t=5
Do \(t\ge0\) nên t=5
\(\Rightarrow\frac{1}{2}\log_2\left|x\right|=25\Leftrightarrow\log_2\left|x\right|=50\Leftrightarrow\left|x\right|=2^{50}\) Thỏa mãn
Vậy \(x=\pm2^{50}\) là nghiệm của phương trình
c) Điều kiện x>0. Phương trình đã cho tương đương với :
\(x^{lg^2x^2-3lgx-\frac{9}{2}}=\left(10^{lgx}\right)^{-2}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow lg^2x^2-3lgx-\frac{9}{2}=-2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow8lg^2x-6lgx-5=0\)
Đặt \(t=lgx\left(t\in R\right)\) thì phương trình trở thành
\(8t^2-6t-5=0\) hay\(t=-\frac{1}{2}\) V \(t=\frac{5}{4}\)
Với \(t=-\frac{1}{2}\) thì \(lgx=-\frac{1}{2}\Leftrightarrow x=\frac{1}{\sqrt{10}}\)
Với \(t=\frac{5}{4}\) thì \(lgx=\frac{5}{4}\Leftrightarrow x=\sqrt[4]{10^5}\)
Vậy phương trình đã cho có nghiệm \(x=\sqrt[4]{10^5}\) và \(x=\frac{1}{\sqrt{10}}\)

a, ĐK: \(x+1>0\Leftrightarrow x>-1\)
\(log\left(x+1\right)=2\\ \Leftrightarrow x+1=10^2\\ \Leftrightarrow x+1=100\\ \Leftrightarrow x=99\left(tm\right)\)
b, ĐK: \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x-3>0\\x>0\end{matrix}\right.\Rightarrow x>3\)
\(2log_4x+log_2\left(x-3\right)=2\\ \Leftrightarrow log_2x+log_2\left(x-3\right)=2\\ \Leftrightarrow log_2\left(x^2-3x\right)=2\\ \Leftrightarrow x^2-3x=4\\ \Leftrightarrow x^2-3x-4=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(x+1\right)\left(x-4\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=-1\left(ktm\right)\\x=4\left(tm\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
c, ĐK: \(x>1\)
\(lnx+ln\left(x-1\right)=ln4x\\ \Leftrightarrow ln\left[x\left(x-1\right)\right]-ln4x=0\\ \Leftrightarrow ln\left(\dfrac{x-1}{4}\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\dfrac{x-1}{4}=1\\ \Leftrightarrow x-1=4\\ \Leftrightarrow x=5\left(tm\right)\)
d, ĐK: \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x^2-3x+2>0\\2x-4>0\end{matrix}\right.\Rightarrow x>2\)
\(log_3\left(x^2-3x+2\right)=log_3\left(2x-4\right)\\ \Leftrightarrow x^2-3x+2=2x-4\\ \Leftrightarrow x^2-5x+6=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(x-2\right)\left(x-3\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=2\left(ktm\right)\\x=3\left(tm\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
Đáp án C