Giải bất phương trình sau: x − 1 12 + x − 6 7 > x + 12 25 + x + 14 27
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


\(a,\dfrac{x-3}{x}=\dfrac{x-3}{x+3}\)\(\left(đk:x\ne0,-3\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{x-3}{x}-\dfrac{x-3}{x+3}=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{\left(x-3\right)\left(x+3\right)-x\left(x-3\right)}{x\left(x+3\right)}=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2-9-x^2+3x=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3x-9=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3x=9\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=3\left(n\right)\)
Vậy \(S=\left\{3\right\}\)
\(b,\dfrac{4x-3}{4}>\dfrac{3x-5}{3}-\dfrac{2x-7}{12}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{4x-3}{4}-\dfrac{3x-5}{3}+\dfrac{2x-7}{12}>0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{3\left(4x-3\right)-4\left(3x-5\right)+2x-7}{12}>0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow12x-9-12x+20+2x-7>0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x+4>0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x>-4\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x>-2\)

a: ĐKXĐ: x>=3
Sửa đề: \(\sqrt{4x-12}-\sqrt{9x-27}+\sqrt{\dfrac{25x-75}{4}}-3=0\)
=>\(2\sqrt{x-3}-3\sqrt{x-3}+\dfrac{5}{2}\sqrt{x-3}-3=0\)
=>\(\dfrac{3}{2}\sqrt{x-3}=3\)
=>\(\sqrt{x-3}=2\)
=>x-3=4
=>x=7(nhận)
b: ĐKXĐ: x>=0
\(\dfrac{\sqrt{x}-2}{\sqrt{x}+1}< =-\dfrac{3}{4}\)
=>\(\dfrac{\sqrt{x}-2}{\sqrt{x}+1}+\dfrac{3}{4}< =0\)
=>\(\dfrac{4\sqrt{x}-8+3\sqrt{x}+3}{4\left(\sqrt{x}+1\right)}< =0\)
=>\(7\sqrt{x}-5< =0\)
=>\(\sqrt{x}< =\dfrac{5}{7}\)
=>0<=x<=25/49
c: ĐKXĐ: x>=5
\(\sqrt{9x-45}-14\sqrt{\dfrac{x-5}{49}}+\dfrac{1}{4}\sqrt{4x-20}=3\)
=>\(3\sqrt{x-5}-14\cdot\dfrac{\sqrt{x-5}}{7}+\dfrac{1}{4}\cdot2\cdot\sqrt{x-5}=3\)
=>\(\dfrac{3}{2}\sqrt{x-5}=3\)
=>\(\sqrt{x-5}=2\)
=>x-5=4
=>x=9(nhận)

\(\dfrac{x^2-26}{10}+\dfrac{x^2-25}{11}\ge\dfrac{x^2-24}{12}+\dfrac{x^2-23}{13}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(\dfrac{x^2-26}{10}-1\right)+\left(\dfrac{x^2-25}{11}-1\right)\ge\left(\dfrac{x^2-24}{12}-1\right)+\left(\dfrac{x^2-23}{13}-1\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{x^2-36}{10}+\dfrac{x^2-36}{11}\ge\dfrac{x^2-36}{12}+\dfrac{x^2-36}{13}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{x^2-36}{10}+\dfrac{x^2-36}{11}-\dfrac{x^2-36}{12}-\dfrac{x^2-36}{13}\ge0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x^2-36\right)\left(\dfrac{1}{10}+\dfrac{1}{11}-\dfrac{1}{12}-\dfrac{1}{13}\right)\ge0\)
Vì \(\dfrac{1}{10}+\dfrac{1}{11}-\dfrac{1}{12}-\dfrac{1}{13}>0\Rightarrow x^2-36\ge0\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x\le-6\\x\ge6\end{matrix}\right.\)
Bất phương trình đó tương đương với:
\(\left(\dfrac{x^2-26}{10}-1\right)+\left(\dfrac{x^2-25}{11}-1\right)\ge\left(\dfrac{x^2-24}{12}-1\right)+\left(\dfrac{x^2-23}{13}-1\right)\)
⇔ \(\dfrac{x^2-36}{10}+\dfrac{x^2-36}{11}\ge\dfrac{x^2-36}{12}+\dfrac{x^2-36}{13}\)
⇔ \(\dfrac{x^2-36}{10}+\dfrac{x^2-36}{11}-\dfrac{x^2-36}{12}-\dfrac{x^2-36}{13}\ge0\)
⇔ \(\left(x^2-36\right)\left(\dfrac{1}{10}+\dfrac{1}{11}-\dfrac{1}{12}-\dfrac{1}{13}\right)\ge0\)
+)Vì \(\dfrac{1}{10}>\dfrac{1}{11}>\dfrac{1}{12}>\dfrac{1}{13}\) nên \(\dfrac{1}{10}+\dfrac{1}{11}-\dfrac{1}{12}-\dfrac{1}{13}>0\)
⇔ \(x^2-36\ge0\)
⇔ \(x^2\ge36\)
⇔ \(\sqrt{x^2}\ge6\)
⇔ \(\left|x\right|\ge6\)
⇔ \(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x\ge6\\x\le-6\end{matrix}\right.\)
➤ Vậy \(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x\ge6\\x\le-6\end{matrix}\right.\)

1:
a: =>3x=6
=>x=2
b: =>4x=16
=>x=4
c: =>4x-6=9-x
=>5x=15
=>x=3
d: =>7x-12=x+6
=>6x=18
=>x=3
2:
a: =>2x<=-8
=>x<=-4
b: =>x+5<0
=>x<-5
c: =>2x>8
=>x>4

x - 1 2 + x - 1 4 = 1 - 2 x - 1 2 ⇔ x - 1 2 + x - 1 4 = 1 - 2 x - 2 3
⇔ 6(x – 1) + 3(x – 1) = 12 – 4(2x – 2)
⇔ 6x – 6 + 3x – 3 = 12 – 8x + 8 ⇔ 6x + 3x + 8x = 12 + 8 + 6 + 3
⇔ 17x = 29 ⇔ x = 29/17
Phương trình có nghiệm x = 29/17

a: =>x-2+2=x^2+2x
=>x^2+2x=x
=>x^2+x=0
=>x(x+1)=0
=>x=0(loại) hoặc x=-1(nhận)
b: =>-9(5x-8)+4(7x-12)=-6(x+18)
=>-45x+72+28x-48=-6x-108
=>-17x+24=-6x-108
=>-11x=-132
=>x=12

\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\dfrac{12}{x-1}+\dfrac{7}{y+3}=19\\\dfrac{2x+6}{x-1}+\dfrac{3y+14}{y+3}=18\end{matrix}\right.\left(x\ne1;y\ne-3\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\dfrac{12}{x-1}+\dfrac{7}{y+3}=19\\\dfrac{2x-2+8}{x-1}+\dfrac{3y+9+5}{y+3}=18\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\dfrac{12}{x-1}+\dfrac{7}{y+3}=19\\\dfrac{2\left(x-1\right)}{x-1}+\dfrac{8}{x-1}+\dfrac{3\left(y+3\right)}{y+3}+\dfrac{5}{y+3}=18\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\dfrac{12}{x-1}+\dfrac{7}{y+3}=19\\2+\dfrac{8}{x-1}+3+\dfrac{5}{y+3}=18\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\dfrac{12}{x-1}+\dfrac{7}{y+3}=19\\\dfrac{8}{x-1}+\dfrac{5}{y+3}=13\end{matrix}\right.\) (I)
Đặt: \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}u=\dfrac{1}{x-1}\\v=\dfrac{1}{y+3}\end{matrix}\right.\)
Hệ (I) trở thành:
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}12u+7v=19\\8u+5v=13\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}24u+14v=38\\24u+15v=39\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}12u+7=19\\v=1\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}12u=12\\v=1\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}u=1\\v=1\end{matrix}\right.\)
Trả ẩn phụ:
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\dfrac{1}{x-1}=1\\\dfrac{1}{y+3}=1\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x-1=1\\y+3=1\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=2\\y=-2\end{matrix}\right.\left(tm\right)\)
Vậy hệ pt có 1 cặp nghiệm duy nhất là: (2;-2)
⎪ ⎪⎨⎪ ⎪ ⎪⎩12x−1+7y+3=192x+6x−1+3y+14y+3=18(x≠1;y≠−3){12�−1+7�+3=192�+6�−1+3�+14�+3=18(�≠1;�≠−3)
⇔⎧⎪ ⎪ ⎪⎨⎪ ⎪ ⎪⎩12x−1+7y+3=192x−2+8x−1+3y+9+5y+3=18⇔{12�−1+7�+3=192�−2+8�−1+3�+9+5�+3=18
⇔⎧⎪ ⎪ ⎪⎨⎪ ⎪ ⎪⎩12x−1+7y+3=192(x−1)x−1+8x−1+3(y+3)y+3+5y+3=18⇔{12�−1+7�+3=192(�−1)�−1+8�−1+3(�+3)�+3+5�+3=18
⇔⎧⎪ ⎪ ⎪⎨⎪ ⎪ ⎪⎩12x−1+7y+3=192+8x−1+3+5y+3=18⇔{12�−1+7�+3=192+8�−1+3+5�+3=18
⇔⎧⎪ ⎪ ⎪⎨⎪ ⎪ ⎪⎩12x−1+7y+3=198x−1+5y+3=13⇔{12�−1+7�+3=198�−1+5�+3=13 (I)
Đặt: ⎧⎪ ⎪ ⎪⎨⎪ ⎪ ⎪⎩u=1x−1v=1y+3{�=1�−1�=1�+3
Hệ (I) trở thành:
⇔{12u+7v=198u+5v=13⇔{12�+7�=198�+5�=13
⇔{24u+14v=3824u+15v=39⇔{24�+14�=3824�+15�=39
⇔{12u+7=19v=1⇔{12�+7=19�=1
⇔{12u=12v=1⇔{12�=12�=1
⇔{u=1v=1⇔{�=1�=1
Trả ẩn phụ:
⇔⎧⎪ ⎪ ⎪⎨⎪ ⎪ ⎪⎩1x−1=11y+3=1⇔{1�−1=11�+3=1
⇔{x−1=1y+3=1⇔{�−1=1�+3=1
⇔{x=2y=−2(tm)⇔{�=2�=−2(��)
Vậy hệ pt có 1 cặp nghiệm duy nhất là: (2;-2)


Bài 2:
a: =>2x^2-4x+1=x^2+x+5
=>x^2-5x-4=0
=>\(x=\dfrac{5\pm\sqrt{41}}{2}\)
b: =>11x^2-14x-12=3x^2+4x-7
=>8x^2-18x-5=0
=>x=5/2 hoặc x=-1/4
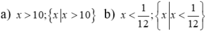
Đáp số: x > 13.