Tính giới hạn hàm số . Chọn kết quả đúng
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.

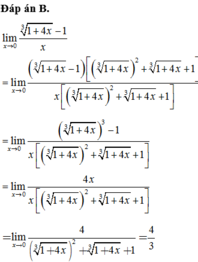

a) \(\sin \left( {x + h} \right) - \sin x = 2\cos \frac{{2x + h}}{2}.\sin \frac{h}{2}\)
b) Với \({x_0}\) bất kì, ta có:
\(\begin{array}{l}f'\left( {{x_0}} \right) = \mathop {\lim }\limits_{x \to {x_0}} \frac{{f\left( x \right) - f\left( {{x_0}} \right)}}{{x - {x_0}}} = \mathop {\lim }\limits_{x \to {x_0}} \frac{{\sin x - \sin {x_0}}}{{x - {x_0}}}\\ = \mathop {\lim }\limits_{x \to {x_0}} \frac{{2\cos \frac{{x + {x_0}}}{2}.\sin \frac{{x - {x_0}}}{2}}}{{x - {x_0}}} = \mathop {\lim }\limits_{x \to {x_0}} \frac{{\sin \frac{{x - {x_0}}}{2}}}{{\frac{{x - {x_0}}}{2}}}.\mathop {\lim }\limits_{x \to {x_0}} \cos \frac{{x + {x_0}}}{2} = \cos {x_0}\end{array}\)
Vậy hàm số y = sin x có đạo hàm là hàm số \(y' = \cos x\)

1: \(-1< =cosx< =1\)
=>\(-3< =3\cdot cosx< =3\)
=>\(y\in\left[-3;3\right]\)
2:
TXĐ là D=R
3: \(L=\lim\limits\dfrac{-3n^3+n^2}{2n^3+5n-2}\)
\(=\lim\limits\dfrac{-3+\dfrac{1}{n}}{2+\dfrac{5}{n^2}-\dfrac{2}{n^3}}=-\dfrac{3}{2}\)
4:
\(L=lim\left(3n^2+5n-3\right)\)
\(=\lim\limits\left[n^2\left(3+\dfrac{5}{n}-\dfrac{3}{n^2}\right)\right]\)
\(=+\infty\) vì \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}lim\left(n^2\right)=+\infty\\\lim\limits\left(3+\dfrac{5}{n}-\dfrac{3}{n^2}\right)=3>0\end{matrix}\right.\)
5:
\(\lim\limits_{n\rightarrow+\infty}n^3-2n^2+3n-4\)
\(=\lim\limits_{n\rightarrow+\infty}n^3\left(1-\dfrac{2}{n}+\dfrac{3}{n^2}-\dfrac{4}{n^3}\right)\)
\(=+\infty\) vì \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\lim\limits_{n\rightarrow+\infty}n^3=+\infty\\\lim\limits_{n\rightarrow+\infty}1-\dfrac{2}{n}+\dfrac{3}{n^2}-\dfrac{4}{n^3}=1>0\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(1,y=3cosx\)
\(+TXD\) \(D=R\)
Có \(-1\le cosx\le1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-3\le3cosx\le3\)
Vậy có tập giá trị \(T=\left[-3;3\right]\)
\(2,y=cosx\)
\(TXD\) \(D=R\)
\(3,L=lim\dfrac{n^2-3n^3}{2n^3+5n-2}=lim\dfrac{\dfrac{1}{n}-3}{2+\dfrac{5}{n^2}-\dfrac{2}{n^3}}\)(chia cả tử và mẫu cho \(n^3\))
\(=\dfrac{lim\dfrac{1}{n}-lim3}{lim2+5lim\dfrac{1}{n^2}-2lim\dfrac{1}{n^3}}=\dfrac{0-3}{2+5.0-2.0}=-\dfrac{3}{2}\)
\(4,L=lim\left(3n^2+5n-3\right)\\ =lim\left(3+\dfrac{5}{n}-\dfrac{3}{n^2}\right)\\ =lim3+5lim\dfrac{1}{n}-3lim\dfrac{1}{n^2}\\ =3\)
\(5,\lim\limits_{n\rightarrow+\infty}\left(n^3-2n^2+3n-4\right)\\ =lim\left(1-\dfrac{2}{n}+\dfrac{3}{n^2}-\dfrac{4}{n^3}\right)\\ =lim1-0\\ =1\)

1: \(\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow4}\dfrac{1-x}{\left(x-4\right)^2}=-\infty\)
vì \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow4}1-x=1-4=-3< 0\\\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow4}\left(x-4\right)^2=\left(4-4\right)^2=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
2: \(\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow3^+}\dfrac{2x-1}{x-3}=+\infty\)
vì \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow3^+}2x-1=2\cdot3-1=5>0\\\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow3^+}x-3=3-3>0\end{matrix}\right.\) và x-3>0
3: \(\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow2^+}\dfrac{-2x+1}{x+2}\)
\(=\dfrac{-2\cdot2+1}{2+2}=\dfrac{-3}{4}\)
4: \(\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow1^-}\dfrac{3x-1}{x+1}=\dfrac{3\cdot1-1}{1+1}=\dfrac{2}{2}=1\)

a. Áp dụng công thức L'Hospital:
\(\lim\limits_{x\to 0}\frac{\sqrt{x+1}-\sqrt{1-x}}{\sqrt[3]{x+1}-\sqrt{1-x}}=\lim\limits_{x\to 0}\frac{\frac{1}{2}(x+1)^{\frac{-1}{2}}+\frac{1}{2}(1-x)^{\frac{-1}{2}}}{\frac{1}{3}(x+1)^{\frac{-2}{3}}+\frac{1}{2}(1-x)^{\frac{-1}{2}}}=\frac{1}{\frac{5}{6}}=\frac{6}{5}\)
b.
\(\lim\limits_{x\to 0}(\frac{1}{x}-\frac{1}{x^2})=\lim\limits_{x\to 0}\frac{x-1}{x^2}=-\infty\)
c. Áp dụng quy tắc L'Hospital:
\(\lim\limits_{x\to +\infty}\frac{x^4-x^3+11}{2x-7}=\lim\limits_{x\to +\infty}\frac{4x^3-3x^2}{2}=+\infty \)
d.
\(\lim\limits_{x\to 5}\frac{7}{(x-1)^2}.\frac{2x+1}{2x-3}=\frac{7}{(5-1)^2}.\frac{2.5+11}{2.5-3}=\frac{11}{16}\)

\(=\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow0}\dfrac{2\left(\sqrt[]{2x+1}-1\right)+2-\sqrt[3]{x^2+x+8}}{x}\)
\(=\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow0}\dfrac{\dfrac{2.2x}{\sqrt[]{2x+1}+1}-\dfrac{x\left(x+1\right)}{\sqrt[3]{\left(x^2+x+8\right)^2}+2\sqrt[3]{x^2+x+8}+4}}{x}\)
\(=\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow0}\left(\dfrac{4}{\sqrt[]{2x+1}+1}-\dfrac{x+1}{\sqrt[3]{\left(x^2+x+8\right)^2}+2\sqrt[3]{x^2+x+8}+4}\right)\)
\(=\dfrac{23}{12}\)

\(\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow2}\frac{\left(x-2\right)\left(x+2\right)}{x-2}=\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow2}\left(x+2\right)=4\)

\(\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow0}\dfrac{\sqrt{x^2+1}-\left(x+1\right)}{2x^2-x}=\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow0}\dfrac{\left(\sqrt{x^2+1}-\left(x+1\right)\right)\left(\sqrt{x^2+1}+x+1\right)}{x\left(2x-1\right)\left(\sqrt{x^2+1}+x+1\right)}\)
\(=\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow0}\dfrac{-2x}{x\left(2x-1\right)\left(\sqrt{x^2+1}+x+1\right)}\)
\(=\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow0}\dfrac{-2}{\left(2x-1\right)\left(\sqrt{x^2+1}+x+1\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{-2}{\left(0-1\right)\left(\sqrt{1}+1\right)}=1\)
a. \(\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow2}\dfrac{x-2}{x^2-4}=\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow2}\dfrac{x-2}{\left(x-2\right)\left(x+2\right)}=\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow2}\dfrac{1}{x+2}=\dfrac{1}{4}\)
b. \(\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow3^-}\dfrac{x+3}{x-3}=\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow3^-}\dfrac{-x-3}{3-x}\)
Do \(\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow3^-}\left(-x-3\right)=-6< 0\)
\(\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow3^-}\left(3-x\right)=0\) và \(3-x>0;\forall x< 3\)
\(\Rightarrow\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow3^-}\dfrac{-x-3}{3-x}=-\infty\)