gải phương trình sau: (x-3)3-2(x-1)=x.(x-2)2-5x2
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


Ta có: \(\dfrac{5}{-x^2+5x-6}+\dfrac{x+3}{2-x}=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{-5}{\left(x-2\right)\left(x-3\right)}-\dfrac{x^2-9}{\left(x-2\right)\left(x-3\right)}=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-5-x^2+9=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=-2\)

Đáp án: D
2 - x = x nên x > 0 kết hợp đkxđ x ≤ 2 khi đó phương trình có nghiệm thỏa mãn 0 < x ≤ 2 ⇒ a sai.
7 - 4 3 = 2 - 3 . ⇒ b sai
2 x - 1 x - 2 = x + 1 x - 2 ⇒ 2x – 1 = x + 1 ( x ≠ 2 ) ⇔ x = 2 (loại).
Vậy phương trình vô nghiệm. ⇒ c đúng.
5 x 2 - 4 5 x + 3 < - 1 ⇔ 5 x 2 - 4 5 x + 4 < 0 ⇔ 5 x - 2 2 < 0 (vô lí) ⇒ d sai.
có 1 mệnh đề đúng.

Lời giải:
$\Delta'=(\sqrt{3}-1)^2+4\sqrt{3}=(\sqrt{3}+1)^2$
Do đó pt có 2 nghiệm:
\(x_1=\frac{-b'+\sqrt{\Delta'}}{a}=\frac{1-\sqrt{3}+\sqrt{3}+1}{\sqrt{3}}=\frac{2}{\sqrt{3}}\)
\(x_2=\frac{-b'-\sqrt{\Delta'}}{a}=\frac{1-\sqrt{3}-\sqrt{3}-1}{\sqrt{3}}=-2\)

1/ \(7x-5=13-5x\)
\(\Leftrightarrow12x=18\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=\dfrac{3}{2}\)
Vậy: \(S=\left\{\dfrac{3}{2}\right\}\)
==========
2/ \(19+3x=5-18x\)
\(\Leftrightarrow21x=-14\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=-\dfrac{2}{3}\)
Vậy: \(S=\left\{-\dfrac{2}{3}\right\}\)
==========
3/ \(x^2+2x-4=-12+3x+x^2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-x=-8\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=8\)
Vậy: \(S=\left\{8\right\}\)
===========
4/ \(-\left(x+5\right)=3\left(x-5\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-x-5=3x-15\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-4x=-10\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=\dfrac{5}{2}\)
Vậy: \(S=\left\{\dfrac{5}{2}\right\}\)
==========
5/ \(3\left(x+4\right)=\left(-x+4\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3x+12=-x+4\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4x=-8\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=-2\)
Vậy: \(S=\left\{-2\right\}\)
[----------]
1. \(7x-5=13-5x\) \(\Leftrightarrow12x=18\Leftrightarrow x=\dfrac{3}{2}\)
2. \(19+3x=5-18x\Leftrightarrow21x=-14\Leftrightarrow x=-\dfrac{2}{3}\)
3. \(x^2+2x-4=-12+3x+x^2\Leftrightarrow-x=-8\Leftrightarrow x=8\)
4. \(-\left(x+5\right)=3\left(x-5\right)\Leftrightarrow-x-5=3x-15\Leftrightarrow4x=10\Leftrightarrow x=\dfrac{5}{2}\)
5. \(3\left(x+4\right)=-x+4\Leftrightarrow3x+12=-x+4\Leftrightarrow4x=-8\Leftrightarrow x=-2\)

Bạn xem lại đề
Dưới căn là \(\sqrt{2x^2+1}\) hay \(\sqrt{2x^2-1}\)
Nguyễn Việt Lâm Mình cũng đang thắc mắc, dường như đề bài thầy bình cho sai hay sao ấy

b) 5x(x-2000)-x+2000=0
\(\Rightarrow5x\left(x-2000\right)-\left(x-2000\right)=0\\ \Rightarrow\left(x-2000\right)\left(5x-1\right)=0\)
\(\Rightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x-2000=0\\5x-1=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=0+2000\\5x=0+1\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=2000\\5x=1\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=2000\\x=\dfrac{1}{5}\end{matrix}\right.\)

a)
5 x 2 − 3 x + 1 = 2 x + 11 ⇔ 5 x 2 − 3 x + 1 − 2 x − 11 = 0 ⇔ 5 x 2 − 5 x − 10 = 0
Có a = 5; b = -5; c = -10 ⇒ a - b + c = 0
⇒ Phương trình có hai nghiệm: x 1 = - 1 v à x 2 = - c / a = 2 .
Vậy phương trình có tập nghiệm S = {-1; 2}.
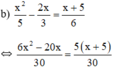
⇔ 6 x 2 − 20 x = 5 ( x + 5 ) ⇔ 6 x 2 − 20 x − 5 x − 25 = 0 ⇔ 6 x 2 − 25 x − 25 = 0
Có a = 6; b = -25; c = -25
⇒ Δ = ( - 25 ) 2 – 4 . 6 . ( - 25 ) = 1225 > 0
⇒ Phương trình có hai nghiệm
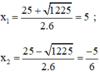
Vậy phương trình có tập nghiệm 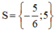
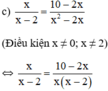
⇔ x 2 = 10 − 2 x ⇔ x 2 + 2 x − 10 = 0
Có a = 1; b = 2; c = -10 ⇒ Δ ’ = 1 2 – 1 . ( - 10 ) = 11 > 0
⇒ Phương trình có hai nghiệm
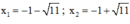
Cả hai nghiệm đều thỏa mãn điều kiện xác định.
Vậy phương trình có tập nghiệm 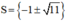
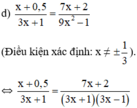
⇔ ( x + 0 , 5 ) ⋅ ( 3 x − 1 ) = 7 x + 2 ⇔ 3 x 2 + 1 , 5 x − x − 0 , 5 = 7 x + 2 ⇔ 3 x 2 − 6 , 5 x − 2 , 5 = 0
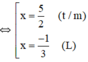
Vậy phương trình có tập nghiệm 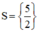
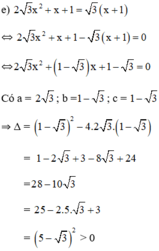
⇒ Phương trình có hai nghiệm
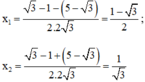
Vậy phương trình có tập nghiệm 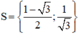
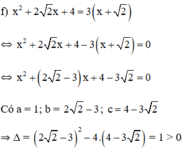
Phương trình có hai nghiệm:
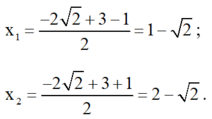
Vậy phương trình có tập nghiệm ![]()

x4+2x3-2x2+2x-3=0
=> (x4 - 1) + (2x3-2x2 )+ (2x-2)=0
=> (x - 1).(x+1).(x2 + 1) + 2x2.(x - 1) + 2.(x -1) = 0
=> (x -1). [(x+1).(x2 + 1) + 2x2 + 2] = 0
<=> (x - 1). (x3 + x + x2 + 1 + 2x2 + 2)= 0
<=> (x - 1). (x3 + x + 3x2 + 3)= 0
<=> x - 1 = 0 hoặc x3 + x + 3x2 + 3 = 0
+) x - 1 = 0 => x =1
+) x3 + x + 3x2 + 3 = 0 <=> x. (x2 + 1) + 3.(x2 + 1) = 0
<=> (x+3). (x2 +1) = 0 <=> x + 3 = 0 (vì x2 + 1 > 0 với mọi x)
<=> x = -3
Vậy pt có 2 nghiệm x = 1 ; x = -3
\(\left(x-3\right)^3-2\left(x-1\right)=x\left(x-2\right)^2-5x^2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^3-6x^2+9x-3x^2+18x-27-2x+2=x^3-4x^2+4x-5x^2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^3-9x^2+25x-25=x^3-9x^2+4x-5x^2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^3-9x^2+25x-25=x^3-9x^2+4x\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-9x^2+25x-25=-9x^2+4x\)
\(\Leftrightarrow25x-25=4x\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-25=4x-25x\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-25=-21x\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=\frac{21}{25}\)
\(Pt\Leftrightarrow x^3-1-3x^2+3x-2x+2-x^3+4x^2-4x+5x^2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow6x^2-5x+1=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=\frac{3\pm\sqrt{3}}{6}\)