Tìm m để hàm số y = -x2 + 2mx + 1 đồng biến trên \(\left(-\infty;3\right)\)
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


Hàm số \(y=-x^2+2mx+1\) có \(a=-1< 0;-\frac{b}{2a}=m\)nên đồng biến trên \(\left(-\infty;m\right)\)
Do đó để hàm số đồng biến trên khoảng \(\left(-\infty;3\right)\)thì ta phải có \(\left(-\infty;3\right)\subset\left(-\infty;m\right)\Leftrightarrow m\ge3.\)

Ta có \(y'=\frac{x^2-2mx+m^2}{\left(x-2m\right)^2},x\ne2m\)
Để y có hai khoảng đồng biến trên toàn miền xác định thì
\(y'\ge0,\forall x\ne2m\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2-4mx+m^2\ge0,\forall x\ne2m\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\Delta'\le0\Leftrightarrow4m^2-m^2\le0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3m^2\le0\Leftrightarrow m=0\)
Câu tiếp theo:
y đồng biến trên\(\left(1,\infty\right)\Leftrightarrow y'\ge0,\forall x\in\left(1,+\infty\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\hept{\begin{cases}f\left(x\right)=x^2-4mx+m^2\ge0,\forall x>1\\2m\notin\left(1,\infty\right)\end{cases}}\)
Để cj suy nghĩ mai lm tiếp=.=
rõ ràng m=0 thì đk trên thõa mãn.
Với \(m=0:\Delta'=3m^2>0\) nên ta có:
\(f\left(x\right)\ge0,\forall x>1\Leftrightarrow x_1< x_2\le1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\hept{\begin{cases}\Delta'>0\\f\left(1\right)\ge\\\frac{S}{2}-1< 0\end{cases}0}\)
\(f\left(1\right)\ge0\Leftrightarrow m^2-4m+1\ge0\Leftrightarrow m\le2-\sqrt{3}\)hay\(m\ge2+\sqrt{3}\)
\(\frac{S}{2}-1< 0\Leftrightarrow2m-1< 0\Leftrightarrow m< \frac{1}{2}\)
\(2m\notin\left(1,\infty\right)\Leftrightarrow2m\le1\Leftrightarrow m\le\frac{1}{2}\)
Vậy \(m\le2-\sqrt{3}\)là giá trị m cần tìm

\(y=\left(m-1\right)x^2-2mx+m+2\)(1)
+) Nếu \(m-1=0\Leftrightarrow m=1\)thì :
(1) \(\Leftrightarrow y=-2x+3\)là hàm số bậc nhất có hệ số góc \(-2< 0\Rightarrow\)hàm số nghịch biến trên \(R\)
=> Hàm số nghịch biến trên \(\left(-\infty;2\right)\)
Vậy khi \(m=1\)hàm số nghịch biến trên \(\left(-\infty;2\right)\)(2)
+) Nếu \(m-1\ne0\Leftrightarrow m\ne1\)thì (1) là hàm số bậc hai
(1) nghịch biến trên \(\left(-\infty;2\right)\)thì đồ thị h/s có bề lõm hướng lên trên
\(\Rightarrow\hept{\begin{cases}a=m-1>0\\-\frac{b}{2a}\ge2\end{cases}}\Leftrightarrow\hept{\begin{cases}m>1\\\frac{2m}{2\left(m-1\right)}\ge2\end{cases}}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\hept{\begin{cases}m>1\\m-2\left(m-1\right)\ge0\end{cases}}\Leftrightarrow\hept{\begin{cases}m>1\\m\le2\end{cases}}\)
\(\Rightarrow1< m\le2\)\(\Leftrightarrow\hept{\begin{cases}m>1\\m-2\left(m-1\right)\ge0\Leftrightarrow\hept{\begin{cases}m>1\\m\le2\end{cases}}\end{cases}}\)(3)
Từ (2) và (3) suy ra hàm số nghịch biến trên \(\left(-\infty;2\right)\)thì \(1\le m\le2\)

\(y'=\dfrac{2x^2-4mx-m^2+2m-1}{\left(x-m\right)^2}\)
Hàm đồng biến trên khoảng đã cho khi với mọi \(x>1\) ta có:
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}2x^2-4mx-m^2+2m-1\ge0\left(1\right)\\m\le1\end{matrix}\right.\)
Xét (1): ta có \(\Delta'=4m^2-2\left(-m^2+2m-1\right)=6m^2-4m+2>0\) ; \(\forall m\)
\(\Rightarrow\) (1) thỏa mãn khi: \(x_1< x_2\le1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\left(x_1-1\right)\left(x_2-1\right)\ge0\\\dfrac{x_1+x_2}{2}< 1\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x_1x_2-\left(x_1+x_2\right)+1\ge0\\x_1+x_2< 2\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\dfrac{-m^2+2m-1}{2}-2m+1\ge0\\2m< 2\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Rightarrow-1-\sqrt{2}\le m\le-1+\sqrt{2}\)



\(y'=3x^2-2\left(m+1\right)x-\left(2m^2-3m+2\right)\)
\(\Delta'=\left(m+1\right)^2+3\left(2m^2-3m+2\right)=7\left(m^2+m+1\right)>0\) ; \(\forall m\)
\(\Rightarrow y'=0\) luôn có 2 nghiệm phân biệt
Bài toán thỏa mãn khi: \(x_1< x_2\le2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\left(x_1-2\right)\left(x_2-2\right)\ge0\\\dfrac{x_1+x_2}{2}< 2\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x_1x_2-2\left(x_1+x_2\right)+4\ge0\\x_1+x_2< 4\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\dfrac{-\left(2m^2-3m+2\right)}{3}-\dfrac{4\left(m+1\right)}{3}+4\ge0\\\dfrac{2\left(m+1\right)}{3}< 4\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}-2m^2-m+6\ge0\\m< 5\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Leftrightarrow-2\le m\le\dfrac{3}{2}\)

\(y'=3x^2-4mx-m-1\)
Hàm đồng biến trên (0;2) khi \(\forall x\in\left(0;2\right)\) ta có:
\(y'\ge0\Leftrightarrow3x^2-4mx-m-1\ge0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3x^2-1\ge m\left(4x+1\right)\) (1)
Do \(4x+1>0\) ; \(\forall x\in\left(0;2\right)\) nên (1) tương đương:
\(m\le\dfrac{3x^2-1}{4x+1}\Leftrightarrow m\le\min\limits_{\left(0;2\right)}\dfrac{3x^2-1}{4x+1}\)
Xét hàm \(f\left(x\right)=\dfrac{3x^2-1}{4x+1}\) trên \(\left(0;2\right)\)
\(f'\left(x\right)=\dfrac{12x^2+6x+4}{\left(4x+1\right)^2}>0\Rightarrow f\left(x\right)\) đồng biến
\(\Rightarrow f\left(x\right)>f\left(0\right)=-1\Rightarrow m\le-1\)


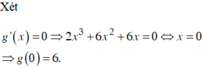
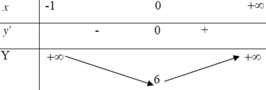
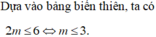
\(a=-1< 0\) ; \(-\frac{b}{2a}=m\Rightarrow\) hàm số đồng biến trên \(\left(-\infty;m\right)\)
Để hàm số đồng biến trên \(\left(-\infty;3\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow m\ge3\)
\(\left(-\infty;3\right)\) phải là m<3 chứ bạn