Giải hệ phương trình sau: \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x^3-12x=y^3-12y\\\left(x+\dfrac{1}{2}\right)^2+\left(y-\dfrac{1}{2}\right)^2=1\end{matrix}\right.\)
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


Thay \(x=\dfrac{3}{4}y\) vào phương trình dưới, ta có:
\(\dfrac{1}{2}\left(\dfrac{3}{4}y+3\right)\left(y-2\right)-\dfrac{1}{2}.\dfrac{3}{4}y^2=9\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{3}{8}y^2-\dfrac{3}{4}y+\dfrac{3}{2}y-3-\dfrac{3}{8}y^2=9\\ \Leftrightarrow\dfrac{3}{4}y=12\\ \Leftrightarrow y=18\Rightarrow x=12\)
Vậy hệ phương trình có nghiệm \(\left(x;y\right)=\left(12;18\right)\)

a) Ta có: \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\sqrt{2}x-y=3\\x+\sqrt{2}y=\sqrt{2}\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\sqrt{2}x-y=3\\\sqrt{2}x+2y=2\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}-3y=1\\x+\sqrt{2}y=\sqrt{2}\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}y=-\dfrac{1}{3}\\x=\sqrt{2}-\sqrt{2}y\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}y=-\dfrac{1}{3}\\x=\sqrt{2}-\sqrt{2}\cdot\dfrac{-1}{3}=\dfrac{4\sqrt{2}}{3}\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy: Hệ phương trình có nghiệm duy nhất là \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{4\sqrt{2}}{3}\\y=-\dfrac{1}{3}\end{matrix}\right.\)
b) Ta có: \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\dfrac{x}{2}-2y=\dfrac{3}{4}\\2x+\dfrac{y}{3}=-\dfrac{1}{3}\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}2x-8y=3\\2x+\dfrac{1}{3}y=-\dfrac{1}{3}\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}-\dfrac{25}{3}y=\dfrac{10}{3}\\2x-8y=3\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}y=-\dfrac{2}{5}\\2x=3+8y=3+8\cdot\dfrac{-2}{5}=-\dfrac{1}{5}\end{matrix}\right.\)
hay \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=-\dfrac{1}{10}\\y=-\dfrac{2}{5}\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy: Hệ phương trình có nghiệm duy nhất là \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=-\dfrac{1}{10}\\y=-\dfrac{2}{5}\end{matrix}\right.\)
c) Ta có: \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\dfrac{2x-3y}{4}-\dfrac{x+y-1}{5}=2x-y-1\\\dfrac{x+y-1}{3}+\dfrac{4x-y-2}{4}=\dfrac{2x-y-3}{6}\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\dfrac{5\left(2x-3y\right)}{20}-\dfrac{4\left(x+y-1\right)}{20}=\dfrac{20\left(2x-y-1\right)}{20}\\\dfrac{4\left(x+y-1\right)}{12}+\dfrac{3\left(4x-y-2\right)}{12}=\dfrac{2\left(2x-y-3\right)}{12}\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}10x-15y-4x-4y+4=40x-20y-20\\4x+4y-4+12x-3y-6=4x-2y-6\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}6x-19y+4-40x+20y+20=0\\16x+y-10-4x+2y+6=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}-34x+y=-24\\12x+3y=4\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}-102x+3y=-72\\12x+3y=4\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}-114x=-76\\12x+3y=4\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{2}{3}\\12\cdot\dfrac{2}{3}+3y=4\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{2}{3}\\3y=4-8=-4\end{matrix}\right.\)
hay \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{2}{3}\\y=-\dfrac{4}{3}\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy: Hệ phương trình có nghiệm duy nhất là \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{2}{3}\\y=-\dfrac{4}{3}\end{matrix}\right.\)

\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}y\left(x+3\right)=1\\y+\dfrac{2}{y}=x+1\end{matrix}\right.\) (y \(\ne\) 0)
\(\Leftrightarrow\) \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}y=\dfrac{1}{x+3}\\\dfrac{1}{x+3}+2\left(x+3\right)=x+1\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\) \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}y=\dfrac{1}{x+3}\\1+2\left(x+3\right)^2=\left(x+1\right)\left(x+3\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\) \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}y=\dfrac{1}{x+3}\\1+2\left(x^2+6x+9\right)=x^2+4x+3\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\) \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}y=\dfrac{1}{x+3}\\1+2x^2+12x+18-x^2-4x-3=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\) \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}y=\dfrac{1}{x+3}\\x^2+8x+16=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\) \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}y=\dfrac{1}{x+3}\\\left(x+4\right)^2=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\) \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}y=\dfrac{1}{x+3}\\x+4=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\) \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=-4\\y=\dfrac{1}{-4+3}\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\) \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=-4\\y=-1\end{matrix}\right.\) (TM)
Vậy ...
Chúc bn học tốt!

=>3|x-1|+2/y-1=8 và 3|x-1|=9/y-1=-3
=>11/y-1=11 và |x-1|-3/y-1=-1
=>y-1=1 và |x-1|=2
=>y=2 và (x-1=2 hoặc x-1=-2)
=>y=2 và (x=3 hoặc x=-1)

`{(x+3y=x(5y-1)),(1/x-3/y=-2):}` `ĐK: x; y ne 0`
`<=>{(x+3y=5xy-x),(-3x+y=-2xy):}`
`<=>{(5xy-2x=3y),(-3x+y=-2xy):}`
`<=>{(x(5y-2)=3y),(-3x+y=-2xy):}`
`<=>{(x=[3y]/[5y-2]),(-3x+y=-2xy):}` `ĐK: y ne 2/5` (TH `y=2/5` ko t/m)
`<=>{(x=[3y]/[5y-2]),(-3[3y]/[5y-2]+y=-2[3y]/[5y-2]y):}`
`<=>{(x=[3y]/[5y-2]),(-9y+5y^2-2y=-6y^2):}`
`<=>{(x=[3y]/[5y-2]),(11y^2-11y=0):}`
`<=>{(x=[3y]/[5y-2]),([(y=0(ko t//m)),(y=1(t//m)):}):}`
`<=>{(x=[3. 1]/[5.1-2]=1),(y=1):}` (t/m)

a: =>xy-2x+2y-4=xy+y và 5xy+10x+y+2=5xy-10x-2y+4
=>-2x+y=4 và 20x+3y=2
=>x=-5/13; y=42/13
b: =>4x+2|y|=8 và 4x-3y=1
=>2|y|-3y=7 và 4x-3y=1
TH1: y>=0
=>2y-3y=7 và 4x-3y=1
=>-y=7 và 4x-3y=1
=>y=-7(loại)
TH2: y<0
=>-2y-3y=7 và 4x-3y=1
=>y=-7/5; 4x=1+3y=1-21/5=-16/5
=>x=-4/5; y=-7/5

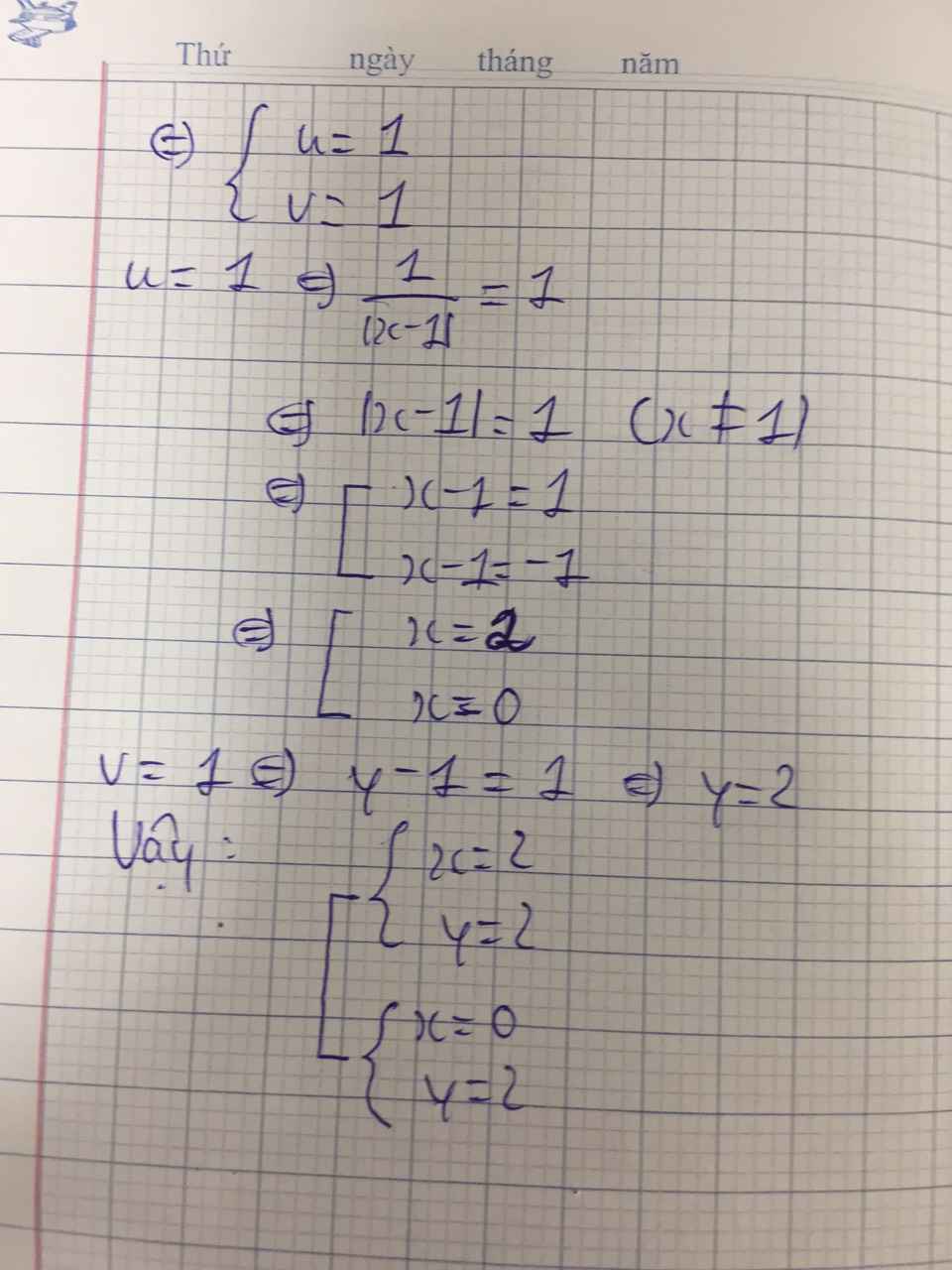
\(x^3-12=y^3-12y\)
lại hệ đối xứng
x + 1/2 trong khi y - 1/2 kìa.