Câu 1: Tìm x
\(\dfrac{x+1}{10}+\dfrac{x+1}{11}+\dfrac{x+1}{12}=\dfrac{x+1}{13}+\dfrac{x+1}{14}\)
Câu 2: Tìm các số nguyên n để A có giá trị nguyên
a) \(A=\dfrac{3n+9}{n-4}\)
Câu 3: Cho hai số hữu tỉ \(\dfrac{a}{b}và\dfrac{c}{d}\) với mẫu dương, trong đó \(\dfrac{a}{b}< \dfrac{c}{d}CMR\)
\(\dfrac{a}{b}< \dfrac{a+c}{b+c}< \dfrac{c}{d}\)
help me

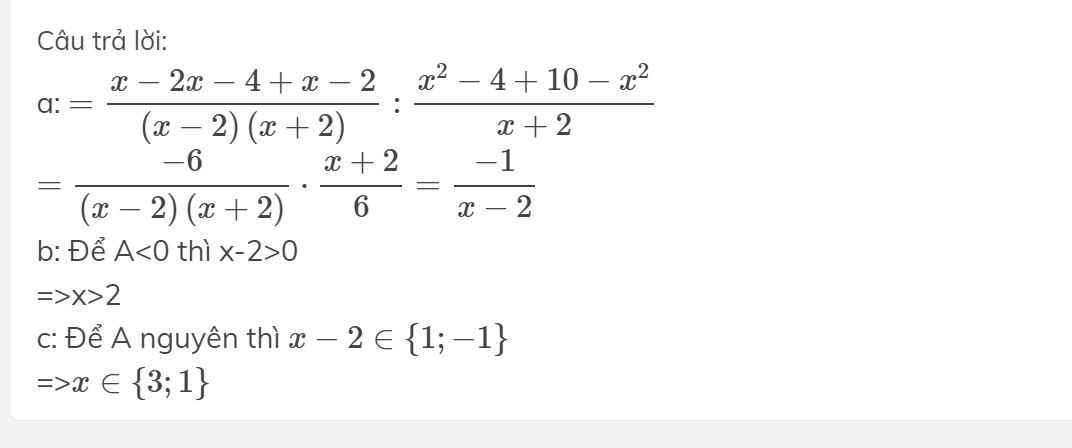
Câu 1:
\(\dfrac{x+1}{10}+\dfrac{x+1}{11}+\dfrac{x+1}{12}=\dfrac{x+1}{13}+\dfrac{x+1}{14}\)
\(\Rightarrow\left(\dfrac{x+1}{10}+\dfrac{x+1}{11}+\dfrac{x+1}{12}\right)\) - \(\left(\dfrac{x+1}{13}+\dfrac{x+1}{14}\right)=0\)
\(\Rightarrow\left(x+1\right).\left(\dfrac{1}{10}+\dfrac{1}{11}+\dfrac{1}{12}-\dfrac{1}{13}-\dfrac{1}{14}\right)\)= 0
Vì \(\dfrac{1}{10}+\dfrac{1}{11}+\dfrac{1}{12}-\dfrac{1}{13}-\dfrac{1}{14}\ne0\)
\(\Rightarrow x+1=0\)
=> x = 0 - 1
=> x = -1
Câu 2:
Ta có: \(A=\dfrac{3n+9}{n-4}=\dfrac{3n-3.4+9+12}{n-4}\)
\(=\dfrac{3.\left(n-4\right)+21}{n-4}=3+\dfrac{21}{n-4}\)
Để A có giá trị nguyên thì:
n - 4 \(\in\) Ư(21)
=> n - 4 \(\in\)