Giải các phương trình
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


Bài 1:
a) Ta có: \(2\left(3-4x\right)=10-\left(2x-5\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow6-8x-10+2x-5=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-6x+11=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-6x=-11\)
hay \(x=\dfrac{11}{6}\)
b) Ta có: \(3\left(2-4x\right)=11-\left(3x-1\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow6-12x-11+3x-1=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-9x-6=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-9x=6\)
hay \(x=-\dfrac{2}{3}\)


Thay x = 3, y = 5 vào vế trái của phương trình (3) ta được:
VT = 5.3 – 2.5 = 15 – 10 = 5 = VP
Vậy (x; y) = (3; 5) là nghiệm của phương trình (3).
Hệ phương trình đã cho có nghiệm (x; ) = (3; 5)


Thay x = -3, y = 31/5 vào vế trái của phương trình (2), ta được:
VT = -3.(-3) + 2.31/5 = 9 + 62/5 = 107/5 ≠ 22 = VP
Vậy (x; y) = (-3; 31/5 ) không phải là nghiệm của phương trình (2).
Hệ phương trình đã cho vô nghiệm.

a)
`x^2+3x+2=0`
`<=>x^2+2x+x+2=0`
`<=>x(x+2)+(x+2)=0`
`<=>(x+2)(x+1)=0`
`<=>x+2=0` hoặc `x+1=0`
`<=>x=-2` hoặc `x=-1`
b)
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x-3y=5\\3x+2y=4\end{matrix}\right.\\ < =>\left\{{}\begin{matrix}3x-9y=15\\3x+2y=4\end{matrix}\right.\\ < =>\left\{{}\begin{matrix}-11y=11\\x-3y=5\end{matrix}\right.\\ < =>\left\{{}\begin{matrix}y=-1\\x-3\cdot\left(-1\right)=5\end{matrix}\right.\\ < =>\left\{{}\begin{matrix}y=-1\\x=2\end{matrix}\right.\)

\(\Leftrightarrow2y^2+2y-3y-3+y^2-2y=3y^2+12y+12\)
=>-3y-3=12y+12
=>-15y=15
hay y=-1

\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x-2=0\\x+7=0\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=2\\x=-7\end{matrix}\right.\)

1) Ta có: \(4x+8=3x-1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4x-3x=-1-8\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=-9\)
2) Ta có: \(10-5\left(x+3\right)>3\left(x-1\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow10-5x-15-3x+3>0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-8x>2\)
hay \(x< \dfrac{-1}{4}\)


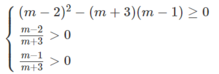
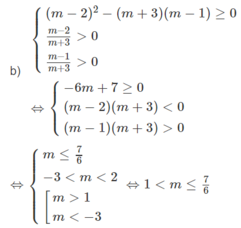
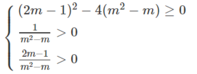
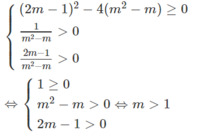
d, \(cosx-\sqrt{3}sinx-1=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{1}{2}cosx-\dfrac{\sqrt{3}}{2}sinx=\dfrac{1}{2}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow cos\left(x+\dfrac{\pi}{3}\right)=\dfrac{1}{2}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x+\dfrac{\pi}{3}=\pm\dfrac{\pi}{3}+k2\pi\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=k2\pi\\x=-\dfrac{2\pi}{3}+k2\pi\end{matrix}\right.\)
e, \(cos3x=1+sin3x\)
\(\Leftrightarrow cos3x-sin3x=1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow cos\left(3x+\dfrac{\pi}{4}\right)=\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{2}}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3x+\dfrac{\pi}{4}=\pm\dfrac{\pi}{4}+k2\pi\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}3x+\dfrac{\pi}{4}=\dfrac{\pi}{4}+k2\pi\\3x+\dfrac{\pi}{4}=-\dfrac{\pi}{4}+k2\pi\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}3x=k2\pi\\3x=-\dfrac{\pi}{2}+k2\pi\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{k2\pi}{3}\\x=-\dfrac{\pi}{6}+\dfrac{k2\pi}{3}\end{matrix}\right.\)