Không sử dụng máy tính, hãy tính :
a) \(\log_2\dfrac{1}{8}\)
b) \(\log_{\dfrac{1}{4}}2\)
c) \(\log_3\sqrt[4]{2}\)
d) \(\log_{0,5}0,125\)
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.

a) \(log_3\dfrac{6}{5}>log_3\dfrac{5}{6}\) vì \(\dfrac{6}{5}>\dfrac{5}{6}\)
b) \(log_{\dfrac{1}{3}}9>log_{\dfrac{1}{3}}17\) vì \(9>17\) và \(0< \dfrac{1}{3}< 1\).
c) \(log_{\dfrac{1}{2}}e>log_{\dfrac{1}{2}}\pi\) vì \(e>\pi\) và \(0< \dfrac{1}{2}< 1\)
d) \(log_2\dfrac{\sqrt{5}}{2}>log_2\dfrac{\sqrt{3}}{2}\) vì \(\dfrac{\sqrt{5}}{2}>\dfrac{\sqrt{3}}{2}\).
Em rất muốn biết ... anh học lớp mấy vậy ??? Đây là bài lớp 12 mà ![]()

a) \(A=\log_{5^{-2}}5^{\frac{5}{4}}=-\frac{1}{2}.\frac{5}{4}.\log_55=-\frac{5}{8}\)
b) \(B=9^{\frac{1}{2}\log_22-2\log_{27}3}=3^{\log_32-\frac{3}{4}\log_33}=\frac{2}{3^{\frac{3}{4}}}=\frac{2}{3\sqrt[3]{3}}\)
c) \(C=\log_3\log_29=\log_3\log_22^3=\log_33=1\)
d) Ta có \(D=\log_{\frac{1}{3}}6^2-\log_{\frac{1}{3}}400^{\frac{1}{2}}+\log_{\frac{1}{3}}\left(\sqrt[3]{45}\right)\)
\(=\log_{\frac{1}{3}}36-\log_{\frac{1}{3}}20+\log_{\frac{1}{3}}45\)
\(=\log_{\frac{1}{3}}\frac{36.45}{20}=\log_{3^{-1}}81=-\log_33^4=-4\)

a) \(\left(\dfrac{1}{9}\right)^{\dfrac{1}{2}log^4_3}=\left(3^{-2}\right)^{\dfrac{1}{2}log^4_3}=\left(3^{log^4_3}\right)^{-2.\dfrac{1}{2}}=4^{-1}=\dfrac{1}{4}\);
b) \(10^{3-log5}=\dfrac{10^3}{10^{log5}}=\dfrac{10^3}{5}=200\);
c) \(2log^{log1000}_{27}=2log^3_{3^3}=\dfrac{2}{3}log^3_3=\dfrac{2}{3}\);
d) \(3log_2^{log_4^{16}}+log^2_{\dfrac{1}{2}}=3log^2_2-log^2_2=3-1=2\).

a) Tập xác định của hàm số là :
\(D=\left(-\infty;-4\right)\cup\left(4;+\infty\right)\)
b) Tập xác định của hàm số là :
\(D=\left(1;+\infty\right)\)
c) Hàm số xác định khi và chỉ khi \(\begin{cases}x^2-3x+2\ge0\\\sqrt{x^2-3x+2}+4-x\ge1^{ }\end{cases}\) \(\Leftrightarrow\) \(x\le1\) V \(x\ge2\)
Tập xác định là \(D=\left(-\infty;1\right)\cup\left(2;+\infty\right)\)
d) Hàm số xác định khi và chỉ khi
\(\begin{cases}\left|x-3\right|-\left|8-x\right|\ge0\\x-1>0\\\log_{0,5}\left(x-1\right)\le0\\x^2-2x-8>0\end{cases}\) \(\Leftrightarrow\) \(\begin{cases}\left(x-3\right)^2\ge\left(8-x\right)^2\\x>1\\x-1\ge1\\x<-2,x>4\end{cases}\) \(\Leftrightarrow\)\(x\ge\frac{11}{2}\)
Vậy tập xác định là \(D=\left(\frac{11}{2};+\infty\right)\)

Câu a đúng là cú lừa, biến đổi logarit thì dễ, đến lúc nó ra pt vô tỉ theo x mới thấy vấn đề :D
a/ĐK: \(0< x< 1\)
\(2log_2x-log_2\left(1-\sqrt{x}\right)=log_2\left(x-2\sqrt{x}+2\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow log_2x^2-log_2\left(1-\sqrt{x}\right)=log_2\left(x-2\sqrt{x}+2\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow log_2\left(\dfrac{x^2}{1-\sqrt{x}}\right)=log_2\left(x-2\sqrt{x}+2\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{x^2}{1-\sqrt{x}}=x-2\sqrt{x}+2=x+2\left(1-\sqrt{x}\right)\)
Đặt \(1-\sqrt{x}=t\) (\(0< t< 1\)) \(\Rightarrow\dfrac{x^2}{t}=x+2t\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2-t.x-2t^2=0\) \(\Rightarrow\Delta=t^2+8t^2=9t^2\)
\(\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{t+3t}{2}=2t\\x=\dfrac{t-3t}{2}=-t< 0\left(l\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Rightarrow x=2\left(1-\sqrt{x}\right)\Rightarrow x+2\sqrt{x}-2=0\) \(\Rightarrow x=4-2\sqrt{3}\)
b/ĐK \(x>0\)
\(log_3\left(x-1\right)^2-log_3x+\left(x-1\right)^2=x\)
\(\Leftrightarrow log_3\left(x-1\right)^2+\left(x-1\right)^2=log_3x+x\)
Xét hàm \(f\left(t\right)=log_3t+t\) \(\left(t>0\right)\Rightarrow f'\left(t\right)=\dfrac{1}{t.ln3}+1>0\Rightarrow f\left(t\right)\) đồng biến
\(\Rightarrow f\left(t_1\right)=f\left(t_2\right)\Leftrightarrow t_1=t_2\)
\(\Rightarrow log_3\left(x-1\right)^2+\left(x-1\right)^2=log_3x+x\Leftrightarrow\left(x-1\right)^2=x\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2-3x+1=0\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{3+\sqrt{5}}{2}\\x=\dfrac{3-\sqrt{5}}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\)
a)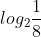 =
= 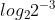 = -3.
= -3.
b)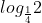 =
= 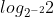 =
= 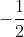 .
.
hoặc dùng công thức đổi cơ số :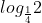 =
= 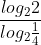 =
= 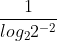 =
= 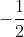 .
.
c)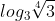 =
= 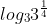 =
=  .
.
d)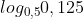 =
= 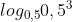 = 3.
= 3.