Tìm GTNN:
a)2x2+12x+21
b)9x2-30x+26
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


a) Ta có: \(\left(x^2-2x\right)^2-6x^2+12x+9=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x^2-2x\right)^2-6\left(x^2-2x\right)+9=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x^2-2x-3\right)^2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2-2x-3=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2-3x+x-3=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x\left(x-3\right)+\left(x-3\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-3\right)\left(x+1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x-3=0\\x+1=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=3\\x=-1\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy: S={3;-1}
b) Ta có: \(\left(x^2+x+1\right)\left(x^2+x+2\right)=12\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x^2+x\right)^2+3\left(x^2+x\right)+2-12=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x^2+x\right)^2+5\left(x^2+x\right)-2\left(x^2+x\right)-10=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x^2+x\right)\left(x^2+x+5\right)-2\left(x^2+x+5\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x^2+x+5\right)\left(x^2+x-2\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2+x-2=0\)(Vì \(x^2+x+5>0\forall x\))
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2+2x-x-2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x\left(x+2\right)-\left(x+2\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x+2\right)\left(x-1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x+2=0\\x-1=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=-2\\x=1\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy: S={-2;1}
2 ý a và b anh CTV nãy đã làm rồi nha, còn câu c này thì làm dài dòng+không chắc :VVV
c)\(\left(2x^2-3x+1\right)\left(2x^2+5x+1\right)-9x^2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(2x^2-3x+1\right)\left(2x^2-3x+1+8x\right)-9x^2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(2x^2-3x+1\right)^2+8x\left(2x^2-3x+1\right)+16x^2-25x^2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(2x^2-3x+1+4x\right)^2-25x^2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(2x^2+x+1\right)^2-25x^2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(2x^2+x+1-5x\right)\left(2x^2+x+1+5x\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(2x^2-4x+1\right)\left(2x^2+6x+1\right)=0\)
\(\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}\left(2x^2-4x+1\right)=0\\\left(2x^2+6x+1\right)=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
Rồi đến đây tự giải nhé, không phân tích được thì bấm máy tính là ra nha:vv

\(a,\Leftrightarrow x^2\left(x-4\right)\left(x+4\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=0\\x=4\\x=-4\end{matrix}\right.\\ b,\Leftrightarrow\left(3x-5\right)^2=0\Leftrightarrow x=\dfrac{5}{3}\)

a) \(9x^2-6x+11=\left(3x\right)^2-2.3x+1+10=\left(3x-1\right)^2+10>0\forall x\)
b) \(3x^2-12x+81=3.\left(x^2-4x+9\right)=3.\left(x-2\right)^2+15>0\forall x\)
c) \(5x^2-5x+4=5.\left(x^2-x+\dfrac{4}{5}\right)=5.\left(x^2-x+\dfrac{1}{4}+\dfrac{11}{20}\right)=5.\left(x-\dfrac{1}{2}\right)^2+\dfrac{11}{4}>0\forall x\)
d) \(2x^2-2x+9=2.\left(x^2-x+\dfrac{9}{2}\right)=2.\left(x-\dfrac{1}{2}\right)^2+\dfrac{17}{2}>0\forall x\)

tham khảo
A=x2+2x+5+x2−4x+4x2+2x+5=1+x2−4x+4x2+2x+5=1+(x−2)2(x+1)2+4≥1A=x2+2x+5+x2−4x+4x2+2x+5=1+x2−4x+4x2+2x+5=1+(x−2)2(x+1)2+4≥1
Dấu "=" xảy ra khi x=2

Ta có: −9x2 + 30x − 25 = 0
⇔ 9x2 − 30x + 25 = 0
⇔ (3x)2 – 2.3.5x + 52 = 0
⇔ (3x – 5)2 = 0 ⇔ 3x – 5 = 0
⇔ x = 5 3
Phương trình có một nghiệm x = 5 3
Đáp án cần chọn là: B

câu a: 9x^2-6x+2=(3x-1)^2+1>=1>0 mọi x
câu b:x^2+x+1=(x-1/2)^2+3/4>0 với mới x

a: Ta có: \(A=x^2-2xy+5y^2+4y+51\)
\(=x^2-2xy+y^2+4y^2+4y+1+50\)
\(=\left(x-y\right)^2+\left(2y+1\right)^2+50\ge50\forall x,y\)
Dấu '=' xảy ra khi \(x=y=-\dfrac{1}{2}\)
a) \(A=x^2-2xy+5y^2+4y+51=\left(x^2-2xy+y^2\right)+\left(4y^2+4y+1\right)+50=\left(x-y\right)^2+\left(2y+1\right)^2+50\ge50\)
\(minA=50\Leftrightarrow x=y=-\dfrac{1}{2}\)
c) \(C=\dfrac{9}{-2x^2+4x-7}=\dfrac{9}{-2\left(x^2-2x+1\right)-5}=\dfrac{9}{-2\left(x-1\right)^2-5}\ge\dfrac{9}{-5}=-\dfrac{9}{5}\)
\(minC=-\dfrac{9}{5}\Leftrightarrow x=1\)
d) \(10x^2+4y^2-4xy+8x-4y+20=\left[4y^2-4y\left(x+1\right)+\left(x+1\right)^2\right]+\left(9x^2+6x+1\right)+18=\left(2y-x-1\right)^2+\left(3x+1\right)^2+18\ge18\)
\(minD=18\Leftrightarrow\) \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=-\dfrac{1}{3}\\y=\dfrac{1}{3}\end{matrix}\right.\)
e) \(E=9x^2+2y^2+6xy-6x-8y+10=\left[9x^2+6x\left(y-1\right)+\left(y-1\right)^2\right]+\left(y^2-6x+9\right)=\left(3x+y-1\right)^2+\left(y-3\right)^2\ge0\)
\(minE=0\Leftrightarrow\) \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=-\dfrac{2}{3}\\y=3\end{matrix}\right.\)

b: Δ=(-12)^2-4*2*(9+4căn 2)
=144-72-32căn 2=72-32căn 2
=(8-2căn 2)^2
=>PT có hai nghiệm pb là:
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{12-8+2\sqrt{2}}{4}=\dfrac{2+\sqrt{2}}{2}\\x_2=\dfrac{2-\sqrt{2}}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\)
c: Δ=(-30)^2-4*3*(-26+8căn 3)
=900+312-96căn 3
=1212-2*căn 3072
=>Phương trình có hai nghiệm pb là:
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{30-2\sqrt{1212-2\sqrt{3072}}}{6}\\x=\dfrac{30+2\sqrt{1212-2\sqrt{3072}}}{6}\end{matrix}\right.\)

+Trước tiên từ đồ thị hàm số y= 2x3- 9x2+12x , ta suy ra đồ thị hàm số y= 2 x 3 - 9 x 2 + 12 x như hình dưới đây:
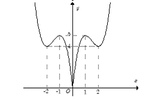
+ Phương trình 2 x 3 - 9 x 2 + 12 x + m = 0 và đường thẳng y= -m
+ Dựa vào đồ thị hàm số y = 2 x 3 - 9 x 2 + 12 x , yêu cầu bài toán trở thành:
4< -m< 5 hay -5<m< -4.
Chọn B.
a/ \(2x^2+12x+21=2\left(x^2+6x+9\right)+3=2\left(x+3\right)^2+3\ge3\)
Min = 3 <=> x = -3
b/ \(9x^2-30x+26=9\left(x-\frac{5}{3}\right)^2+1\ge1\)
Min = 1 <=> x = 5/3
a)2x2+12x+21
Ta có:2x2+12x+21=2.(x2+6x+32)+3
=2.(x+3)2+3
Vì 2.(x+3)2\(\ge\)0
Suy ra:2.(x+3)2+3\(\ge\)3
Dấu = xảy ra khi x+3=0
x=-3
Vậy MinA=3 khi x=-3
b)9x2-30x+26
Ta có:9x2-30x+26=(3x)2-2.15x+52+1
=(3x-5)2+1
Vì (3x-5)2\(\ge\)0
Suy ra:(3x-5)2+1\(\ge\)1
Dấu = xảy ra khi 3x-5=0
3x=5
x=\(\frac{5}{3}\)
Vậy Min B=1 khi x=\(\frac{5}{3}\)