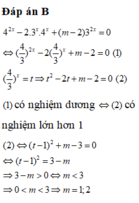Giải phương trình nghiệm nguyên: \(9x^2+12x=4y^2+17\)
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


\(9x^2+12x-4y^2-17=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(3x+2\right)^2-4y^2-21=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(3x+2y+2\right)\left(3x-2y+2\right)=21\)
Xét
TH1:\(\hept{\begin{cases}3x+2y+2=1\\3x-2y+2=21\end{cases}\Leftrightarrow x=3;y=-5\left(thỏa\right)}\)
TH2:\(\hept{\begin{cases}3x+2y+2=21\\3x-2y+2=1\end{cases}\Leftrightarrow x=3;y=5\left(thỏa\right)}\)
TH3:\(\hept{\begin{cases}3x+2y+2=-1\\3x-2y+2=-21\end{cases}\Leftrightarrow x=\frac{-13}{3};y=5\left(k.thỏa\right)}\)
TH4:\(\hept{\begin{cases}3x+2y+2=-21\\3x-2y+2=-1\end{cases}\Leftrightarrow x=\frac{-13}{3};y=-5\left(k.thỏa\right)}\)
TH5:\(\hept{\begin{cases}3x+2y+2=3\\3x-2y+2=7\end{cases}\Leftrightarrow x=1;y=-1\left(thỏa\right)}\)
TH6:\(\hept{\begin{cases}3x+2y+2=7\\3x-2y+2=3\end{cases}\Leftrightarrow x=y=1\left(thỏa\right)}\)
TH7:\(\hept{\begin{cases}3x+2y+2=-3\\3x-2y+2=-7\end{cases}\Leftrightarrow x=\frac{-7}{3};y=1\left(k.thỏa\right)}\)
TH7:\(\hept{\begin{cases}3x+2y+2=-7\\3x-2y+2=-3\end{cases}\Leftrightarrow x=\frac{-7}{3};y=-1\left(k.thỏa\right)}\)
Vậy \(\left(a;b\right)=\left(3;5\right)=\left(3;-5\right)=\left(1;1\right)=\left(1;-1\right)\)

a: 2x-3>3(x-2)
=>2x-3>3x-6
=>-x>-3
hay x<3
b: \(\dfrac{12x+1}{12}< =\dfrac{9x+1}{3}-\dfrac{8x+1}{4}\)
=>12x+1<=36x+4-24x-3
=>12x+1<=12x+1(luôn đúng)

Lớp 8 chx học cái đó, này bài của đứa em :((
Còn mình thì học r, tại lớp 9 học r nhm sợ đứa e ko hiểu cái đăng lên , k ngờ rằng ....

\(\Leftrightarrow x^4-4x^3+12x^2-32x+32=\left(y-5\right)^2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-2\right)^2\left(x^2+8\right)=\left(y-5\right)^2\)
- Với \(x=2\Rightarrow y=5\)
- Với \(x\ne2\Rightarrow x-2\) là ước của \(y-5\)
Đặt \(y-5=n\left(x-2\right)\)
\(\Rightarrow\left(x-2\right)^2\left(x^2+8\right)=n^2\left(x-2\right)^2\)
\(\Rightarrow x^2+8=n^2\)
\(\Rightarrow\left(n-x\right)\left(n+x\right)=8\)
\(\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=1;n=-3\Rightarrow y=8\\x=-1;n=-3\Rightarrow y=14\\x=1;n=3\Rightarrow y=2\\x=-1;n=3\Rightarrow y=-4\end{matrix}\right.\)

\(Pt\Leftrightarrow3x^2+12x+4y^2+3y+5=0\)
Coi pt trên là pt bậc 2 ẩn x
Ta có : \(\Delta'=36-12y^2-9y-15\)
\(=-12y^2-9y+21\)
Pt có nghiệm \(\Leftrightarrow\Delta'=-12y^2-9y+21\ge0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-\frac{7}{4}\le y\le1\)
Mà \(y\inℤ\Rightarrow y\in\left\{-1;0;1\right\}\)
Rồi làm nốt

a) Điều kiện xác định \(16x+8\ge0\Leftrightarrow x\ge-\frac{1}{2}.\)
Theo bất đẳng thức Cô-Si cho 4 số ta được
\(4\sqrt[4]{16x+8}=4\sqrt[4]{2\cdot2\cdot2\cdot\left(2x+1\right)}\le2+2+2+2x+1=2x+7\)
Do vậy mà \(4x^3+4x^2-5x+9\le2x+7\Leftrightarrow\left(2x-1\right)^2\left(x+2\right)\le0\).
Vì \(x\ge-\frac{1}{2}\to x+2>0\to\left(2x-1\right)^2\le0\to x=\frac{1}{2}.\)
b. Ta viết phương trình dưới dạng sau đây \(9x^4-21x^3+27x^2+16x+16=0\Leftrightarrow3x^2\left(3x^2-7x+7\right)+4\left(x+2\right)^2=0\)
Vì \(3x^2-7x+7=\frac{36x^2-2\cdot6x\cdot7+49+35}{12}=\frac{\left(6x-7\right)^2+35}{12}>0\) nên vế trái dương, suy ra phương trinh vô nghiệm.