x3-6x2-9x+14=0
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


\(a,\Leftrightarrow x^3-8-x^3-2x=12\Leftrightarrow-2x=20\Leftrightarrow x=-10\\ b,\Leftrightarrow x^2-6x+9-x^2+4=16\Leftrightarrow=-6x=3\Leftrightarrow x=-\dfrac{1}{2}\\ c,\Leftrightarrow x\left(x^2-9\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow x\left(x-3\right)\left(x+3\right)=0\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=0\\x=3\\x=-3\end{matrix}\right.\\ d,\Leftrightarrow x^2\left(x-6\right)+9\left(x-6\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(x^2+9\right)\left(x-6\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow x=6\left(x^2+9>0\right)\)

\(a,\Leftrightarrow2x^2-10x-2x^2-x=-11\\ \Leftrightarrow-11x=-11\Leftrightarrow x=1\\ b,\Leftrightarrow x\left(x^2-6x+9\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow x\left(x-3\right)^2=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=0\\x=3\end{matrix}\right.\\ c,\Leftrightarrow x\left(x-2018\right)-2017\left(x-2018\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(x-2017\right)\left(x-2018\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=2017\\x=2018\end{matrix}\right.\)

Chọn B
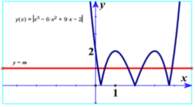
+ Đồ thị hàm số y = | x 3 - 6 x 2 + 9 x - 2 | có được bằng cách biến đổi đồ thị (C) hàm số y = x 3 - 6 x 2 + 9 x - 2
Giữ nguyên phần đồ thị (C) nằm trên trục hoành.
Lấy đồi xứng phần đồ thị của (C) phần dưới trục hoành qua trục hoành.
Xóa phần đồ thị còn lại (C) phía dưới trục hoành.
+ Số nghiệm của phương trình | x 3 - 6 x 2 + 9 x - 2 | = m là số giao điểm của đồ thị hàm số
y = | x 3 - 6 x 2 + 9 x - 2 | và đồ thị hàm số y=m. Để phương trình có 6 nghiệm phân biệt thì điều kiện cần và đủ là 0<m<2.

f: Ta có: \(x\left(2x-9\right)-4x+18=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(2x-9\right)\left(x-2\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{9}{2}\\x=2\end{matrix}\right.\)
g: Ta có: \(4x\left(x-1000\right)-x+1000=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-1000\right)\left(4x-1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=1000\\x=\dfrac{1}{4}\end{matrix}\right.\)
f. x(2x - 9) - 4x + 18 = 0
<=> x(2x - 9) - 2(2x - 9) = 0
<=> (x - 2)(2x - 9) = 0
<=> \(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x-2=0\\2x-9=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
<=> \(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=2\\x=\dfrac{9}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\)
g. 4x(x - 1000) - x + 1000 = 0
<=> 4x(x - 1000) - (x - 1000) = 0
<=> (4x - 1)(x - 1000) = 0
<=> \(\left[{}\begin{matrix}4x-1=0\\x-1000=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
<=> \(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{1}{4}\\x=1000\end{matrix}\right.\)
h. 2x(x - 4) - 6x2(-x + 4) = 0
<=> 2x(x - 4) + 6x2(x - 4) = 0
<=> (2x + 6x2)(x - 4) = 0
<=> 2x(1 + 3x)(x - 4) = 0
<=> \(\left[{}\begin{matrix}2x=0\\1+3x=0\\x-4=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
<=> \(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=0\\x=\dfrac{-1}{3}\\x=4\end{matrix}\right.\)
i. 2x(x - 3) + x2 - 9 = 0
<=> 2x(x - 3) + (x - 3)(x + 3) = 0
<=> (2x + x + 3)(x - 3) = 0
<=> (3x + 3)(x + 3) = 0
<=> \(\left[{}\begin{matrix}3x+3=0\\x+3=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
<=> \(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=-1\\x=-3\end{matrix}\right.\)
j. 9x - 6x2 + x3 = 0
<=> x(9 - 6x + x2) = 0
<=> x(3 - x)2 = 0
<=> \(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=0\\3-x=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
<=> \(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=0\\x=3\end{matrix}\right.\)

\(a,=5xy\left(2x-y+3z\right)\\ b,=x^2\left(x-1\right)-4\left(x-1\right)=\left(x-2\right)\left(x+2\right)\left(x-1\right)\\ c,=x\left(x^2-6x+9\right)=x\left(x-3\right)^2\)

Đáp án B
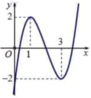
Ta có f x = x x − 3 2 ; f x = 0 ⇔ x = 0 x = 3 .
Gọi a k là số nghiệm của phương trình f k x = 0 và b k là số nghiệm của phương trình f k x = 3.
Khi đó a k = a k − 1 + b k − 1 b k = 3 k k ∈ ℕ * , k ≥ 2
suy ra a n = a n − 1 + 3 n − 1 → a n = a 1 + 3 n − 3 2 * .
Mà a 1 = 2 nên suy ra * ⇔ a n = 2 + 3 n − 3 2 = 3 n + 1 2 .
Với n = 6 ⇒ f 6 x = 0 có 3 6 + 1 2 = 365 nghiệm.




x3 - 6x2 - 9x + 14 = 0
<=> (x3 - x2) - 5x2 + 5x - 14x + 14 = 0
<=> x2(x - 1) - 5x(x - 1) - 14(x - 1) = 0
<=> (x2 - 5x - 14)(x - 1) = 0
<=> (x2 + 2x - 7x - 14)(x - 1) = 0
<=> (x + 2)(x - 7)(x - 1) = 0
<=> \(x\in\left\{1;-2;7\right\}\)
\(x^3-6x^2-9x+14=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^3-7x^2+x^2-7x-2x+14=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2\left(x-7\right)+x\left(x-7\right)-2\left(x-7\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-7\right)\left(x^2+x-2\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-7\right)\left(x+2\right)\left(x-1\right)=0\)
\(\Rightarrow x=\left\{7;-2;1\right\}\)